Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) Khi \(m=1\) thì pt đã cho trở thành \(x^2-2x-10=0\) (*)
pt (*) có \(\Delta'=\left(-1\right)^2-\left(-10\right)=11>0\)
Do đó (*) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-\left(-1\right)+\sqrt{11}}{1}=1+\sqrt{11}\\x_2=\dfrac{-\left(-1\right)-\sqrt{11}}{1}=1-\sqrt{11}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) Xét pt đã cho \(x^2-mx-10=0\) \(\left(a=1;b=-m;c=-10\right)\)
Nhận thấy \(ac=1\left(-10\right)=-10< 0\) nên pt đã cho luôn có 2 nghiệm phân biệt \(x_1,x_2\).
Áp dụng hệ thức Vi-ét, ta có \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{-m}{1}=m\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{-10}{1}=-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có \(x_1^2+x_2^2=29\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=29\Leftrightarrow m^2-2\left(-10\right)=29\)\(\Leftrightarrow m^2+20=29\Leftrightarrow m^2=9\Leftrightarrow m=\pm3\)
Vậy để pt đã cho có 2 nghiệm phân biệt thỏa mãn đề bài thì \(m=\pm3\)

b) phương trình có 2 nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m-1\right)^2-\left(m-1\right)\left(m+3\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-2m+1-m^2-3m+m+3\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4m+4\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\le1\)
Ta có: \(x_1^2+x_1x_2+x_2^2=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=1\)
Theo viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=2\left(m-1\right)\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=m+3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[-2\left(m-1\right)^2\right]-2\left(m+3\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-8m+4-2m-6-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-10m-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m_1=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{37}}{4}\left(ktm\right)\\m_2=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{37}}{4}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow m=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{37}}{4}\)

\(ac=-2< 0\Rightarrow\) phương trình luôn có 2 nghiệm pb trái dấu
Mà \(x_1>x_2\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_2< 0\\x_1>0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|x_1\right|=x_1\\\left|x_2\right|=-x_2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=m-1\\x_1x_2=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left|2x_1\right|-\left|x_2\right|=2+x_1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x_1+x_2=2+x_1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1+x_2=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m-1=2\)
\(\Rightarrow m=3\)

\(ac=-1< 0\Rightarrow\) pt luôn có 2 nghiệm pb trái dấu với mọi m
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2m\\x_1x_2=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
a.
\(x_1^2+x_2^2-x_1x_2=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-3x_1x_2=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2+3=7\)
\(\Rightarrow m^2=1\Rightarrow m=\pm1\)
b.
\(x_1-x_2=0\Rightarrow x_1=x_2\Rightarrow x_1x_2=x_2^2\ge0\) (vô lý do \(x_1x_2=-1< 0\) với mọi m)
Vậy ko tồn tại m thỏa mãn yêu cầu

b: Δ=(-2m)^2-4(m^2-2m+2)
=4m^2-4m^2+8m-8=8m-8
Để pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt thì 8m-8>0
=>m>1
x1^2+x2^2=x1+x2+8
=>(x1+x2)^2-2x1x2-(x1+x2)=8
=>(2m)^2-2(m^2-2m+2)-2m=8
=>4m^2-2m^2+4m-4-2m=8
=>2m^2+2m-12=0
=>m^2+m-6=0
=>(m+3)(m-2)=0
mà m>1
nên m=2

\(\Delta=\left(-m\right)^2-2.1.\left(m-1\right)\\ =m^2-2m+1\\ =\left(m-1\right)^2\)
Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt :
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta>0\\ \Rightarrow\left(m-1\right)^2>0\\ \Rightarrow m\ne1\)
Theo vi ét :
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=m\\x_1x_2=m-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x^2_1+x^2_2=x_1+x_2\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2_1+x^2_2=m\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2_1+2x_1x_2+x_2^2\right)-2x_1x_2=m\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2-m=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m^2-2\left(m-1\right)-m=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m^2-2m+2-m=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m^2-3m+2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=1\left(loại\right)\\m=2\left(t/m\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(m=2\)
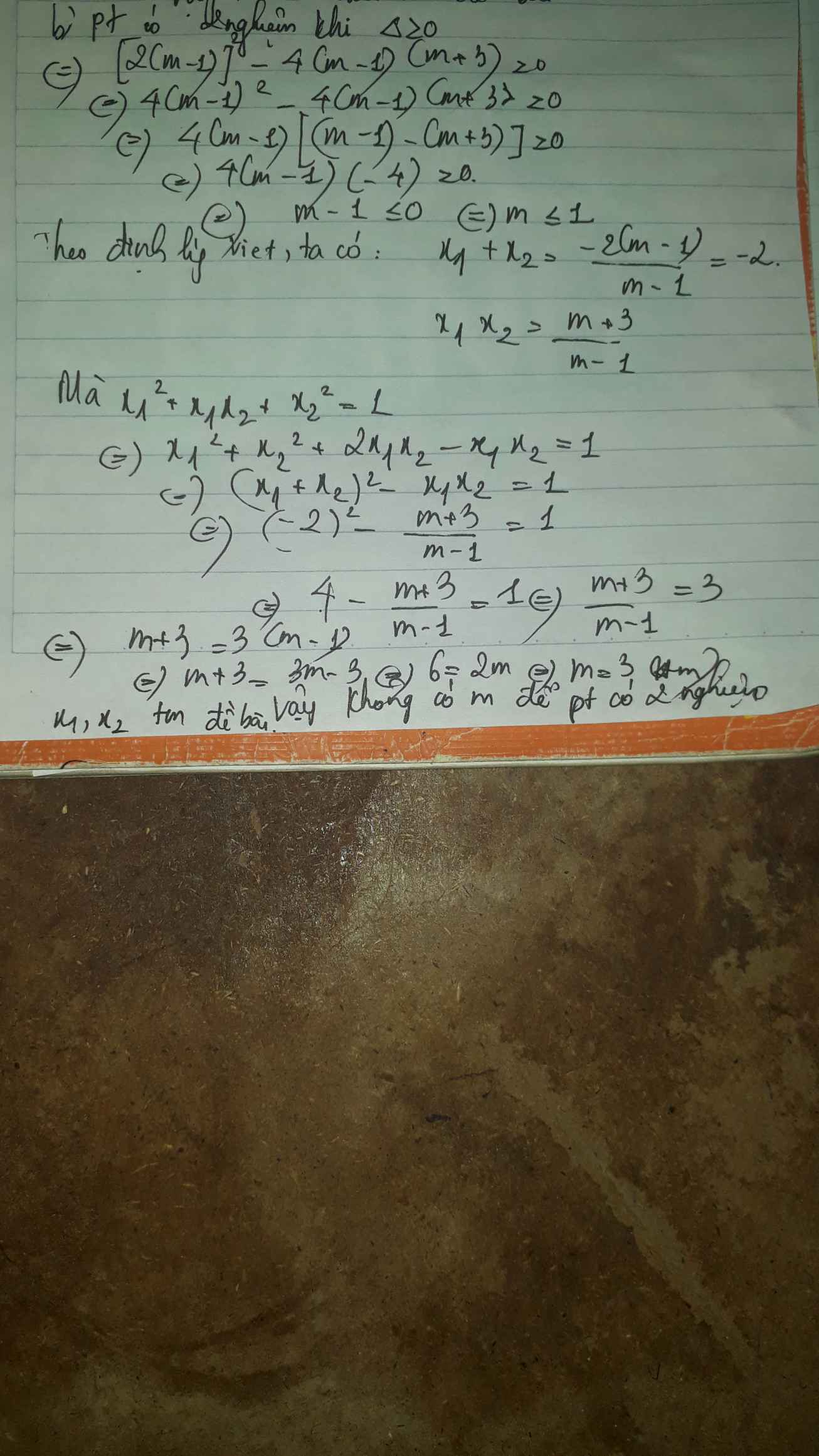

Bạn nên viết lại đề bằng công thức toán (biểu tượng $\sum$ góc trái khung soạn thảo) để mọi người hiểu đề của bạn hơn nhé.