
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


d: Ta có: ƯCLN(a,b)=2
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2x\\b=2y\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(a\cdot b=120\)
=>\(2x\cdot2y=120\)
=>\(x\cdot y=30\)
mà x,y là các số nguyên dương
nên \(\left(x,y\right)\in\left\{\left(1;30\right);\left(2;15\right);\left(3;10\right);\left(5;6\right);\left(6;5\right);\left(10;3\right);\left(15;2\right);\left(30;1\right)\right\}\)
=>\(\left(a,b\right)\in\left\{\left(2;60\right);\left(4;30\right);\left(6;20\right);\left(10;12\right);\left(12;10\right);\left(20;6\right);\left(30;4\right);\left(60;2\right)\right\}\)

\(2n+3⋮3n+4\Leftrightarrow6n+9⋮3n+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(3n+4\right)+1⋮3n+4\Leftrightarrow1⋮3n+4\)
\(\Rightarrow3n+4\inƯ\left(1\right)=\left\{\pm1\right\}\)
| 3n + 4 | 1 | -1 |
| 3n | -3 | -5 |
| n | 1 | -5/3 |
\(2n+3⋮3n+4\)
Ta có: \(2n+3=3\left(2n+3\right)=6n+9\)
\(3n+4⋮3n+4\Leftrightarrow2\left(3n+4\right)⋮3n+4\Leftrightarrow6n+8⋮3n+4\Leftrightarrow\left(6n+9\right)-\left(6n+8\right)⋮3n+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1⋮3n+4\Leftrightarrow3n+4\inƯ\left(1\right)=\left\{\pm1\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow n\in\left\{-1;\frac{-5}{3}\right\}\)

Đề: Có ở trên
a) Khi nào nó là 1 phân số?
b) Khi nào nó là một số nguyên?

73\(x-2\) -3.73 = 73.4
7\(3x-2\) = 73.4 + 73.3
73\(x-2\) = 73.(4 + 3)
73x - 2 = 73.7
73\(x-2\) = 74
3\(x\) - 2 = 4
3\(x\) = 4 + 2
3\(x\) = 6
\(x\) = 6 : 3
\(x\) = 2

2.0=3.0=0
=> 2=3
1+1=2=3
=> ĐPCM
#Học-tốt

Ta có: A = 3 + 32 + 33 + ... + 3100
=> 3A = 32 + 33 + 34 + ... + 3101
=> 3A - A = 3101 - 3
=> 2A = 3101 - 3
=> 2A + 3 = 3101
=> x = 101
\(2A=3^2+3^3+...+3^{101}\)
\(2A-A=3^2-3^2+3^3-3^3+...+3^{101}-3\)
\(A=3^{101}-3\)
\(2.3^{101}-6+3=3^x\)
\(3.\left(2.3^{100}-1\right)=3^x\)


100=25 .4 =5^2.4
5^2019:( 5^2013-5^2.4.5^2010)=5^2019: ( 5^2013-5^2012.4)=5^2019: (5^2012.(5-4))
=5^2019:5^2012=5^7(=78125)
Học tốt
5x = 52019 : (52013 -100*52010)
<=> 5x = 52019 : (52010 .(53-100))
<=> 5x = 52019 : (52010 . 25)
<=> 5x = 52019 : 52012
<=> 5x = 57
<=> x = 7
Vậy x = 7

Bài 3:
Gọi số cây là x
Theo đề, ta có: \(x\in BC\left(3;8;10\right)\)
hay x=600

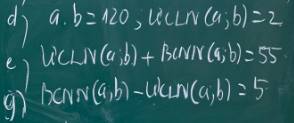


4.
\(\dfrac{x-7}{y-6}=\dfrac{7}{6}\Rightarrow\dfrac{x-7}{7}=\dfrac{y-6}{6}=\dfrac{-y+6}{-6}\)
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau:
\(\dfrac{x-7}{7}=\dfrac{-y+6}{-6}=\dfrac{x-7-y+6}{7-6}=\dfrac{x-y-1}{1}=-5\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-7=7.\left(-5\right)=-35\\-y+6=\left(-6\right).\left(-5\right)=30\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-28\\y=-24\end{matrix}\right.\)
5.
Ta có:
\(A^2=\dfrac{2^2.4^2.6^2...4998^2.5000^2}{3^2.5^2.7^2...4999^2.5001^2}< \dfrac{2^2.4^2.6^2.4998^2.5000^2}{\left(3^2-1\right)\left(5^2-1\right)\left(7^2-1\right)...\left(4999^2-1\right)\left(5001^2-1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow A^2< \dfrac{2^2.4^4.6^2...4998^2.5000^2}{2.4.4.6.6.8...4998.5000.5000.5002}=\dfrac{2^2.4^4.6^2...4998^2.5000^2}{2.4^4.6^2...4998^2.5000^2.5002}\)
\(\Rightarrow A^2< \dfrac{2}{5002}=\dfrac{1}{2501}< \dfrac{1}{2500}\)
\(\Rightarrow A< \dfrac{1}{50}\)
\(\Rightarrow A< 0,02\)
Bài 3:
\(A=B\) khi:
\(\dfrac{7}{y-2}=x+1\left(y\ne2\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(y-2\right)=7\)
Mà: x,y nguyên \(\Rightarrow x+1,y-2\inƯ\left(7\right)=\left\{1;-1;7;-7\right\}\)
Ta có bảng sau: