
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



Bài 3:
a: Gọi OK là khoảng cách từ O đến AB
Suy ra: K là trung điểm của AB
hay \(AK=BK=\dfrac{AB}{2}=\dfrac{8}{2}=4\left(cm\right)\)
Áp dụng định lí Pytago vào ΔOKA vuông tại K, ta được:
\(OA^2=OK^2+KA^2\)
hay OK=3(cm)

Lời giải:
a. ĐKXĐ: $x>0; x\neq 4$
b.
\(M=\sqrt{x}.\left[\frac{1}{\sqrt{x}-2}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{x}+2}\right].\frac{x-4}{2\sqrt{x}}\)
\(=\frac{2\sqrt{x}}{(\sqrt{x}-2)(\sqrt{x}+2)}.\frac{x-4}{2}=\frac{2\sqrt{x}}{x-4}.\frac{x-4}{2}=\sqrt{x}\)
c. Để $M>3\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{x}>3\Leftrightarrow x>9$
Kết hợp đkxđ suy ra $x>9$ thì $M>3$


a: Xét ΔSBM và ΔSNB có
\(\widehat{SBM}=\widehat{SNB}\)
\(\widehat{BSM}\) chung
Do đó: ΔSBM\(\sim\)ΔSNB
Suy ra: SB/SN=SM/SB
hay \(SB^2=SM\cdot SN\)
b: Xét (O) có
SA là tiếp tuyến
SB là tiếp tuyến
Do đó: SA=SB
mà OA=OB
nên SO là đường trung trực của AB
=>SO⊥AB
Xét ΔOBS vuông tại B có BH là đường cao
nên \(SH\cdot SO=SB^2=SM\cdot SN\)

a) \(A=\sqrt{1-x}+\sqrt{1+x}\)
\(\Rightarrow A^2=1-x+1+x+2\sqrt{\left(1-x\right)\left(1+x\right)}=2+2\sqrt{1-x^2}\)
Do \(-x^2\le0\Rightarrow1-x^2\le1\Rightarrow A^2=2+2\sqrt{1-x^2}\le2+2=4\)
\(\Rightarrow A\le2\)
\(maxA=2\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
Áp dụng bất đẳng thức: \(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\ge\sqrt{x+y}\)(với \(x,y\ge0\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)^2\ge x+y\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+y+2\sqrt{xy}\ge x+y\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{xy}\ge0\left(đúng\right)\)
\(A=\sqrt{1-x}+\sqrt{1+x}\ge\sqrt{1-x+1+x}=\sqrt{2}\)
\(maxA=\sqrt{2}\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}1-x=0\\1+x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(x^2-2\left(m-2\right)x+m^2+2m-3=0\left(1\right)\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì Δ' > 0
\(\Rightarrow\left(m-2\right)^2-m^2-2m+3>0\Leftrightarrow m^2-4m+4-m^2-2m+3>0\Leftrightarrow-6m+7>0\Leftrightarrow m< \dfrac{7}{6}\)\)
Theo viét : \(\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m-2\right)\\x_1x_2=m^2+2m-3\end{matrix}\right.\)\)
Lại có :\( \dfrac{1}{x_1}+\dfrac{1}{x_2}=\dfrac{x_1+x_2}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x_1+x_2}{x_1x_2}=\dfrac{x_1+x_2}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)\left(x_1x_2\right)=5\left(x_1+x_2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m-4\right)\left(m^2+2m-3\right)=5\left(2m-4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m^3+4m^2-6m-4m^2-8m+12=10m-20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m^3-24m+32=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=-4\left(n\right)\\m=2\left(l\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(m=-4\) thì thỏa điều kiện

Bài 11:
a: Ta có: \(P=\dfrac{x^2-\sqrt{x}}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}\)
\(=\sqrt{x}\cdot\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\)
\(=x-\sqrt{x}\)
b: Để P=2 thì \(x-\sqrt{x}-2=0\)
hay x=4
Bài 10:
a: Ta có: \(A=\left(1+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{x+1}\right):\left(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}-1}-\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}}{x\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{x}-x-1}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{x+\sqrt{x}+1}{x+1}:\dfrac{x-2\sqrt{x}+1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+\sqrt{x}+1}{x+1}\cdot\dfrac{x+1}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
b: Để A<0 thì \(\sqrt{x}-1< 0\)
hay x<1
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được: \(0\le x< 1\)
Để A=-1 thì \(x+\sqrt{x}+1=-\sqrt{x}+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
c: Thay x=4 vào A, ta được:
\(A=\dfrac{4+2+1}{2-1}=7\)

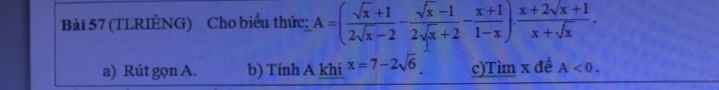
 , mình đang cần giải gấp. Cảm ơn mn nhiều.
, mình đang cần giải gấp. Cảm ơn mn nhiều.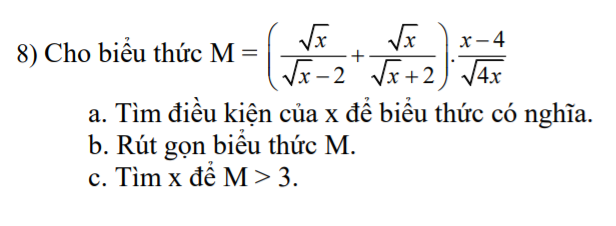
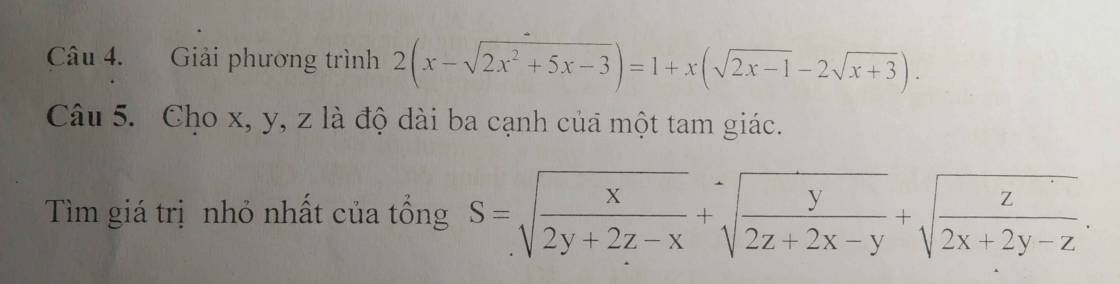





5:
Th1: m=0
=>6x-27=0
=>x=27/6(loại)
TH2: m<>0
Δ=(6m-6)^2-4m(9m-27)
=36m^2-72m+36-36m^2+108m=36m+36
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm pb thì 36m+36>0
=>m>-1
x1+x2=x1x2
=>6(m-1)=9(m-3)
=>9m-27=6m-6
=>3m=21
=>m=7