
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: Ta có: ΔABC vuông tại A
=>\(AB^2+AC^2=BC^2\)
=>\(BC^2=6^2+8^2=100\)
=>\(BC=\sqrt{100}=10\left(cm\right)\)
Xét ΔABC có AB<AC<BC
mà \(\widehat{ACB};\widehat{ABC};\widehat{BAC}\) lần lượt là góc đối diện của các cạnh AB,AC,BC
nên \(\widehat{ACB}< \widehat{ABC}< \widehat{BAC}\)
b: Xét ΔABH vuông tại H và ΔKIH vuông tại H có
HA=HK
HB=HI
Do đó: ΔABH=ΔKIH
c: Xét ΔIAK có
IH là đường cao
IH là đường trung tuyến
Do đó: ΔIAK cân tại I
Ta có: ΔIAK cân tại I
mà IB là đường cao
nên IB là phân giác của góc AIK
d: Ta có: IA=IK
IA=ID
Do đó: IK=ID=DA/2
Ta có: ID=IA
I nằm giữa D và A
Do đó: I là trung điểm của DA
Xét ΔDKA có
KI là đường trung tuyến
\(KI=\dfrac{DA}{2}\)
Do đó: ΔKDA vuông tại K

a: để y>0 thì 2a-1<0
hay a<1/2
b: Để y<0 thì 2a-1>0
hay a>1/2
c) Để y ko là số dương của ko là số âm thì:
\(y=\dfrac{2a-1}{-3}=0\Rightarrow2a-1=0\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{1}{2}\)


\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}+\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{13}-\dfrac{1}{14}\right)=0\)
=>x+1=0
hay x=-1
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right).\left(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}+\dfrac{1}{12}\right)=\left(x+1\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{13}+\dfrac{1}{14}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}+\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{13}-\dfrac{1}{14}\right)=0\)
mà \(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}+\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{13}-\dfrac{1}{14}\ne0\)
\(=>x+1=0\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)

\(a)P\left(x\right)=5x^5+3x-4x^4-2x^3+6+4x^2\)
\(P\left(x\right)=5x^5-4x^4-2x^3+4x^2+3x+6\)
\(Q\left(x\right)=2x^4-x+3x^2-2x^3+\dfrac{1}{4}-x^5\)
\(Q\left(x\right)=-x^5+2x^4-2x^3+3x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(a)P\left(x\right)-Q\left(x\right)=\left(5x^5-4x^4-2x^3+4x^2+3x+6\right)+\left(-x^5+2x^4-2x^3+3x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)\)
\(P\left(x\right)-Q\left(x\right)=5x^5-4x^4-2x^3+4x^2+3x+6+x^5-2x^4+2x^3-3x^2+x-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(P\left(x\right)-Q\left(x\right)=\left(5x^5+x^5\right)+\left(-4x^4-2x^4\right)+\left(-2x^3+2x^3\right)+\left(4x^2-3x^2\right)+\left(3x+x\right)+\left(6-\dfrac{1}{4}\right)\)
\(P\left(x\right)-Q\left(x\right)=6x^5-6x^4+x^2+4x+\dfrac{23}{4}\)
\(\text{c)Thay x=-1 vào biểu thức P(x),ta được:}\)
\(P\left(x\right)=5.\left(-1\right)^5-4.\left(-1\right)^4-2.\left(-1\right)^3+4.\left(-1\right)^2+3.\left(-1\right)+6\)
\(P\left(x\right)=\left(-5\right)-4-\left(-2\right)+4+\left(-3\right)+6\)
\(P\left(x\right)=\left(-9\right)-\left(-2\right)+4+\left(-3\right)+6\)
\(P\left(x\right)=\left(-7\right)+4+\left(-3\right)+6\)
\(P\left(x\right)=\left(-3\right)+\left(-3\right)+6\)
\(P\left(x\right)=\left(-6\right)+6=0\)
\(\text{Vậy giá trị của P(x) tại x=-1 là:0}\)
\(\text{Vậy =-1 là nghiệm của P(x)}\)
\(\text{Thay x=-1 vào biểu thức Q(x),ta được:}\)
\(Q\left(x\right)=\left(-1\right).5+2.\left(-1\right)^4-2.\left(-1\right)^3+3.\left(-1\right)^2-\left(-1\right)+\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(Q\left(x\right)=\left(-5\right)+2-\left(-2\right)+3-\left(-1\right)+\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(Q\left(x\right)=\left(-3\right)-\left(-2\right)+3-\left(-1\right)+\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(Q\left(x\right)=\left(-5\right)+3-\left(-1\right)+\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(Q\left(x\right)=\left(-2\right)-\left(-1\right)+\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(Q\left(x\right)=\left(-3\right)+\dfrac{1}{4}=\dfrac{-13}{4}\)
\(\text{Vậy x=-1 không phải là nghiệm của Q(x)}\)
\(\text{d)Thay x=-1 vào biểu thức }P\left(x\right)-Q\left(x\right),\text{ta được:}\)
\(P\left(x\right)-Q\left(x\right)=6.\left(-1\right)^5-6.\left(-1\right)^4+\left(-1\right)^2+4.\left(-1\right)+\dfrac{23}{4}\)
\(P\left(x\right)-Q\left(x\right)=\left(-6\right)-6+1+\left(-4\right)+\dfrac{23}{4}\)
\(P\left(x\right)-Q\left(x\right)=\left(-12\right)+1+\left(-4\right)+\dfrac{23}{4}\)
\(P\left(x\right)-Q\left(x\right)=\left(-11\right)+\left(-4\right)+\dfrac{23}{4}\)
\(P\left(x\right)-Q\left(x\right)=\left(-15\right)+\dfrac{23}{4}=\dfrac{-37}{4}\)
\(\text{Vậy giá trị của P(x)-Q(x) tại x=-1 là:}\dfrac{-37}{4}\)

Áp dụng định lí Pytago ta có
\(DE^2=DF^2+FE^2\\ \Rightarrow DF=\sqrt{15^2-12^2}=9\)

ÉT Ô ÉT
Câu 3: Tìm x biết:
|x + 1| + |x + 2| + |x + 2020| = 4x
Giúp mik với!!!
Mik hứa Tick cho… Pls

TH1 : \(x< -2020\)
<=> | x + 1 | + | x + 2 | + | x + 2020 | = - ( x + 1 ) - ( x + 2 ) - ( x + 2020 ) = 4x
<=> -3x - 2023 = 4x <=> -7x = 2023 <=> x = -289
TH2 : \(-2020\le x< -2\)
<=> | x + 1 | + | x + 2 | + | x + 2020 | = - ( x + 1 ) - ( x + 2 ) + x + 2020 = 4x
<=> -x + 2017 = 4x
<=> -5x = -2017 <=> x = 2017/5 ( = 403,4 )
TH3 : \(-2\le x< -1\)
<=> | x + 1 | + | x + 2 | + | x + 2020 | = - ( x + 1 ) + x + 2 + x + 2020 = 4x
<=> x + 2021 = 4x <=> -3x = -2021 <=> x = 2021/3
TH4 : \(x>-1\)
<=> | x + 1 | + | x + 2 | + | x + 2020 | = x + 1 + x + 2 + x + 2020 = 4x
<=> 3x + 2023 = 4x
<=> -x = -2023 <=> x = 2023
Vậy...
TH1: x ≥ 0
Khi đó \(\left|x+1\right|+\left|x+2\right|+\left|x+2020\right|=x+1+x+2+x+2020\)
\(=3x+2023=4x\)
Suy ra \(4x-3x=x=2023\) (thỏa mãn điều kiện)
TH2: x < 0
Khi đó 4x < 0 hay vế phải luôn là một số âm. Tuy nhiên vế trái luôn luôn có giá trị lớn hơn 0 nên luôn là 0 hoặc là một số dương, suy ra vô lí.
Tóm lại, x = 2023.
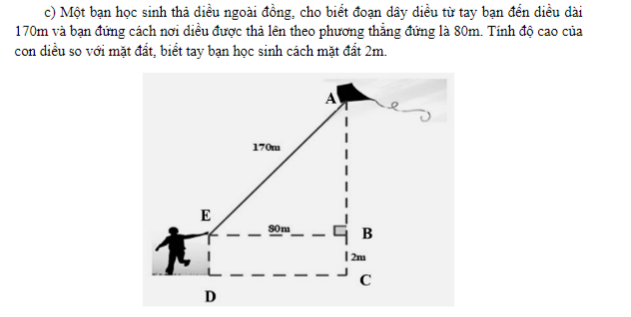
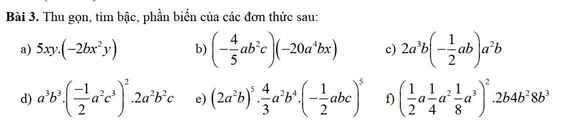


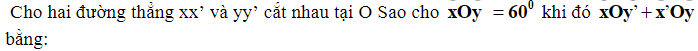
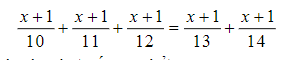
Lx
cái j vậy q như