Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a, \(n_{HCl}=0,2.0,1=0,02\left(mol\right)=n_{H^+}=n_{Cl^-}\)
\(n_{H_2SO_4}=0,2.0,15=0,03\left(mol\right)=n_{SO_4^{2-}}\) \(\Rightarrow n_{H^+}=2n_{H_2SO_4}=0,06\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\Sigma n_{H^+}=0,02+0,06=0,08\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2}=0,3.0,05=0,015\left(mol\right)=n_{Ba^{2+}}\)
\(\Rightarrow n_{OH^-}=2n_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2}=0,03\left(mol\right)\)
\(H^++OH^-\rightarrow H_2O\)
0,03___0,03 (mol) ⇒ nH+ dư = 0,05 (mol)
\(Ba^{2+}+SO_4^{2-}\rightarrow BaSO_4\)
0,015___0,015______0,015 (mol) ⇒ nSO42- dư = 0,015 (mol)
⇒ m = mBaSO4 = 0,015.233 = 3,495 (g)
\(\left[Cl^-\right]=\dfrac{0,02}{0,2+0,3}=0,04\left(M\right)\)
\(\left[H^+\right]=\dfrac{0,05}{0,2+0,3}=0,1\left(M\right)\)
\(\left[SO_4^{2-}\right]=\dfrac{0,015}{0,2+0,3}=0,03\left(M\right)\)
b, pH = -log[H+] = 1

Đáp án A
nH+ = 0,2.0,1 + 0,2.2.0,05 = 0,04
Sau phản ứng thu được 500ml dung dịch có pH =13 ⇒ nOH- lúc sau = 0,05
⇒ nBa =1/2 nOH- ban đầu = 0,045 ⇒ a = 0,045 ÷ 0,3 = 0,15
nH2SO4 = 0,2.0,05 = 0,01< n Ba = 0,045 ⇒ n↓ = n H2SO4 = 0,01 mol
⇒ m↓ = 2,33g
Đáp án A.

`100mL=0,1L`
`n_{H^+}=0,1.0,05.2+0,1.0,1=0,02(mol)`
`n_{SO_4^{2-}}=0,1.0,05=0,005(mol)`
`n_{OH^-}=0,1.0,2+0,1.0,1.2=0,04(mol)`
`n_{Ba^{2+}}=0,1.0,1=0,01(mol)`
`Ba^{2+}+SO_4^{2-}->BaSO_4`
Do `0,01>0,005->` Tính theo `SO_4^{2-}`
`n_{BaSO_4}=n_{SO_4^{2-}}=0,005(mol)`
`->m_↓=0,005.233=1,165(g)`
`H^{+}+OH^{-}->H_2O`
Do `0,02<0,04->OH^-` dư
`n_{OH^{-}\ pu}=n_{H^+}=0,02(mol)`
`->n_{OH^{-}\ du}=0,04-0,02=0,02(mol)`
Trong X: `[OH^-]={0,02}/{0,1+0,1}=0,1M`
`->pH=14-pOH=14+lg[OH^-]=13`

Câu 15 :
$n_{HCl} = 0,2.0,1 = 0,02(mol)$
$n_{H_2SO_4} = 0,2.0,05 = 0,01(mol)$
$\Rightarrow n_{H^+} = 0,02 + 0,01.2 = 0,04(mol)$
$n_{OH^-\ dư} = 0,5.(10-14 : 10-13) = 0,05(mol)$
$H^+ + OH^- \to H_2O$
$n_{OH^-} = 0,04 + 0,05 = 0,09(mol)$
$n_{Ba(OH)_2} = \dfrac{1}{2}n_{OH^-} = 0,045(mol)$
$a = 0,045 : 0,3 = 0,15(M)$
$Ba^{2+} + SO_4^{2-} \to BaSO_4$
$n_{Ba^{2+}} = 0,045 > n_{SO_4^{2-}} = 0,01$ nên $Ba^{2+}$ dư
n BaSO4 = n SO4 = 0,01(mol)
=> m = 0,01.233 = 2,33(gam)
Đáp án A

• 0,1 mol HCl + 0,02 mol Al2(SO4)3 → ddX
ddX + 0,125 mol Ba(OH)2 → ↓
• 2HCl + Ba(OH)2 → BaCl2 + 2H2O (*)
Al2(SO4)3 + 3Ba(OH)2 → 2Al(OH)3↓ + 3BaSO4↓ (**)
2Al(OH)3 + Ba(OH)2 → Ba(AlO2)2 + 4H2O (***)
Theo (*) nBa(OH)2 = 0,1 : 2 = 0,05 mol.
Theo (**) nBa(OH)2 = 0,02 × 3 = 0,06 mol; nAl(OH)3 = 0,04 mol; nBaSO4 = 0,06 mol.
Theo (***) nBa(OH)2 = 0,125 - 0,05 - 0,06 = 0,015 mol → nAl(OH)3 = 0,04 - 0,015 × 2 = 0,01 mol.
→ m↓ = mBaSO4 + mAl(OH)3 = 0,06 × 233 + 0,01 × 78 = 14,76 gam
→ Đáp án đúng là đáp án C

a, \(n_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2}=0,1.0,1=0,01\left(mol\right)=n_{Ba^{2+}}\)
\(\Rightarrow n_{OH^-}=2n_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2}=0,02\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{NaOH}=0,1.0,1=0,01\left(mol\right)=n_{Na^+}=n_{OH^-}\)
⇒ ΣnOH- = 0,02 + 0,01 = 0,03 (mol)
\(n_{H_2SO_4}=0,4.0,0175=0,007\left(mol\right)=n_{SO_4^{2-}}\)
\(\Rightarrow n_{H^+}=2n_{H_2SO_4}=0,014\left(mol\right)\)
\(H^++OH^-\rightarrow H_2O\)
0,014___0,014 (mol) ⇒ nOH- dư = 0,03 - 0,014 = 0,016 (mol)
\(Ba^{2+}+SO_4^{2-}\rightarrow BaSO_4\)
0,007____0,007_____0,007 (mol) ⇒ nBa2+ dư = 0,01 - 0,007 = 0,003 (mol)
⇒ m = 0,007.233 = 1,631 (g)
\(\left[OH^-\right]=\dfrac{0,016}{0,1+0,4}=0,032\left(M\right)\)
\(\left[Ba^{2+}\right]=\dfrac{0,003}{0,1+0,4}=0,006\left(M\right)\)
\(\left[Na^+\right]=\dfrac{0,01}{0,1+0,4}=0,02\left(M\right)\)
b, pH = 14 - (-log[OH-]) ≃ 12,505
\(n_{Ba^{2+}}=0,1.0,1=0,01\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{SO_4^{2-}}=0,4.0,0175=7.10 ^{-3}\left(mol\right)\)
\(Ba^{2+}+SO_4^{2-}\rightarrow BaSO_4\downarrow\)
\(\Rightarrow m=m_{BaSO_4}=7.10^{-3}.233=1,631\left(g\right)\)
Ta có:
\(n_{H^+}=0,4.0,0175.2=0,014\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{OH^-}=0,1.0,1.2+0,1.0,1=0,03\left(mol\right)\)
Trong dung dịch X:
\(n_{OH^-}=0,03-0,014=0,016\left(mol\right)\)\(\Rightarrow\left[OH^-\right]=\dfrac{0,016}{0,1+0,4}=0,032\left(M\right)\)
\(n_{Ba^{2+}}=0,01-7.10^{-3}=3.10^{-3}\left(mol\right)\Rightarrow\left[Ba^{2+}\right]=\dfrac{3.10^{-3}}{0,1+0,4}=6.10^{-3}\left(M\right)\)
\(n_{Na^+}=0,1.0,1=0,01\left(mol\right)\Rightarrow\left[Na^+\right]=0,02\)
\(pOH=-lg\left(0,032\right)\approx1,5\Rightarrow pH=14-1,5=12,5\)
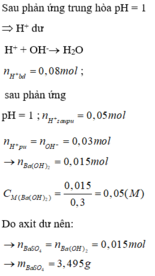
Ta có
\(\text{nHCl=0,2.0,1=0,02(mol)}\)
\(\text{nH2SO4=0,2.0,05=0,01(mol)}\)
2HCl+Ba(OH)2\(\rightarrow\)BaCl2+2H2O
H2SO4+Ba(OH)2\(\rightarrow\)BaSO4+2H2O
Ta có pH=13\(\rightarrow\)Ba(OH)2 dư
pH=13\(\rightarrow\)pOH=1\(\Rightarrow\)CM[OH-]=0,1(M)
\(\rightarrow\)CMBa(OH)2 dư=0,05(M)
\(\text{nBa(OH)2 dư=0,05.0,5=0,025(mol)}\)
\(\text{m=0,01.233=2,33(g)}\)
nBa(OH)2=0,025+0,02/2+0,01=0,045(mol)
\(\rightarrow\)a=\(\frac{0,045}{0,3}\)=0,15(M)