
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a.\(ĐKXĐ:\hept{\begin{cases}x^2-2x\ne0\\x-2\ne0\\x\left(x+1\right)\ne0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\left(x-2\right)\ne0\\x-2\ne0\\x\left(x+1\right)\ne0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne2\\x\ne-1\end{cases}}}\)
b.\(M=\left(\frac{1}{x^2-2x}+\frac{2}{x-2}\right)\div\frac{2x+1}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\left(\frac{1}{x\left(x-2\right)}+\frac{2}{x-2}\right)\div\frac{2x+1}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\left(\frac{1}{x\left(x-2\right)}+\frac{2x}{x\left(x-2\right)}\right)\div\frac{2x+1}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\frac{2x+1}{x\left(x-2\right)}\div\frac{2x+1}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\frac{2x+1}{x\left(x-2\right)}.\frac{x\left(x+1\right)}{2x+1}=\frac{x\left(2x+1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(2x+1\right)}=\frac{x+1}{x-2}\)
c.Để \(M>1\)thì
\(\frac{x+1}{x-2}>1\)
c, Ta có : \(M>1\Rightarrow\frac{x+1}{x-2}>1\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+1}{x-2}-1>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+1-x+2}{x-2}>0\Leftrightarrow\frac{3}{x-2}>0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-2>0\Leftrightarrow x>2\)vì 3 > 0
d, Để M nguyên khi \(x+1⋮x-2\Leftrightarrow x-2+3⋮x-2\)ĐK : \(x\ne2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3⋮x-2\Rightarrow x-2\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm3\right\}\)
| x - 2 | 1 | -1 | 3 | -3 |
| x | 3 | 1 | 5 | -1 |

a, \(A=\frac{x^2+3x-x+3-x^2+1}{x^2-9}\)\(.\frac{x+3}{2}\) \(\left(x\ne3;-3\right)\)
\(A=\frac{2x+4}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}.\frac{x+3}{2}\)\(=\frac{2\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}.\frac{x+3}{2}\)\(=\frac{x+2}{x-3}\)
b, để \(A\in Z\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x+2⋮x-3\\x-3⋮x-3\end{cases}}\)\(\Rightarrow x+2-x+3=5⋮x-3\)\(\leftrightarrow x+3\in\left(1;5;-1;-5\right)\)
\(\leftrightarrow x\in\left(-2;2;-4;-8\right)\)

Trả lời:
a, \(A=\frac{x+5}{x+2}=\frac{x+2+3}{x+2}=\frac{x+2}{x+2}+\frac{3}{x+2}=1+\frac{3}{x+2}\)
Để \(A\inℤ\) thì \(\frac{3}{x+2}\inℤ\)
\(\Rightarrow3⋮x+2\Rightarrow x+2\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm3\right\}\)
Ta có bảng sau:
| x+2 | 1 | -1 | 3 | -3 |
| x | -1 | -3 | 1 | -5 |
Vậy \(x\in\left\{-1;-3;1;-5\right\}\)
b, \(B=\frac{x+1}{x+2}=\frac{x+2-1}{x+2}=\frac{x+2}{x+2}-\frac{1}{x+2}=1-\frac{1}{x+2}\)
Để A là số nguyên thì \(1⋮x+2\Rightarrow x+2\inƯ\left(1\right)=\left\{\pm1\right\}\)
Ta có bảng sau:
| x+2 | 1 | -1 |
| x | -1 | -3 |
Vậy \(x\in\left\{-1;-3\right\}\)
c, \(C=\frac{2x-1}{x+1}=\frac{2\left(x+1\right)-3}{x+1}=\frac{2\left(x+1\right)}{x+1}-\frac{3}{x+1}=2-\frac{3}{x+1}\)
Để C là số nguyên thì \(3⋮x+1\Rightarrow x+1\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm3\right\}\)
| x+1 | 1 | -1 | 3 | -3 |
| x | 0 | -2 | 2 | -4 |
Vậy \(x\in\left\{0;-2;2;-4\right\}\)

\(ĐKXĐ:x\ne2;x\ne-2;x\ne0\)
\(a,P=\left(\frac{-1}{2-x}-\frac{2x}{4-x^2}+\frac{1}{2+x}\right)\left(\frac{2}{x}-1\right)\)
\(P=\left(\frac{-2-x+2-x-2x}{\left(2-x\right)\left(2+x\right)}\right)\left(\frac{2-x}{x}\right)\)
\(P=\frac{-4x}{\left(2-x\right)\left(2+x\right)}\frac{2-x}{x}\)
\(P=\frac{-4}{2+x}\)
\(b,P=\frac{-4}{2+x}=\frac{1}{2}\)
\(2+x=-8\)
\(x=-10\)
\(c,P=-\frac{4}{2+x}\)
\(< =>-4⋮x+2\)
lập bảng ra thì bạn ra đc \(x=\left\{2;-1;-3;-6\right\}\)
a)\(P=\left(\frac{1}{x-2}-\frac{2x}{4-x^2}+\frac{1}{2+x}\right)\left(\frac{2}{x}-1\right)\)
\(P=\left(\frac{1}{x-2}+\frac{2x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\frac{1}{2+x}\right).\frac{2-x}{x}\)
\(P=\frac{x+2+2x+x-2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}.\frac{2-x}{x}\)
\(P=\frac{4x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}.\frac{2-x}{x}\)
\(P=\frac{-4}{x+2}\)
b) Để P=1/2
\(\Rightarrow-\frac{4}{x+2}=\frac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-8=x+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-10\)
c) Để P nhận GT nguyên
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+2\right)\inƯ_{\left(-4\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+2\right)\in\left\{-1;1;-2;2;-4;4\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\left\{-3;-1;-4;0;-6;2\right\}\)
#H

d, \(\frac{x+1}{9}+\frac{x+2}{8}=\frac{x+3}{7}+\frac{x+4}{6}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+1}{9}+1+\frac{x+2}{8}+1=\frac{x+3}{7}+1+\frac{x+4}{6}+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+10}{9}+\frac{x+10}{8}-\frac{x+10}{7}-\frac{x+10}{6}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+10\right)\left(\frac{1}{9}+\frac{1}{8}-\frac{1}{7}-\frac{1}{6}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+10=0\) (Vì \(\frac{1}{9}+\frac{1}{8}-\frac{1}{7}-\frac{1}{6}\) ≠ 0)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-10\)
Vậy x = -10 là nghiệm của phương trình.

Trả lời:
a, \(A=\frac{x^2-9}{x^2-6x+9}=\frac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)^2}=\frac{x+3}{x-3}\)
b, \(B=\frac{9x^2-16}{3x^2-4x}=\frac{\left(3x-4\right)\left(3x+4\right)}{x\left(3x-4\right)}=\frac{3x+4}{x}\)
c, \(C=\frac{x^2+4x+4}{2x+4}=\frac{\left(x+2\right)^2}{2\left(x+2\right)}=\frac{x+2}{2}\)
d, \(D=\frac{2x-x^2}{x^2-4}=\frac{x\left(2-x\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=-\frac{x\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=-\frac{x}{x+2}\)
e, \(E=\frac{3x^2+6x+12}{x^3-8}=\frac{3\left(x^2+2x+4\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+4\right)}=\frac{3}{x-2}\)

\(a,\frac{-2,6}{x}=-\frac{12}{42}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(-2,6\right).42=-12x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-12x=-\frac{546}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{91}{10}\)
\(b,\frac{x^2}{6}=\frac{24}{25}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow25x^2=24.6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow25x^2=144\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=\frac{144}{25}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{12}{5}\)

\(\frac{x+2}{2019}+\frac{x+3}{2018}=\frac{x+4}{2017}+\frac{x}{2021}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+2}{2019}+1+\frac{x+3}{2018}+1=\frac{x+4}{2017}+1+\frac{x}{2021}+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+2021}{2019}+\frac{x+2021}{2018}=\frac{x+2021}{2017}+\frac{x+2021}{2021}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2021=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2021\)
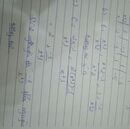


\(-\frac{2,6}{x}=-\frac{12}{42}\)
\(-2,6\cdot42=-12\cdot x\)
\(\frac{109,2}{12}=x\Rightarrow x=9,1\)