

Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.




a. \(lim_{x\rightarrow3}\dfrac{x^3-27}{3x^2-5x-2}=\dfrac{3^3-27}{3.3^2-5.3-2}=\dfrac{0}{10}=0\)
b. \(lim_{x\rightarrow2}\dfrac{\sqrt{x+2}-2}{4x^2-3x-2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2+2}-2}{4.2^2-3.2-2}=\dfrac{0}{8}=0\)
c. \(lim_{x\rightarrow1}\dfrac{1-x^2}{x^2-5x+4}=lim_{x\rightarrow1}\dfrac{\left(1-x\right)\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-4\right)}=lim_{x\rightarrow1}\dfrac{-\left(x+1\right)}{x-4}=\dfrac{-\left(1+1\right)}{1-4}=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
d. Câu này mình chịu, nhìn đề hơi lạ so với bình thường hehe

a: \(27^{2-x}< =9\)
=>\(\left(3^3\right)^{2-x}< =3^2\)
=>\(3^{6-3x}< =3^2\)
=>6-3x<=2
=>-3x<=-4
=>\(x>=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
b: \(7^{3-x}< 49\)
=>\(7^{3-x}< 7^2\)
=>3-x<2
=>-x<2-3=-1
=>x>1
c: \(27^{3-x}>9\)
=>\(\left(3^3\right)^{3-x}>3^2\)
=>\(3^{9-3x}>3^2\)
=>9-3x>2
=>-3x>-7
=>\(x< \dfrac{7}{3}\)
d: \(2^{3-x}< 2^3\)
=>3-x<3
=>-x<0
=>x>0
e: \(27^{3-x^2}< 27^{x+1}\)
=>\(3-x^2< x+1\)
=>\(-x^2-x+2< 0\)
=>\(x^2+x-2>0\)
=>(x+2)(x-1)>0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>1\\x< -2\end{matrix}\right.\)

Giới hạn đã cho hữu hạn nên \(a=-1\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-\infty}\dfrac{\left(b-x\right)^2-\left(x^2-6x+2\right)}{b-x+\sqrt{x^2-6x+2}}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-\infty}\dfrac{\left(6-2b\right)x+b^2-2}{-x+\sqrt{x^2-6x+2}+b}\)
\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-\infty}\dfrac{6-2b+\dfrac{b^2-2}{x}}{-1-\sqrt{1-\dfrac{6}{x}+\dfrac{2}{x^2}}+\dfrac{b}{x}}=\dfrac{6-2b}{-2}=5\)
\(\Rightarrow b=8\)
Cả 4 đáp án đều sai, số lớn hơn là 8

heo me tim gtnn gtln cua bieu thuc:asinx + bcosx (a,b la hang so,a^2+b^2=/o)? | Yahoo Hỏi & Đáp

Trình bày công thức các thứ khá dài nên tôi thử nói hướng, nếu bạn hiểu đc và làm đc thì ok còn nếu k hiểu thì bảo mình, mình làm full cho
Bây giờ phân tích mẫu trước, ra (x-1)2(x+2)
Để cái lim này nó ra đc 1 số thực thì tử và mẫu cùng phải triệt tiêu (x-1)2 đi, tức là tử phải chia hết (x-1)2, tức là tử cũng phải có nghiệm kép x=1
Do đó \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}f\left(1\right)=0\\f'\left(1\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)

Bạn xem lại đề, với a;b;c dương thì biểu thức P không tồn tại max nếu đề hoàn toàn đúng
Muốn P tồn tại max thì a;b;c cần không âm (nghĩa là có thể bằng 0)

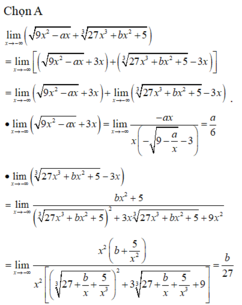
a/ \(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-\infty}\dfrac{x^2+1-x^2}{\sqrt{x^2+1}-x}+\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-\infty}\dfrac{3x^3-1-x^3}{\sqrt[3]{\left(3x^3-1\right)^2}+x\sqrt[3]{3x^3-1}+x^2}\)
\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-\infty}\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{x}}{-\sqrt{\dfrac{x^2}{x^2}+\dfrac{1}{x^2}}-\dfrac{x}{x}}+\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-\infty}\dfrac{-\dfrac{1}{x^2}}{\dfrac{\sqrt[3]{\left(3x^3-1\right)^2}}{x^2}+\dfrac{x\sqrt[3]{3x^3-1}}{x^2}+\dfrac{x^2}{x^2}}=0\)
b/ \(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow+\infty}\dfrac{x^2+x-x^2}{\sqrt{x^2+x}+x}+\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow+\infty}\dfrac{x^3-x^3+x^2}{x^2+x\sqrt[3]{x^3-x^2}+\sqrt[3]{\left(x^3-x^2\right)^2}}\)
\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow+\infty}\dfrac{\dfrac{x}{x}}{\sqrt{\dfrac{x^2}{x^2}+\dfrac{x}{x^2}}+\dfrac{x}{x}}+\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow+\infty}\dfrac{\dfrac{x^2}{x^2}}{\dfrac{x^2}{x^2}+\dfrac{x\sqrt[3]{x^3-x^2}}{x^2}+\dfrac{\sqrt[3]{\left(x^3-x^2\right)^2}}{x^2}}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{3}=\dfrac{5}{6}\)
c/ \(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow+\infty}\dfrac{2x-1-2x-1}{\sqrt[3]{\left(2x-1\right)^2}+\sqrt[3]{4x^2-1}+\sqrt[3]{\left(2x+1\right)^2}}\)
\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow+\infty}\dfrac{-\dfrac{2}{x^{\dfrac{2}{3}}}}{\dfrac{\sqrt[3]{\left(2x-1\right)^2}}{x^{\dfrac{2}{3}}}+\dfrac{\sqrt[3]{4x^2-1}}{x^{\dfrac{2}{3}}}+\dfrac{\sqrt[3]{\left(2x+1\right)^2}}{x^{\dfrac{2}{3}}}}=0\)
Check lai ho minh nhe :v