
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\left|x+1\right|và\left|x+2\right|\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+2\right)=3\\\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+2\right)=-3\end{cases}}\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}2x+3=3\\2x+3=-3\end{cases}}\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}2x=0\\2x=-6\end{cases}}\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=-3\end{cases}}\)
\(\left|x+1\right|+\left|x+2\right|=3\)
Xét \(x+1\ge0;x+2\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\ge-1;x\ge-2\Rightarrow x\ge-1\) ta có : \(\hept{\begin{cases}\left|x+1\right|=x+1\\\left|x+2\right|=x+2\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|x+1\right|+\left|x+2\right|=3\Leftrightarrow x+1+x+2=3\Leftrightarrow2x+3=3\Rightarrow x=0\)(TM)
Xét \(x+1\le0;x+2\ge0\Leftrightarrow-2\le x\le-1\) ta có : \(\hept{\begin{cases}\left|x+1\right|=-x-1\\\left|x+2\right|=x+2\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|x+1\right|+\left|x+2\right|=3\Leftrightarrow-x-1+x+2=3\Leftrightarrow1=3\) (loại)
Xét \(x+1\le0;x+2\le0\Leftrightarrow x\le-1;x\le-2\Leftrightarrow x\le-2\) ta có : \(\hept{\begin{cases}\left|x+1\right|=-x-1\\\left|x+2\right|=-x-2\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|x+1\right|+\left|x+2\right|=-x-1-x-2=-2x-3=3\Rightarrow x=-3\)(TM)
Vậy \(x=\left\{-3;0\right\}\)

a) Từ x - y = 2(x + y) = x : y
x - y = 2(x + y)
=> x - y = 2x + 2y
=> x = -3y
=> => x : y = - 3
Khi đó 2(x + y) = - 3
=> x + y = -1,5 (1)
=> x - y = -3 (2)
Từ (1) (2) => x = [(-1,5) + (-3)] : 2 = -2,25
=> y = -1,5 - (-2,25) = 0,75
Vậy x = -2,25 ; y = 0,75
b) Từ x + y = x.y = x : y (1)
=> xy = x : y
=> \(xy=\frac{x}{y}\Rightarrow y=\frac{x}{y}:x\Rightarrow y=\frac{1}{y}\Rightarrow y^2=1\Rightarrow y=\pm1\)
Từ (1) => x + y = xy
TH1 : Nếu y = 1
=> x + 1 = x
=> 0x = 1 (loại)
TH2 : Nếu y = -1
=> x - 1 = -x
=> 2x = 1
=> x = 0,5 (tm)
Vây y = - 1 ; x = 0,5

Ta có:
\(\dfrac{a\dfrac{1}{b}}{b\dfrac{1}{a}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{ab+1}{b}}{\dfrac{ab+1}{a}}=\dfrac{ab+1}{b}.\dfrac{a}{ab+1}=\dfrac{a}{b}\)
Vậy...........
Chúc bạn học tốt!!!

Dạng nâng cao:
Tìm x để `A=x/(x^2+1) in ZZ`
Tìm x để `B=(2-x)/x^2 in ZZ`.

\(\text{Ta có:}\)
\(y^2=xz\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{y}=\dfrac{y}{z}\left(1\right)\)
\(z^2=yt\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{y}=\dfrac{t}{x}\left(2\right)\)
\(\text{Từ (1) và (2)}\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{y}=\dfrac{y}{z}=\dfrac{t}{x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^3}{y^3}=\dfrac{y^3}{z^3}=\dfrac{t^3}{x^3}\)
\(\text{Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau:}\)
\(\dfrac{x^3}{y^3}=\dfrac{y^3}{z^3}=\dfrac{t^3}{x^3}=\dfrac{x^3+y^3+t^3}{y^3+z^3+x^3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^3}{t^3}=\dfrac{y^3+z^3+x^3}{y^3+z^3+x^3}\left(đpcm\right)\)

10:
Vì n là số lẻ nên n=2k-1
Số số hạng là (2k-1-1):2+1=k(số)
Tổng là (2k-1+1)*k/2=2k*k/2=k^2 là số chính phương
11:
n^3-n^2+2n+7 chia hết cho n^2+1
=>n^3+n-n^2-1+n+8 chia hết cho n^2+1
=>n+8 chia hết cho n^2+1
=>n^2-64 chia hết cho n^2+1
=>n^2+1-65 chia hết cho n^2+1
=>n^2+1 thuộc {1;5;13;65}
=>\(n\in\left\{0;2;-2;2\sqrt{3};-2\sqrt{3};8;-8\right\}\)
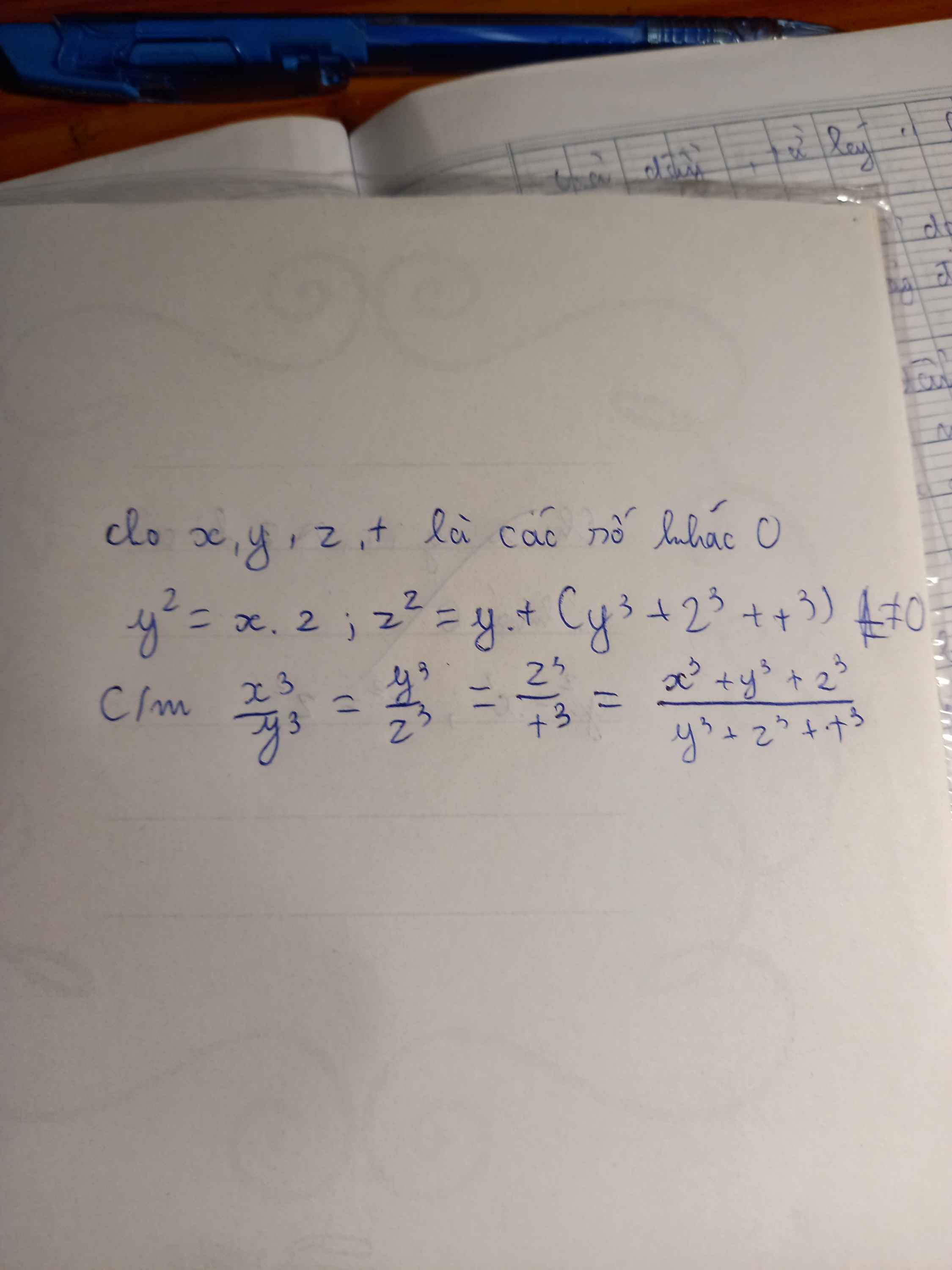
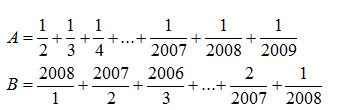
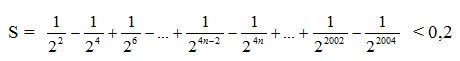
Ta có: \(x^2=x^5\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{0;1\right\}\)
Vậy ...........
\(Ta \) \(có : x^2 =x^5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(x^2 -x^5 = 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(x^2 . (1 - x^3 )=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\)\(x^2 = 0 \) \(hoặc \) \(1 - x^3 = 0\)
\(\Rightarrow\)\(x = 0 \) \(hoặc\) \(x^3=1\)
\(\Rightarrow\)\(x = 0\) \(hoặc\) \(x = 1\)
\(Vậy : x = 0\) \(hoặc \) \(x = 1\)