
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1" =>-4y-y=-5-13
=>-5y=-18
=>y=18/5
2: =>2x+x=2/3+3/5
=>3x=19/15
=>x=19/45
3: =>17-14x-14=13-5x+15
=>-14x+3=-5x+28
=>-9x=25
=>x=-25/9
4: =>3(3x-7)+2(x+1)=-96
=>9x-21+2x+2=-96
=>11x=-96+19=-77
=>x=-7
5: =>15x-5x-5=6x+3
=>10x-5=6x+3
=>4x=8
=>x=2


1.
\(A=\dfrac{x\left(x^2+x-6\right)}{x\left(x^2-4\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x^2-4\right)+x-2}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)+x-2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2+1\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{x+3}{x+2}\)
thay x = 98 ta được: \(A=\dfrac{101}{100}\)
2. (đkxd \(x\ne\pm1\))
\(B=\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}+\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}+\dfrac{5x}{1-x^2}=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}-\dfrac{5x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(x+1\right)^2-5x}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{x^2-2x+1+x^2+2x+1-5x}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{2x^2-5x+2}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{2x^2-4x-x+2}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{2x\left(x-2\right)-\left(x-2\right)}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-1\right)}{x^2-1}\)để B bằng 0 thì: \(\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\left(x^2-1\ge0\forall x\ne\pm1\right)\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\2x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\left(tm\right)\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) \(M=\dfrac{x}{x-2}:\left(\dfrac{2x}{x^2-2x}-\dfrac{3}{x}\right)\)
\(M=\dfrac{x}{x-2}:\left(\dfrac{2x}{x\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)}{x\left(x-2\right)}\right)\)
\(M=\dfrac{x}{x-2}:\left(\dfrac{2x-3x+6}{x\left(x-2\right)}\right)\)
\(M=\dfrac{x}{x-2}.\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{6-x}\)
\(M=\dfrac{x^2}{6-x}\)
b) \(x^2-3x=0\)
\(x\left(x-3\right)=0\)
x=0 (KTMĐK) hoặc x=3 (TMĐK)
Thay x=3 vào M ta có :
\(M=\dfrac{3^2}{6-3}=\dfrac{9}{3}=3\)
c) \(M\ge0\rightarrow\dfrac{x^2}{6-x}\ge0\)
\(x^2\ge0\rightarrow6-x\ge0\)
\(x\le6\)
Kết hợp với ĐK, ta có : \(x\le6,x\ne0,x\ne2\)

Bài 1:
a) ĐKXĐ: $x\neq 0$
PT $\Leftrightarrow \frac{x(x-1)+3(x+3)}{3x}=2$
$\Rightarrow x^2+2x+9=6x$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+9=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)^2=-5<0$ (vô lý)
Do đó pt vô nghiệm
b)
$x^2-25=(2x-1)(x+5)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-5)(x+5)=(2x-1)(x+5)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-5)(x+5)-(2x-1)(x+5)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+5)[(x-5)-(2x-1)]=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+5)(-x-4)=0$
$\Rightarrow x+5=0$ hoặc $-x-4=0$
$\Rightarrow x=-5$ hoặc $x=-4$
c) ĐKXĐ: $x\neq 0; x\neq -2$
PT $\Leftrightarrow \frac{x(x-2)}{x(x+2)}-\frac{x^2+2}{x(x+2)}=\frac{3(x+2)}{x(x+2)}$
$\Rightarrow x(x-2)-(x^2+2)=3(x+2)$
$\Leftrightarrow -8=5x$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-8}{5}$ (thỏa mãn)
Bài 2:
a)
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{\begin{matrix}
x-3\neq 0\\
9-x^2\neq 0\\
x+3\neq 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\neq \pm 3\)
\(M=\left(\frac{(x+3)^2}{(x-3)(x+3)}-\frac{18}{(x-3)(x+3)}+\frac{(x-3)^2}{(x+3)(x-3)}\right):\frac{2}{x+3}\)
\(=\frac{(x+3)^2-18+(x-3)^2}{(x-3)(x+3)}.\frac{x+3}{2}=\frac{2x^2}{(x-3)(x+3)}.\frac{x+3}{2}=\frac{x^2}{x-3}\)
b)
\(M=\frac{x^2}{x-3}=\frac{x^2-9+9}{x-3}=x+3+\frac{9}{x-3}\)
Với $x$ nguyên, để $M$ nguyên thì $\frac{9}{x-3}$ nguyên
Với $x$ nguyên, để $\frac{9}{x-3}$ nguyên thì $x-3$ là ước của $9$
$\Rightarrow x-3\in\left\{\pm 1;\pm 3;\pm 9\right\}$
$\Rightarrow x\in\left\{2;4;6;0;12;-6\right\}$ (đều thỏa)

\(P=x^2+20y^2+8xy-4y+2009\)
\(=\left(x^2+8xy+16y^2\right)+\left(4y^2-4y+1\right)+2008\)
\(=\left(x+4y\right)^2+\left(2y-1\right)^2+2008\)
Vì: \(\begin{cases}\left(x+4y\right)^2\ge0\\\left(2y-1\right)^2\ge0\end{cases}\)\(\Rightarrow\left(x+4y\right)^2+\left(2y-1\right)^2\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+4y\right)^2+\left(2y-1\right)^2+2008\ge2008\)
Vậy GTNN của bt trên là 2008 khi \(\begin{cases}x+4y=0\\2y-1=0\end{cases}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}x=-2\\y=\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}\)


a: Xét ΔBAC có
D là trung điểm của AB
M là trung điểm của AC
Do đó: DM là đường trung bình của ΔABC
Suy ra: DM//BC và \(DM=\dfrac{BC}{2}=3.5\left(cm\right)\)

Đk: \(\hept{\begin{cases}x^2-9\ge0\\2x-6+\sqrt{x^2-9}\ne0\end{cases}}\)
\(A=\frac{\sqrt{\left(x+3\right)^2}+2\sqrt{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}}{2\sqrt{\left(x-3\right)^2}+\sqrt{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}}\)
TH1: \(\hept{\begin{cases}x+3\ge0\\x-3\ge0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}x\ge3\)
\(A=\frac{\sqrt{x+3}.\sqrt{x+3}+2\sqrt{x-3}.\sqrt{x+3}}{2\sqrt{x-3}\sqrt{x-3}+\sqrt{x+3}.\sqrt{x-3}}\)
\(A=\frac{\sqrt{x+3}\left(\sqrt{x+3}+2\sqrt{x-3}\right)}{\sqrt{x-3}\left(2\sqrt{x-3}+\sqrt{x+3}\right)}=\frac{\sqrt{x+3}}{\sqrt{x-3}}=\frac{\sqrt{x^2-9}}{x-3}\)
TH2: \(\hept{\begin{cases}x+3\le0\\x-3\le0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}x\le-3\)
\(A=\frac{\sqrt{\left(-x-3\right)^2}+2\sqrt{\left(-x+3\right)\left(-x-3\right)}}{2\sqrt{\left(-x+3\right)^2}+\sqrt{\left(-x+3\right)\left(-x-3\right)}}\)
\(A=\frac{\sqrt{-x-3}\left(\sqrt{-x-3}+2\sqrt{-x+3}\right)}{\sqrt{-x+3}\left(2\sqrt{-x+3}+\sqrt{-x-3}\right)}=\frac{\sqrt{-x-3}}{\sqrt{-x+3}}=\frac{\sqrt{x^2-9}}{3-x}\)
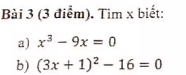 Mn giups em với
Mn giups em với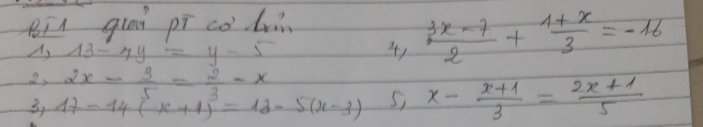




a) \(x^3-9x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2-9\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(\left(3x+1\right)^2-16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1-4\right)\left(3x+1+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x-1\right)\left(3x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-\dfrac{5}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
a: Ta có: \(x^3-9x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: Ta có: \(\left(3x+1\right)^2-16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-2\right)\left(3x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)