Giúp e câu c với ạ. Giải bất phương trình sử dụng dấu nhị thức bậc nhất
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\frac{-3x+1}{2x+1}+2\le0\)
\(\frac{-3x+1+4x+2}{2x+1}\le0\)
\(\frac{x+3}{2x+1}\le0\)
Lập bảng xet dấu, chú ý các mốc x = -3, x = -1/2
Nghiệm bpt là \(-3\le x<-\frac{1}{2}\)

Quy tắc xét dấu một nhị thức dựa trên định lí :
“Nhị thức f(x) = ax + b (a≠0) có dấu cùng với hệ số a khi x lấy giá trị trong khoảng (−ba,+∞)(−ba,+∞) và trái dấu với hệ số a khi x lấy các giá trị thuộc khoảng (−∞,−ba)(−∞,−ba)”.
Áp dụng: Ta lập bảng xét dấu của vế trái f(x) của bất phương trình:
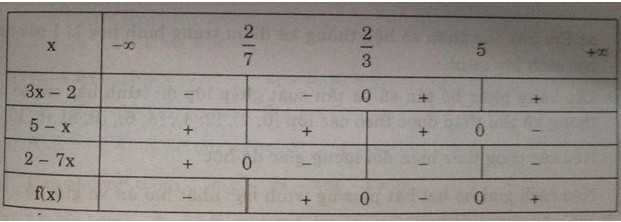
Tập nghiệm của bất phương trình: S=(27,23]∪[5,+∞)

\(\left(4A\right)\\ a,\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[\left(x-2\right)\left(2x+3\right)\right]\left[\left(x-2\right)\left(2x+3\right)\right]=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(-x-5\right)\left(3x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-x-5=0\\3x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-5\\x=\dfrac{-1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\\ b,\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[3\left(2x+1\right)\right]^2-\left[2\left(x+1\right)\right]^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[3\left(2x+1\right)-2\left(x+1\right)\right]\left[3\left(2x+1\right)+2\left(x+1\right)\right]=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(4x+1\right)\left(8x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x+1=0\\8x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-1}{4}\\x=\dfrac{-5}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\\ c,\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[\left(x+1\right)+1\right]^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)+1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x+2=0\Rightarrow x=-2\\ d,\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)+\left(x+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left[\left(x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)+1\right]=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2-4x+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\\left(x+2\right)^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(4B\right)\\ a,\\ \Leftrightarrow49-14x+x^2-4\left(x+25\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow49-14x+x^2-4x^2-40x-100=0\\ \Leftrightarrow3x^2-54x-51=0\\ \Leftrightarrow-3\left(x^2+18x+17\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x+17\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0\\x+17=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=-17\end{matrix}\right.\\ b,\\ \Leftrightarrow4x^2\left(x^2-2x+1\right)-\left(4x^2+4x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-6x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-6=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c,\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)=\left(x+1\right)\left(2-x\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left[\left(x^2-x+1\right)-\left(2-x\right)\right]=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^1-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0\\x-1=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=1\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\\ d,\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)

Do \(x^2+x+1=\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}>0;\forall x\) nên BPT tương đương:
\(-3\left(x^2+x+1\right)\le x^2-3x-1\le3\left(x^2+x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-3x-1\ge-3x^2-3x-3\\x^2-3x-1\le3x^2+3x+3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x^2\ge-2\left(luôn-đúng\right)\\2x^2+6x+4\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge-1\\x\le-2\end{matrix}\right.\)