Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a: \(A=\left(\dfrac{2\left(2x+1\right)}{2\left(2x+4\right)}-\dfrac{x}{3x-6}-\dfrac{2x^3}{3x^3-12x}\right):\dfrac{6x+13x^2}{24x-12x^2}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{2\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{x}{3\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{2x^3}{3x\left(x^2-4\right)}\right):\dfrac{x\left(13x+6\right)}{x\left(24-12x\right)}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{2\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{x}{3\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{2x^2}{3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\right):\dfrac{13x+6}{-12\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\left(2x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)-2x\left(x+2\right)-4x^2}{6\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\cdot\dfrac{-12\left(x-2\right)}{13x+6}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\left(2x^2-3x-2\right)-2x^2-4x-4x^2}{x-2}\cdot\dfrac{-2}{13x+6}\)
\(=\dfrac{6x^2-9x-6-6x^2-4x}{x-2}\cdot\dfrac{-2}{13x+6}\)
\(=\dfrac{-\left(13x+6\right)\cdot\left(-2\right)}{\left(13x+6\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{2}{x-2}\)
b: Để A>0 thì x-2>0
hay x>2
Để A>-1 thì A+1>0
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2+x-2}{x-2}>0\)
=>x/x-2>0
=>x>2 hoặc x<0

Bài 1.
a)
\((x-2)(2x-1)-(2x-3)(x-1)-2\\=2x^2-x-4x+2-(2x^2-2x-3x+3)-2\\=2x^2-5x+2-(2x^2-5x+3)-2\\=2x^2-5x+2-2x^2+5x-3-2\\=(2x^2-2x^2)+(-5x+5x)+(2-3-2)\\=-3\)
b)
\(x(x+3y+1)-2y(x-1)-(y+x+1)x\\=x^2+3xy+x-2xy+2y-xy-x^2-x\\=(x^2-x^2)+(3xy-2xy-xy)+(x-x)+2y\\=2y\)
Bài 2.
a)
\((14x^3+12x^2-14x):2x=(x+2)(3x-4)\\\Leftrightarrow 14x^3:2x+12x^2:2x-14x:2x=3x^2-4x+6x-8\\ \Leftrightarrow 7x^2+6x-7=3x^2+2x-8\\\Leftrightarrow (7x^2-3x^2)+(6x-2x)+(-7+8)=0\\\Leftrightarrow 4x^2+4x+1=0\\\Leftrightarrow (2x)^2+2\cdot 2x\cdot 1+1^2=0\\\Leftrightarrow (2x+1)^2=0\\\Leftrightarrow 2x+1=0\\\Leftrightarrow 2x=-1\\\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-1}2\)
b)
\((4x-5)(6x+1)-(8x+3)(3x-4)=15\\\Leftrightarrow 24x^2+4x-30x-5-(24x^2-32x+9x-12)=15\\\Leftrightarrow 24x^2-26x-5-(24x^2-23x-12)=15\\\Leftrightarrow 24x^2-26x-5-24x^2+23x+12=15\\\Leftrightarrow -3x+7=15\\\Leftrightarrow -3x=8\\\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-8}3\\Toru\)

a/ \(P=\frac{2\left(x^2-4x+4\right)}{\left(x^3-8\right)-\left(6x^2-12x\right)}=\frac{2\left(x-2\right)^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+4\right)-6x\left(x-2\right)}=\frac{2\left(x-2\right)^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2-4x+4\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{2\left(x-2\right)^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2-4x+4\right)}=\frac{2\left(x-2\right)^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-2\right)^2}=\frac{2}{x-2}\)
b/ Để P nguyên thì 2 phải chia hết cho x-2
=> x-2=(-2; -1; 1; 2) => x={0; 1; 3; 4}
a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc
Ta sẽ thêm và bớt 3a2b +3ab2 sau đó nhóm để phân tích tiếp
a3 + b3 + c3 = (a3 + 3a2b +3ab2 + b3) + c3 – (3a2b +3ab2 + 3abc)
= (a + b)3 +c3 – 3ab(a + b + c)
= (a + b + c)[(a + b)2 – (a + b)c + c2 – 3ab]
= (a + b + c)(a2 + 2ab + b2 – ac – bc + c2 – 3ab]
= (a + b + c)(a2 + b2 + c2 – ab – ac – bc)

a)\(P=\frac{2x^2-8x+8}{x^3-6x^2+12x-8}\left(x\ne2\right)\)
\(P=\frac{2\left(x-2\right)^2}{\left(x-2\right)^3}\)
\(P=\frac{2}{x-2}\)
b)Để P nguyên thì \(2⋮x-2\).Hay \(\left(x-2\right)\inƯ\left(2\right)\)
Ư(2) là:[1,-1,2,-2]
Do đó ta có bảng sau:
| x-2 | -2 | -1 | 1 | 2 |
| x | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 |

b: \(x^2-6x+xy-6y\)
\(=x\left(x-6\right)+y\left(x-6\right)\)
\(=\left(x-6\right)\left(x+y\right)\)
c: \(2x^2+2xy-x-y\)
\(=2x\left(x+y\right)-\left(x+y\right)\)
\(=\left(x+y\right)\left(2x-1\right)\)
e: \(x^3-3x^2+3x-1=\left(x-1\right)^3\)

a) (6x+1)2 + (6x-1)2 - 2(1+6x)(6x-1)
= (6x+1+6x-1)2
=144x2
b) x(2x2 -3) - x2(5x+1) +x2
=2x3 - 3x - 5x3 -x2+x2
=-3x3-3x
=-3x(x2+1)
c) 3(22+1)(24+1)(28+1)(216+1)
= (22-1)(22+1)(24+1)(28+1)(216+1)
= (24-1)(24+1)(28+1)(216+1)
= (28-1)(28+1)(216+1)
= (216-1)(216+1)
= 232 -1
d) 3x(x-2) - 5x(1-x) - 8(x2 -3)
= 3x2-6x - 5x + 5x2 - 8x2 +24
= -11x +24
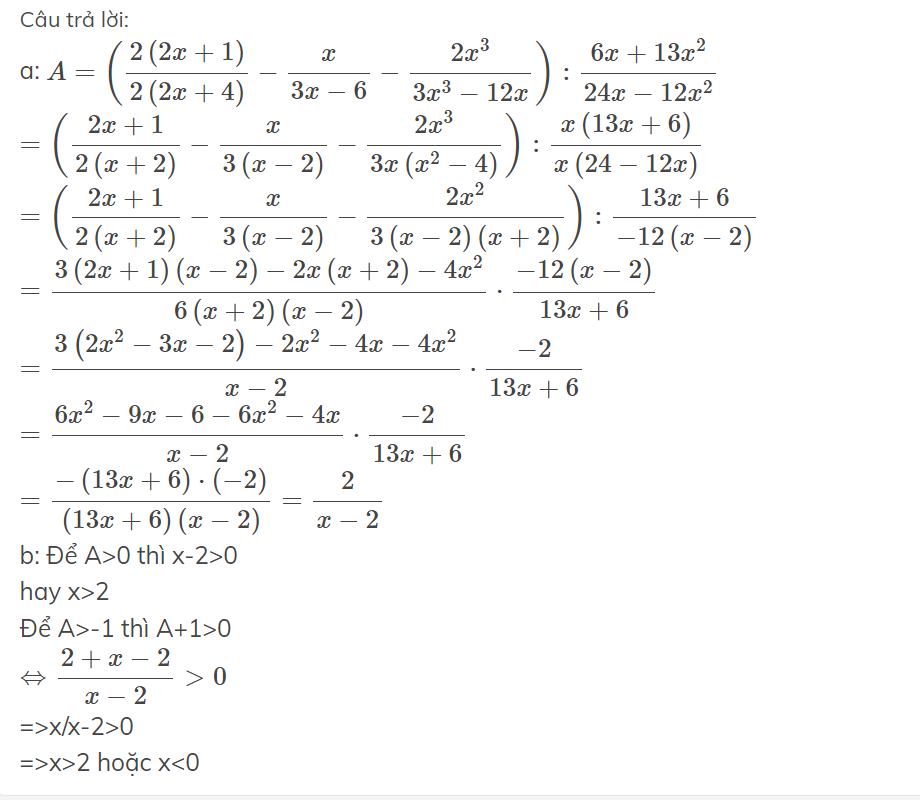
a: \(=\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)^3}=\dfrac{3}{\left(x-2\right)^2}\)
b: \(=\dfrac{x^2\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)^3}=\dfrac{x^2}{\left(x+2\right)^2}\)
Mik cảm ơn ạ