Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Mấy này bạn quy đồng lên cùng mẫu xong khử mẫu rồi giải. Dễ mà.

Câu 2:
ĐKXĐ: \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}1-9x^2\ne0\\1+3x\ne0\\1-3x\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow \left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ne\dfrac{-1}{3}\\x\ne\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{12}{1-9x^2}=\dfrac{1-3x}{1+3x}-\dfrac{1+3x}{1-3x}\left(1\right)\)
\(\left(1\right):\dfrac{12}{\left(1-3x\right)\left(1+3x\right)}-\dfrac{\left(1-3x\right)\left(1-3x\right)}{\left(1-3x\right)\left(1+3x\right)}+\dfrac{\left(1+3x\right)\left(1+3x\right)}{\left(1-3x\right)\left(1+3x\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 12-\left(1-3x-3x+9x^2\right)+\left(1+3x+3x+9x^2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 12-1+3x+3x-9x^2+1+3x+3x+9x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+12=0\\ \Leftrightarrow12x=-12\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-1\left(TM\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{-1\right\}\)

a) ĐKXĐ: x # -5
\(\dfrac{2x-5}{x+5}=3\) ⇔ \(\dfrac{2x-5}{x+5}=\dfrac{3\left(x+5\right)}{x+5}\)
⇔ 2x - 5 = 3x + 15
⇔ 2x - 3x = 5 + 20
⇔ x = -20 thoả ĐKXĐ
Vậy tập hợp nghiệm S = {-20}
b) ĐKXĐ: x # 0
\(\dfrac{x^2-6}{x}=x+\dfrac{3}{2}\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\left(x^2+6\right)}{2x}=\dfrac{2x^2+3x}{2x}\)
Suy ra: 2x2 – 12 = 2x2 + 3x ⇔ 3x = -12 ⇔ x = -4 thoả x # 0
Vậy tập hợp nghiệm S = {-4}.
c) ĐKXĐ: x # 3
\(\dfrac{\left(x^2+2x\right)-\left(3x+6\right)}{x-3}=0\) ⇔ x(x + 2) - 3(x + 2) = 0
⇔ (x - 3)(x + 2) = 0 mà x # 3
⇔ x + 2 = 0
⇔ x = -2
Vậy tập hợp nghiệm S = {-2}
d) ĐKXĐ: x # \(-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(\dfrac{5}{3x+2}=2x-1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5}{3x+2}=\dfrac{\left(2x-1\right)\left(3x+2\right)}{3x+2}\)
⇔ 5 = (2x - 1)(3x + 2)
⇔ 6x2 – 3x + 4x – 2 – 5 = 0
⇔ 6x2 + x - 7 = 0
⇔ 6x2 - 6x + 7x - 7 = 0
⇔ 6x(x - 1) + 7(x - 1) = 0
⇔ (6x + 7)(x - 1) = 0
⇔ x = \(-\dfrac{7}{6}\) hoặc x = 1 thoả x # \(-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm S = {1;\(-\dfrac{7}{6}\)}.
a)ĐKXĐ:x≠-5
Khử mẫu:2x-5=3(x+5) (1)
giải phương trình (1),ta được:
(1)⇔2x-5=3x+15
⇔2x-3x=15+5
⇔-x=20⇔x=-20(TM)
vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm x=-20
giải các phương trình sau:
a) 6x-3= 4x+5
b) \(\dfrac{2x+3}{x+1}\)- \(\dfrac{6}{x}\)= 2
c) \(|3x-1|\)=3x

a)\(6x-3=4x+5\)
\(\Rightarrow6x-3-4x-5=0\)
\(\Rightarrow2x-8=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=4\)
Vậy x=4
b)\(\frac{2x+3}{x+1}-\frac{6}{x}=2\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne-1;0\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{2x^2+3x}{x\left(x+1\right)}-\frac{6x+6}{x\left(x+1\right)}=2\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{2x^2+3x-6x-6}{x\left(x+1\right)}=2\)
\(\Rightarrow2x^2-3x-6=2\left(x^2+x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow2x^2-3x-6-2x^2-2x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow-5x-6=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-\frac{6}{5}\)
Vậy \(x=-\frac{6}{5}\)
c)\(\left|3x-1\right|=3x\left(1\right)\)
TH1:\(x\ge\frac{1}{3}\).PT(1) có dạng:3x-1=3x
0x=1
PT vô nghiệm
TH2:\(x< \frac{1}{3}\).PT(1) có dạng:1-3x=3x
\(\Rightarrow6x=1\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{1}{6}\left(TM\right)\)
Vậy PT có nghiệm là \(\frac{1}{6}\)
a, \(6x-3=4x+5 \)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x-4x=5+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=4\)
vậy no của pt là : x = 4
b, \(\frac{2x+3}{x+1}-\frac{6}{x}=2\)
ĐKXĐ : \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne-1\\x\ne0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x^2+3x-6x-6}{x\left(x+1\right)}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x^2-3x-6}{x\left(x+1\right)}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-3x-6=2x^2+2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-5x=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-6}{5}\)
vậy no của pt là x=-6/5
c, \(\left|3x-1\right|=3x\)
Với \(3x-1\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow3x-1=3x\Leftrightarrow-1=0\)( vô lí )

a: =>5-x+6=12-8x
=>-x+11=12-8x
=>7x=1
hay x=1/7
b: \(\dfrac{3x+2}{2}-\dfrac{3x+1}{6}=2x+\dfrac{5}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x+6-3x-1=12x+10\)
=>12x+10=6x+5
=>6x=-5
hay x=-5/6
d: =>(x-2)(x-3)=0
=>x=2 hoặc x=3

a: \(\Leftrightarrow20x^2-12x+15x+5< 10x\left(2x+1\right)-30\)
\(\Leftrightarrow20x^2+3x+5< 20x^2+10x-30\)
=>3x+5<10x-30
=>-7x<-35
hay x>5
b: \(\Leftrightarrow4\left(5x-20\right)-6\left(2x^2+x\right)>4x\left(1-3x\right)-15x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow20x-80-12x^2-6x>4x-12x^2-15x\)
=>14x-80>-11x
=>25x>80
hay x>16/5
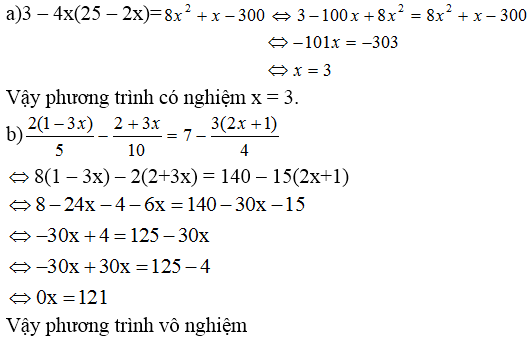




\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(3x+2\right)-3x-1=12x+10\)
=>9x+6-3x-1=12x+10
=>12x+10=3x+5
=>9x=-5
hay x=-5/9
\(9x+6-3x-1=12x+10\Leftrightarrow6x+5=12x+10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x=-5\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{5}{6}\)