giúp mik câu c,d va ạ
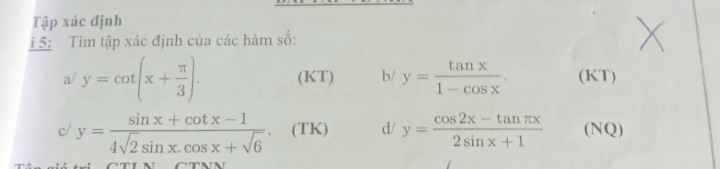
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(c,\Rightarrow\left|x-\dfrac{1}{9}\right|=-\dfrac{4}{5}\\ \Rightarrow x\in\varnothing\left(\left|x-\dfrac{1}{9}\right|\ge0>-\dfrac{4}{5}\right)\\ d,\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-2=0\\4y-7=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\y=\dfrac{7}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\\ e,\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=0\\x-y=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow x=y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)

\(D=10\cdot\left(-2.5\right)\cdot0.4\cdot\left(-0.1\right)\)
\(=10\cdot1\cdot2.5\cdot0.4\)
=10

a: \(\left(x-1.2\right)^2=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1.2=2\\x-1.2=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3.2\\x=-0.8\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: Ta có: \(\left(x+1\right)^3=-125\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+1=-5\)
hay x=-6

c) \(\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{12}\le x\le\dfrac{7}{10}+\dfrac{27}{6}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2}{3}\le x\le\dfrac{26}{5}=5,2\), mà \(x\in Z\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{1;2;3;4;5\right\}\)
d) \(-\dfrac{31}{14}+\dfrac{115}{131}+\dfrac{111}{74}\le x\le\dfrac{6}{36}+\dfrac{9}{27}+\dfrac{48}{96}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{150}{917}\le x\le1\) , mà \(x\in Z\)
\(\Rightarrow x=1\)

c/Theo công thức pascal trong Nhị Thức Newton ta có: \(C_{n-1}^{n-1}\) + \(C_{n-1}^k\) = \(C_n^k\)
C = \(C_{19}^0\) + \(C_{19}^1\) + \(C_{19}^2\) + ....+ \(C_{19}^{18}\) + \(C_{19}^{19}\)
C = (1+1)19 = 524288
còn câu d hình như đề sai

Để phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt thì:
\(\Delta>0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(-5\right)^2-4.1.\left(m+4\right)>0\\ \Leftrightarrow25-4m-16>0\\\Leftrightarrow9-4m>0\\ \Leftrightarrow m< \dfrac{9}{4}\)
Theo viét:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=5\\x_1x_2=m+4\end{matrix}\right.\)
c,
\(\left|x_1-x_2\right|=3\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1-x_2\right)^2=9\\ \Leftrightarrow x_1^2-2x_1x_2+x_2^2=9\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2=9\\ \Leftrightarrow5^2-4\left(m+4\right)=9\\ \Leftrightarrow25-4m-16=9\\ \Leftrightarrow m=0\left(nhận\right)\)
d.
\(\left|x_1\right|+\left|x_2\right|=4\\ \)
Xét trường hợp 1: hai nghiệm đều dương:
ta có:
\(x_1+x_2=4\)
5 = 4 (vô lý)
Loại trường hợp này.
Xét trường hợp 2: hai nghiệm đều âm, tương tự ta loại trường hợp này.
Xét trường hợp 3:
\(x_1< 0< x_2\)
=> \(x_2-x_1=4\)
<=> \(x_2+x_1-2x_1=4\)
=> \(5-2x_1=4\)
=> \(x_1=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(x_2< 0< x_1\)
\(x_1-x_2=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x_1+x_2-2x_2=4\\ \Leftrightarrow5-2x_2=4\\ \Rightarrow x_2=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Có: \(x_1x_2=m+4\\\)
<=> \(\dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{1}{2}=m+4\)
=> m = -3,75 (nhận)
e.
Theo viét và theo đề ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x_1+4x_2=6\left(1\right)\\x_1+x_2=5\left(2\right)\\x_1x_2=m+4\left(3\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Từ (1) có \(x_1=\dfrac{6-4x_2}{3}=2-\dfrac{4}{3}x_2\) (x)
Thế (x) vào (2) được \(2-\dfrac{4}{3}x_2+x_2=5\)
=> \(x_2=-9\) (xx)
Thế (xx) vào (1) được \(3x_1+4.\left(-9\right)=6\)
=> \(x_1=14\) (xxx)
Thế (xx) và (xxx) vào (3) được:
\(14.\left(-9\right)=m+4\)
=> m = -130 (nhận)
h.
\(x_1\left(1-3x_2\right)+x_2\left(1-3x_1\right)=m^2-23\)
<=> \(x_1-3x_1x_2+x_2-3x_1x_2=m^2-23\)
<=> \(x_1+x_2-6x_1x_2=m^2-23\)
<=> \(5-6.\left(m+4\right)=m^2-23\)
<=> \(5-6m-20-m^2+23=0\)
<=> \(-m^2-6m+8=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(-6\right)^2-4.\left(-1\right).8=68\)
\(m_1=\dfrac{6+\sqrt{68}}{2.\left(-1\right)}=-3-\sqrt{17}\left(nhận\right)\)
\(m_2=\dfrac{6-\sqrt{68}}{2.\left(-1\right)}=-3+\sqrt{17}\left(nhận\right)\)
☕T.Lam
Mình không chắc chắn ở câu d, mình lên đây để ôn bài thi tiện thể giúp được bạn phần nào.

Câu 3:
a: Áp dụng tính chất của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau, ta được:
\(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{y}{2}=\dfrac{x+y}{3+2}=\dfrac{90}{5}=18\)
Do đó: x=54; y=36


Câu 3:
3)
d) \(3x^2+x-6-\sqrt{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+\dfrac{1}{3}x-2-\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+\dfrac{1}{3}x-\dfrac{6+\sqrt{2}}{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2.\dfrac{1}{6}x+\dfrac{1}{36}-\dfrac{6+\sqrt{2}}{3}-\dfrac{1}{36}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+\dfrac{1}{6}\right)^2-\dfrac{73+12\sqrt{2}}{36}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+\dfrac{1}{6}+\dfrac{\sqrt{73+12\sqrt{2}}}{6}\right)\left(x+\dfrac{1}{6}-\dfrac{\sqrt{73+12\sqrt{2}}}{6}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{-1\pm\sqrt{73+12\sqrt{2}}}{6}\)
-Vậy \(S=\left\{\dfrac{-1\pm\sqrt{73+12\sqrt{2}}}{6}\right\}\)
d: ĐKXĐ: 2sin x+1<>0
=>sin x<>-1/2
=>x<>-pi/6+k2pi và x<>7/6pi+k2pi
c: ĐKXĐ: \(4\sqrt{2}\cdot sinx\cdot cosx+\sqrt{6}< >0\)
=>\(2\sqrt{2}\cdot sin2x+\sqrt{6}< >0\)
=>\(2sin2x+\sqrt{3}\ne0\)
=>\(sin2x\ne-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
=>2x<>-pi/3+k2pi và 2x<>4/3pi+k2pi
=>x<>-pi/6+kpi và x<>2/3pi+kpi