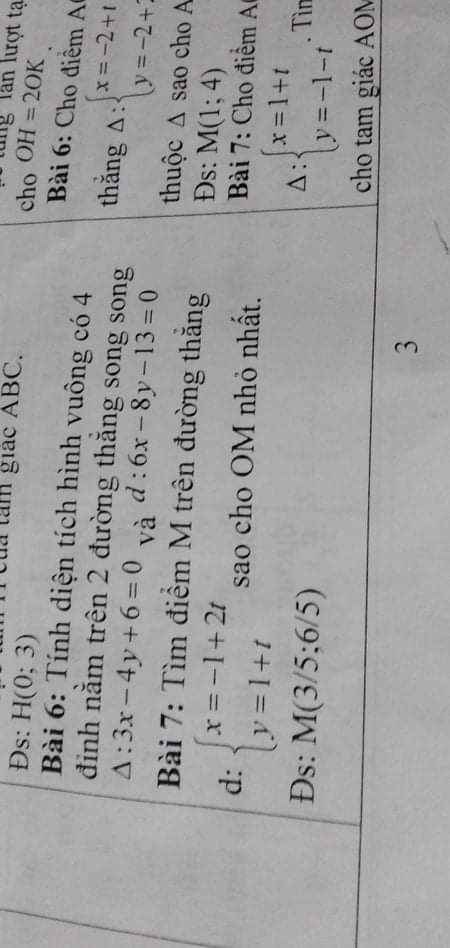Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Do M thuộc d nên tọa độ có dạng: \(M\left(2t-1;t+1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{OM}=\left(2t-1;t+1\right)\Rightarrow OM=\sqrt{\left(2t-1\right)^2+\left(t+1\right)^2}\)
\(OM=\sqrt{5t^2-2t+2}=\sqrt{5\left(t-\dfrac{1}{5}\right)^2+\dfrac{9}{5}}\ge\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{5}}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(t-\dfrac{1}{5}=0\Rightarrow t=\dfrac{1}{5}\Rightarrow M\left(-\dfrac{3}{5};\dfrac{6}{5}\right)\)
Đáp án của bài toán bị sai (nhầm dấu hoành độ)

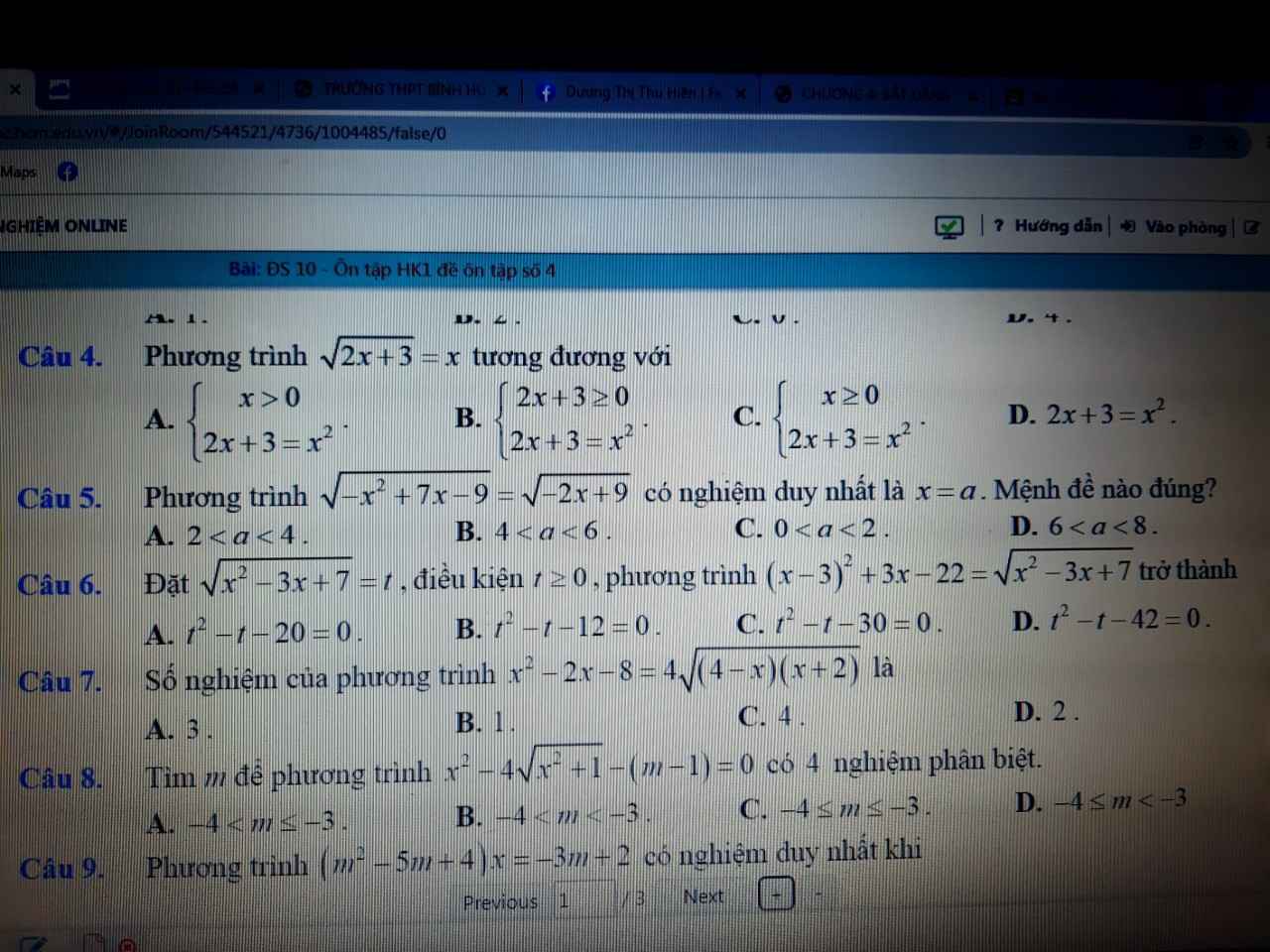
Câu 5:
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^2+7x-9+2x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9x+18=0\)
=>x=3
=>Chọn A

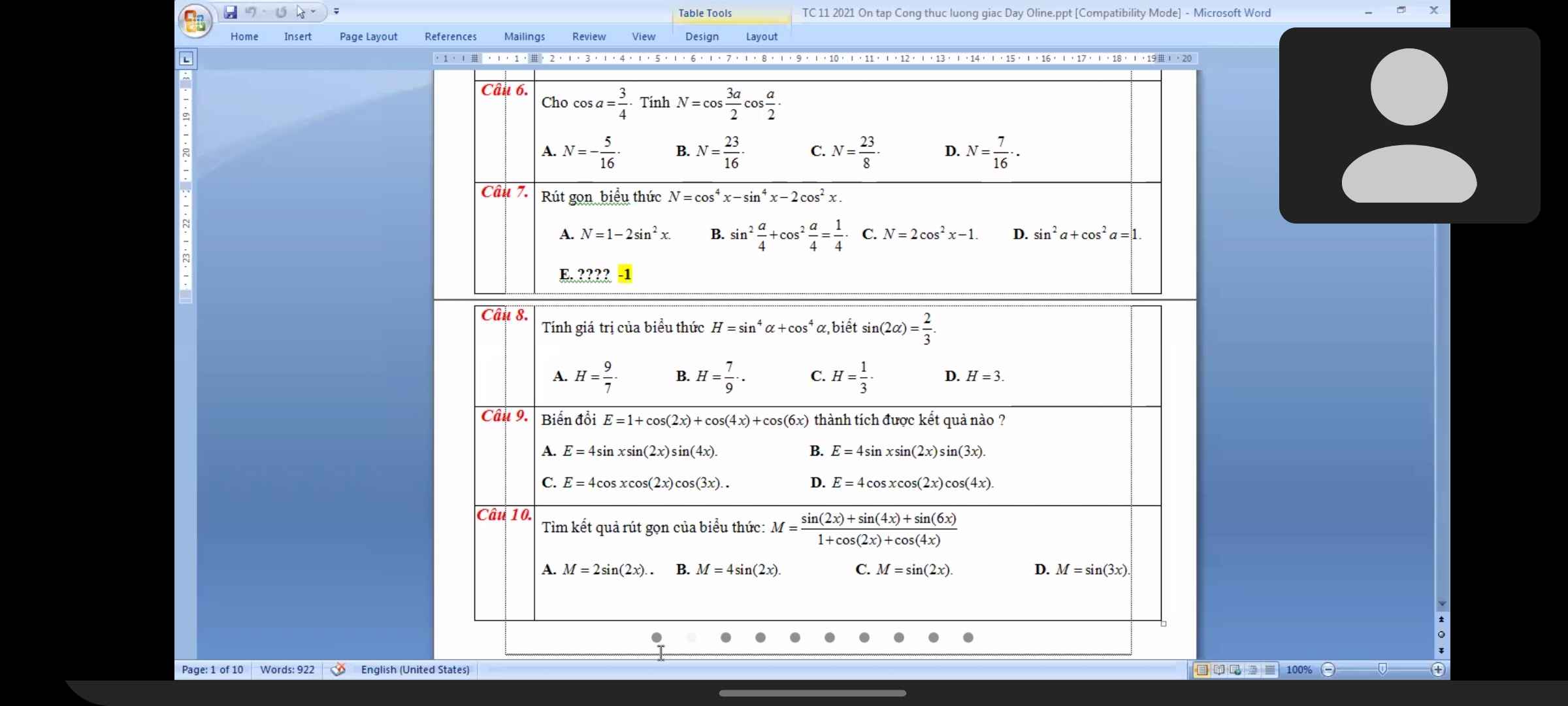
Lời giải:
$H=(\sin ^2a+\cos ^2a)^2-2\sin ^2a\cos ^2a$
$=1-\frac{1}{2}(2\sin a\cos a)^2=1-\frac{1}{2}(\sin 2a)^2=1-\frac{2}{9}=\frac{7}{9}$
Đáp án B.


\(x^2-6x+1>\left(2x-3\right)\sqrt{x^2+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+1-9\right)-3\left(2x-3\right)-\left(2x-3\right)\sqrt{x^2+1}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x^2+1}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x^2+1}+3\right)-\left(2x-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x^2+1}+3\right)>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x^2+1}+3\right)\left(\sqrt{x^2+1}-3-\left(2x-3\right)\right)>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x^2+1}-2x>0\) (do \(\sqrt{x^2+1}+3>0\) với mọi x)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x^2+1}>2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\le0\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\x^2+1>4x^2\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\le0\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{3}< x< \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\)

Con ko hiểu ngay chỗ khoanh tròn đỏ ạ. Sao thầy ghi là x<=0 , x>0 mà công thức là x<0, x>=0

Câu 6:
Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+5y-7=0\\x+3y-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+5y=7\\x+3y=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+5y-x-3y=7-3\\x+3y=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=2\\x=3-3\cdot2=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: A(-3;2)
M(-1;0) là trung điểm của AB
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_A+x_B=2\cdot x_M\\y_A+y_B=2\cdot y_M\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_B-3=2\cdot\left(-1\right)=-2\\y_B+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow B\left(1;-2\right)\)
Phương trình đường cao kẻ từ A xuống BC là x+3y-3=0
=>VTPT là (1;3)
=>BC nhận vecto (-3;1) làm vecto pháp tuyến
Phương trình đường thẳng CB là:
-3(x-1)+1(y+2)=0
=>-3x+3+y+2=0
=>-3x+y+5=0
Gọi N là trung điểm của BC
=>N là giao điểm của hai đường thẳng -3x+y+5=0 và x+5y-7=0
Tọa độ N là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-3x+y+5=0\\x+5y-7=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-3x+y=-5\\x+5y=7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-3x+y=-5\\3x+15y=21\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-3x+y+3x+15y=-5+21\\x+5y=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}16y=16\\x=7-5y\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=1\\x=7-5=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy: N(2;1)
Xét ΔABC có
N,M lần lượt là trung điểm của BC,BA
=>NM là đường trung bình
=>NM//AC
N(2;1); M(-1;0)
=>\(\overrightarrow{NM}=\left(-3;-1\right)=\left(3;1\right)\)
=>AC nhận vecto (3;1) làm vecto chỉ phương
=>VTPT là (-1;3)
Phương trình đường thẳng AC là:
-1(x+3)+3(y-2)=0
=>-x-3+3y-6=0
=>-x+3y-9=0

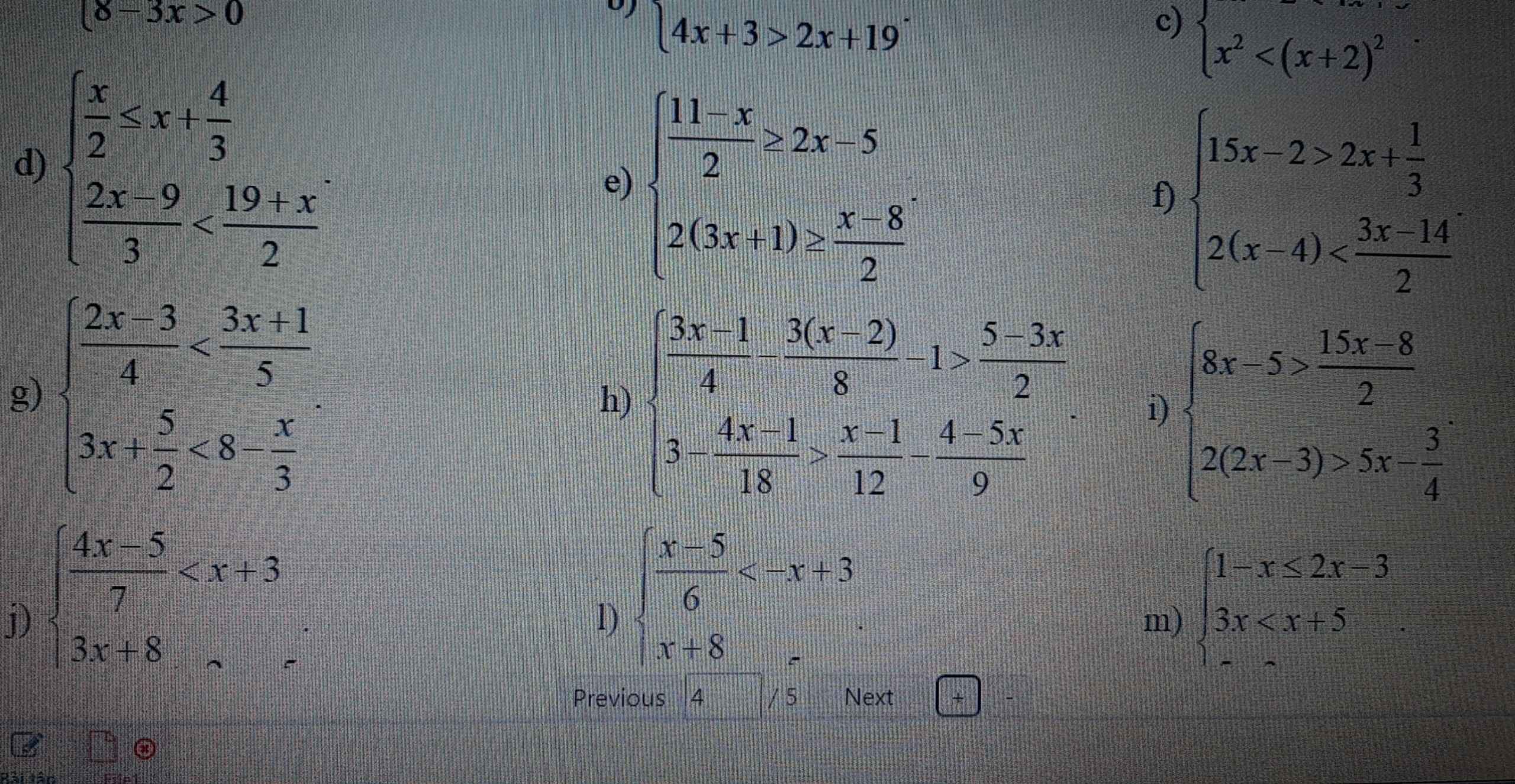
m: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-3x< =-4\\2x< 5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4}{3}< x< \dfrac{5}{2}\)