Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Noob ơi, bạn phải đưa vào máy tính ý solve cái là ra x luôn, chỉ tội là đợi hơi lâu
a, 4.(18 - 5x) - 12(3x - 7) = 15(2x - 16) - 6(x + 14)
=> 72 - 20x - 36x + 84 = 30x - 240 - 6x - 84
=> (72 + 84) + (-20x - 36x) = (30x - 6x) + (-240 - 84)
=> 156 - 56x = 24x - 324
=> 24x + 56x = 324 + 156
=> 80x = 480
=> x = 480 : 80 = 6
Vậy x = 6

Bài 1:
- \(\dfrac{11}{2}x\) + 1 = \(\dfrac{1}{3}x-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
- \(\dfrac{11}{2}\)\(x\) - \(\dfrac{1}{3}\)\(x\) = - \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) - 1
-(\(\dfrac{33}{6}\) + \(\dfrac{2}{6}\))\(x\) = - \(\dfrac{5}{4}\)
- \(\dfrac{35}{6}\)\(x\) = - \(\dfrac{5}{4}\)
\(x=-\dfrac{5}{4}\) : (- \(\dfrac{35}{6}\))
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{3}{14}\)
Vậy \(x=\dfrac{3}{14}\)
Bài 2: 2\(x\) - \(\dfrac{2}{3}\) - 7\(x\) = \(\dfrac{3}{2}\) - 1
2\(x\) - 7\(x\) = \(\dfrac{3}{2}\) - 1 + \(\dfrac{2}{3}\)
- 5\(x\) = \(\dfrac{9}{6}\) - \(\dfrac{6}{6}\) + \(\dfrac{4}{6}\)
- 5\(x\) = \(\dfrac{7}{6}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{7}{6}\) : (- 5)
\(x\) = - \(\dfrac{7}{30}\)
Vậy \(x=-\dfrac{7}{30}\)

bài 1 .
a. 3 x(5x2 – 2x -1) = 15x3 – 6x2 – 3x
b. (x2+2xy -3)(-xy) = – x3y – 2x2y2 + 3xy
c. 1/2 x2y ( 2x3 – 2/5 xy2 -1 )= x5y – 1/5 x3y3 – 1/2 x2y
bài 2 .
a) 2x^3-3x-5x^3-x^2+x^2=-3x-3x^3
b) 3x^2-6x-5x+5x^2-8x^2+24=-11x+24
c) 3x^3-3/2x^2-x^3-x/2+x/2+2=2x^3-3/2x^2+2
bài 3 .
?????????? bài 3 thì tui ko biết
Bài 3 :
\(P=5x\left(x^2-3\right)+x^2\left(7-5x\right)-7x^2\)
\(=5x^3-15x+7x^2-5x^3-7x^2=-15x\)
Thay x = -5 vào biểu thức trên ta được
\(-15.\left(-5\right)=75\)
Vậy x = -5 thì P = 75

1/
a/ Đặt f (x) = x2 - 3
Khi f (x) = 0
=> \(x^2-3=0\)
=> \(x^2=3\)
=> \(x=\sqrt{3}\)
Vậy \(\sqrt{3}\)là nghiệm của đa thức x2 - 3.
b/ Đặt g (x) = x2 + 2
Khi g (x) = 0
=> \(x^2+2=0\)
=> \(x^2=-2\)
=> \(x\in\varnothing\)
Vậy x2 + 2 vô nghiệm.
c/ Đặt P (x) = x2 + (x2 + 3)
Khi P (x) = 0
=> \(x^2+\left(x^2+3\right)=0\)
=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}x^2=0\\x^2+3=0\end{cases}}\)=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=\sqrt{3}\end{cases}}\)(loại)
Vậy x2 + (x2 + 3) vô nghiệm.
d/ Đặt \(Q\left(x\right)=2x^2-\left(1+2x^2\right)+1\)
Khi Q (x) = 0
=> \(2x^2-\left(1+2x^2\right)+1=0\)
=> \(2x^2-\left(1+2x^2\right)=-1\)
=> \(2x^2-1-2x^2=-1\)
=> -1 = -1
Vậy đa thức \(2x^2-\left(1+2x^2\right)+1\)có vô số nghiệm.
e/ Đặt \(h\left(x\right)=\left(2x-1\right)^2-16\)
Khi h (x) = 0
=> \(\left(2x-1\right)^2-16=0\)
=> \(\left(2x-1\right)^2=16\)
=> \(2x-1=4\)
=> 2x = 5
=> \(x=\frac{5}{2}\)
Vậy đa thức \(\left(2x-1\right)^2-16\)có nghiệm là \(\frac{5}{2}\).

* Trả lời:
\(\left(1\right)\) \(-3\left(1-2x\right)-4\left(1+3x\right)=-5x+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3+6x-4-12x=-5x+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x-12x+5x=3+4+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=12\)
\(\left(2\right)\) \(3\left(2x-5\right)-6\left(1-4x\right)=-3x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x-15-6+24x=-3x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x+24x+3x=15+6+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow33x=28\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{28}{33}\)
\(\left(3\right)\) \(\left(1-3x\right)-2\left(3x-6\right)=-4x-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-3x-6x+12=-4x-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x-6x+4x=-1-12-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-5x=-18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{18}{5}\)
\(\left(4\right)\) \(x\left(4x-3\right)-2x\left(2x-1\right)=5x-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-3x-4x^2+2x=5x-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x-5x=-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x=-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{7}{6}\)
\(\left(5\right)\) \(3x\left(2x-1\right)-6x\left(x+2\right)=-3x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-3x-6x^2-12x=-3x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-15x+3x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-12x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\)

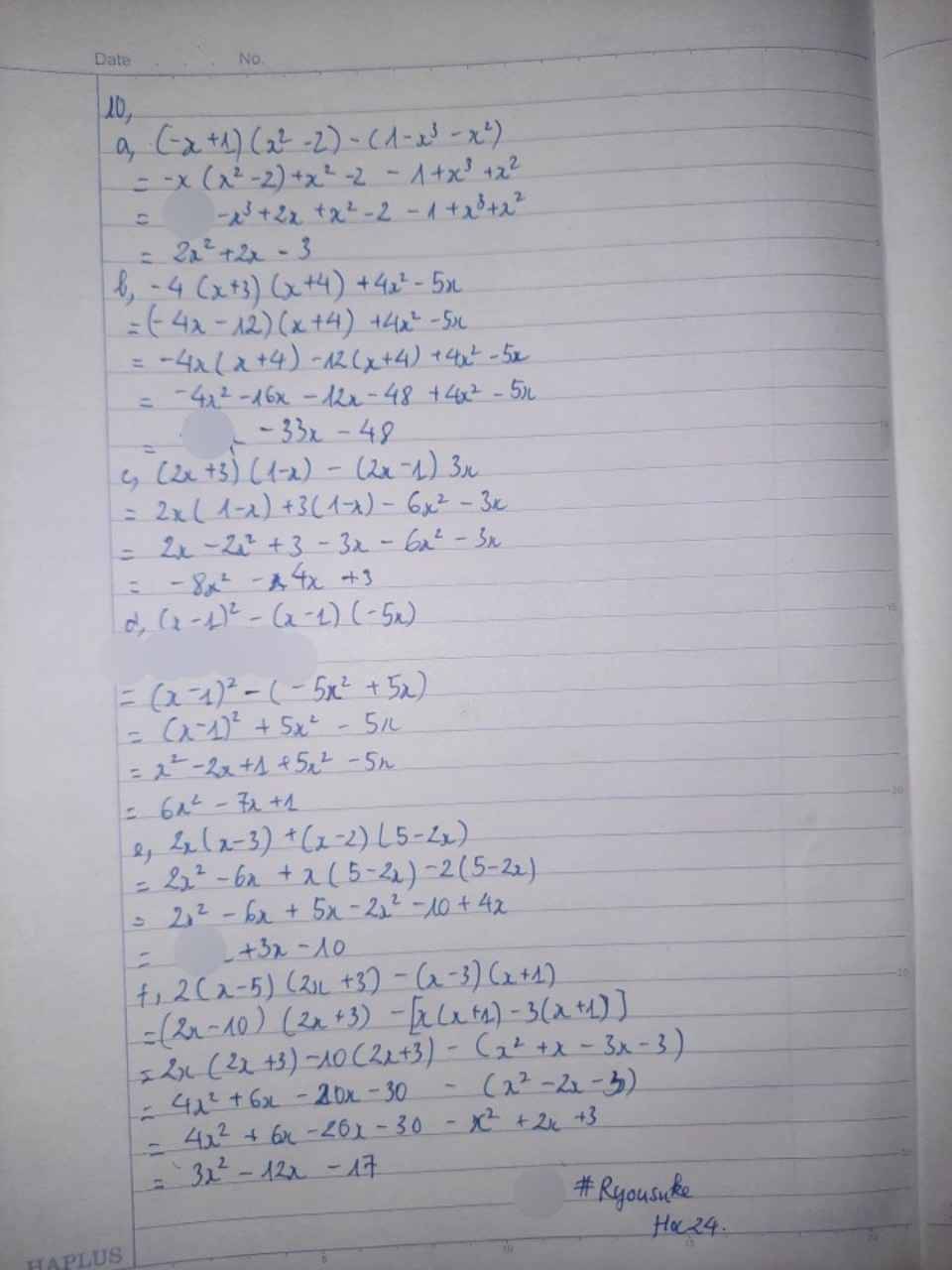
Khó nhìn qá bn à