x2-13x+42=0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\left\{-4;-5;-6;-7\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{x^2+9x+20}+\dfrac{1}{x^2+11x+30}+\dfrac{1}{x^2+13x+42}=\dfrac{1}{18}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{\left(x+4\right)\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+5\right)\left(x+6\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+6\right)\left(x+7\right)}=\dfrac{1}{18}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x+4}-\dfrac{1}{x+5}+\dfrac{1}{x+5}-\dfrac{1}{x+6}+\dfrac{1}{x+6}-\dfrac{1}{x+7}=\dfrac{1}{18}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x+4}-\dfrac{1}{x+7}=\dfrac{1}{18}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{\left(x+4\right)\left(x+7\right)}=\dfrac{1}{18}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+4\right)\left(x+7\right)=54\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+11x-26=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+13x-26=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)+13\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+13\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-13\end{matrix}\right.\)

Để olm giúp em em nhé!
a, \(\dfrac{x+2}{7x+42}\) = \(\dfrac{x+2}{7.\left(x+6\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-6\right)}{7\left(x-6\right)\left(x+6\right)}\) (đk \(x\ne\) \(\mp\) 6)
\(\dfrac{-13x}{x^2-36}\) = \(\dfrac{-13x}{\left(x-6\right)\left(x+6\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{-7.13.x}{7.\left(x-6\right).\left(x+6\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{-91x}{7.\left(x-6\right)\left(x+6\right)}\)
b, \(\dfrac{7}{4x+16}\) = \(\dfrac{7\left(x-4\right)}{4.\left(x+4\right).\left(x-4\right)}\) (đk \(x\ne\) \(\pm\) 4)
\(\dfrac{15}{x^2-16}\) = \(\dfrac{15.4}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right).4}\) = \(\dfrac{60}{4.\left(x-4\right).\left(x+4\right)}\)

\(x^3+6x^2-13x-42=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^3-3x^2\right)+\left(9x^2-27x\right)+\left(14x-42\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-3\right)+9x\left(x-3\right)+14\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)+\left(x^2+9x+14\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+7x+2x+14\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left[x\left(x+7\right)+2\left(x+7\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}x-3=0\\x+2=0\\x+7=0\end{array}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}x=3\\x=-2\\x=-7\end{array}\right.\)
x3 + 6x2 - 13x - 42 = 0
=> x3 - 3x2 + 9x2 - 27x + 14x - 42 = 0
=> x2 ( x - 3 ) + 9x ( x - 3 ) + 14 ( x - 3 ) = 0
=> ( x - 3 ) ( x2 + 9x + 14) = 0
=> ( x - 3 ) ( x2 + 2x + 7x + 14 ) = 0
=> ( x - 3 ) [ x ( x + 2 ) + 7 ( x + 2 ) ] = 0
=> ( x - 3 ) ( x + 2 ) ( x + 7 ) = 0
=> x - 3 = 0 => x = 3
=> x + 2 = 0 => x = -2
=> x + 7 = 0 => x = -7

Ta có
3 x 2 + 13 x + 10 = 0 ⇔ 3 x 2 + 3 x + 10 x + 10 = 0
ó 3x(x + 1) + 10(x + 1) = 0
ó (x + 1)(3x + 10) = 0
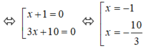
=> 2 x 1 x 2 = 2 . ( - 1 ) . - 10 3 = 20 3
Đáp án cần chọn là: B

Gọi nghiệm của phương trình (2) là x0 (x0 ≠ 0)
thì nghiệm phương trình (1) là 2x0
Thay x0; 2x0 lần lượt vào phương trình (2) và (1)
ta được
2 x 0 2 − 13.2 x 0 + 2 m = 0 x 0 2 − 4 x 0 + m = 0
⇔ 4 x 0 2 − 26 x 0 + 2 m = 0 x 0 2 − 4 x 0 + m = 0 ⇔ 4 x 0 2 − 26 x 0 + 2 m = 0 4 x 0 2 − 16 x 0 + 4 m = 0
⇔ 10x0 = −2m ⇔ x 0 = − m 5
Do x0 ≠ 0 nên m ≠ 0
Thay x 0 = − m 5 vào phương trình (2)
ta được − m 5 2 − 4. − m 5 + m = 0
⇔ m 2 25 + 4 m 5 + m = 0
⇔ m 2 25 + 9 m 5 = 0 ⇒ m = 0 m = − 45
Kết hợp m ≠ 0 ta được m = −45
Đáp án cần chọn là: A

a: Ta có: \(\left(2x-3\right)^2+6\left(2x-1\right)=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-3\right)^2+6\left(2x-1\right)-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-12x+9+12x-6-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=1\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
b: Ta có: \(x^2-7x+10=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) \(\left(2x-3\right)^2+6\left(2x-1\right)=7\\ \Rightarrow4x^2-12x+9+12x-6-7=0\\ \Rightarrow4x^2-4=0\\ \Rightarrow x^2-1=0\\ \Rightarrow x^2=1\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(x^2-7x+10=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x^2-2x\right)-\left(5x-10\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) \(-6x^2+13x-5=0\\ \Rightarrow-\left(6x^2-13x+5\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow-\left[\left(6x^2-10x\right)-\left(3x-5\right)\right]=0\\ \Rightarrow-\left[2x\left(3x-5\right)-\left(3x-5\right)\right]=0\\ \Rightarrow-\left(2x-1\right)\left(3x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-\left(2x-1\right)=0\\3x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=0\\3x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=\dfrac{5}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Theo hệ thức Vi-ét ta có: x 1 + x 2 =13
Suy ra 12,5 + x 2 = 13 ⇔ x 2 = 0,5
Cũng theo hệ thức Vi-ét ta có: x 1 x 2 = m
Suy ra: m = 12,5.0,5 ⇔ m =6,25
Vậy với m = 6,25 thì phương trình x 2 -13x + m = 0 có hai nghiệm
x 1 =12,5 , x 2 =0,5
x2+13x+42=0
Two solutions were found :
Step by step solution :
Step 1 :
Trying to factor by splitting the middle term
1.1 Factoring x2+13x+42
The first term is, x2 its coefficient is 1 .
The middle term is, +13x its coefficient is 13 .
The last term, "the constant", is +42
Step-1 : Multiply the coefficient of the first term by the constant 1 • 42 = 42
Step-2 : Find two factors of 42 whose sum equals the coefficient of the middle term, which is 13 .
Step-3 : Rewrite the polynomial splitting the middle term using the two factors found in step 2 above, 6 and 7
x2 + 6x + 7x + 42
Step-4 : Add up the first 2 terms, pulling out factors :
x • (x+6)
Add up the last 2 terms, pulling out common factors :
7 • (x+6)
Step-5 : Add up the four terms of step 4 :
(x+7) • (x+6)
Which is the desired factorization
Equation at the end of step 1 :
(x + 7) • (x + 6) = 0