
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1) PT \(\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{x+1}{35}+1\right)+\left(\dfrac{x+3}{33}+1\right)=\left(\dfrac{x+5}{31}+1\right)+\left(\dfrac{x+7}{29}+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+36}{35}+\dfrac{x+36}{33}=\dfrac{x+36}{31}+\dfrac{x+36}{29}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+36\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{29}+\dfrac{1}{31}-\dfrac{1}{33}-\dfrac{1}{35}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+36=0\) (Do \(\dfrac{1}{29}+\dfrac{1}{31}-\dfrac{1}{33}-\dfrac{1}{35}>0\))
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-36\).
Vậy nghiệm của pt là x = -36.

a) Ta có: \(\dfrac{AE}{AB}=\dfrac{2}{5}\)
\(\dfrac{AF}{AC}=\dfrac{4}{10}=\dfrac{2}{5}\)
Do đó: \(\dfrac{AE}{AB}=\dfrac{AF}{AC}\)\(\left(=\dfrac{2}{5}\right)\)
Xét ΔAEF và ΔABC có
\(\dfrac{AE}{AB}=\dfrac{AF}{AC}\)(cmt)
\(\widehat{A}\) chung
Do đó: ΔAEF\(\sim\)ΔABC(c-g-c)
Suy ra: \(\dfrac{AE}{AB}=\dfrac{EF}{BC}\)(Các cặp cạnh tương ứng tỉ lệ)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2}{5}=\dfrac{EF}{12}\)
hay EF=4,8(cm)
Vậy: EF=4,8cm

x3 _ x2 _ 4x - 4 = 0
x mũ 2(x+1)- 4(x+1)=0
(x mũ 2 - 4) (x+1)=0
(x+2) (x-2) (x+1) =0
suy ra (x+2)=0
(x-2)=0
(x+1)=0
vậy x=-2
x=2
x= -1
good luck!
Sửa đề : \(x^3-x^2-4x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)-4\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-4\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=\pm2;1\)

$P=4a^2+4a(b-3)+b^2-6b+9+3b^2-6b+3$
$=4a^2+2.2a.(b-3)+(b-3)^2+3.(b-1)^2$
$=(2a+b-3)^2+3.(b-1)^2$
Mà $(2a+b-3)^2 \geq 0;3.(b-1)^2 \geq 0$ với mọi $a;b$
Nên $P=(2a+b-3)^2+3.(b-1)^2 \geq 0$
Dấu $=$ xảy ra $⇔(2a+b-3)^2=0;3.(b-1)^2=0⇔2a+b-3=0;b=1⇔a=1;b=1$
Vậy $MinP=0$ tại $a=b=1$

a) Xét ΔAEB vuông tại E và ΔAFC vuông tại F có
\(\widehat{FAC}\) chung
Do đó: ΔAEB∼ΔAFC(g-g)
b) Ta có: ΔAEB∼ΔAFC(cmt)
nên \(\dfrac{AE}{AF}=\dfrac{AB}{AC}\)(Các cặp cạnh tương ứng tỉ lệ)
hay \(\dfrac{AE}{AB}=\dfrac{AF}{AC}\)
Xét ΔAEF và ΔABC có
\(\dfrac{AE}{AB}=\dfrac{AF}{AC}\)(cmt)
\(\widehat{BAC}\) chung
Do đó: ΔAEF∼ΔABC(c-g-c)

a) (Bạn tự vẽ hình ạ)
Ta có AD.AB = AE.AC
⇒ \(\dfrac{AD}{AC}=\dfrac{AE}{AB}\)
Xét \(\Delta ABC\) và \(\Delta AED\) có:
\(\dfrac{AD}{AC}=\dfrac{AE}{AB}\)
\(\widehat{A}:chung\)
⇒ \(\Delta ABC\sim\Delta AED\) \(\left(c.g.c\right)\)
⇒ DE // BC


a) Xét ΔAHB vuông tại H và ΔDAB vuông tại A có
\(\widehat{ABH}\) chung
Do đó: ΔAHB∼ΔDAB(g-g)

Lời giải:
Vận tốc trung bình đi từ A đến B là:
$\frac{20+30}{2}=25$ (km/h)
Kiến thức cần nhớ:
Vận tốc trung bình bằng tổng quãng đường chia cho tổng thời gian đi hết quãng đường đó!
Công thức Vtb = \(\dfrac{S_1+S_2+...+S_n}{t_1+t_2+...+t_n}\)
Giải chi tiết:
Gọi quãng đường AB là: S (km); S > 0
Thời gian người đó đi hết nửa quãng đường đầu là:
\(\dfrac{S}{2}\) : 20 = \(\dfrac{S}{40}\) (giờ)
Thời gian người đó đi hết nửa quãng đường sau là:
\(\dfrac{S}{2}\) : 30 = \(\dfrac{S}{60}\) (giờ)
Vận tốc trung bình của người đó đi từ A đến B là:
Áp dụng công thức Vtb = \(\dfrac{S_1+S_2}{t_1+t_2}\) ta có
Vtb = \(\dfrac{S}{\dfrac{S}{40}+\dfrac{S}{60}}\)
Vtb = \(\dfrac{S}{S.\left(\dfrac{1}{40}+\dfrac{1}{60}\right)}\)
Vtb = \(\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{1}{24}}\)
Vtb = 24 (km/h)

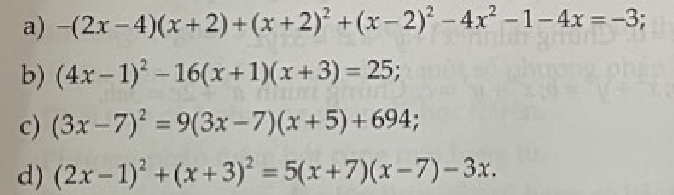



a) $-(2x-4)(x+2)+(x+2)^2+(x-2)^2-4x^2-1-4x=-3$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)^2-2(x-2)(x+2)+(x+2)^2-4x^2-4x+2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2+x+2)^2-4x^2-4x+2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (2x)^2-4x^2-4x=-2$
$\Leftrightarrow -4x=-2$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\frac12$
b) $(4x-1)^2-16(x+1)(x+3)=25$
$\Leftrightarrow (4x)^2-2.4x.1+1^2-16(x^2+4x+3)=25$
$\Leftrightarrow 16x^2-8x+1-16x^2-64x-48=25$
$\Leftrightarrow -72x-47=25$
$\Leftrightarrow -72x=72$
$\Leftrightarrow x=-1$
c) $(3x-7)^2=9(3x-7)(x+5)+694$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x)^2-2.3x.7+7^2=9(3x^2+8x-35)+694$
$\Leftrightarrow 9x^2-42x+49=27x^2+72x-315+694$
$\Leftrightarrow 18x^2+114x+330=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 9x^2+57x+165=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 9\left(x+\frac{19}{6}\right)^2+\frac{299}{4}=0$ (vô lí)
=> Pt vô nghiệm
d) $(2x-1)^2+(x+3)^2=5(x+7)(x-7)-3x$
$\Leftrightarrow 4x^2-4x+1+x^2+6x+9=5(x^2-49)-3x$
$\Leftrightarrow 5x^2+2x+10=5x^2-3x-245$
$\Leftrightarrow 5x=-255$
$\Leftrightarrow x=-51$
#$\mathtt{Toru}$