
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1) \(HPT.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6\sqrt{x}+4\sqrt{y}=32.\\6\sqrt{x}-9\sqrt{y}=-33.\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\left(x\ge0;y\ge0\right).\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3\sqrt{x}+2\sqrt{y}=16.\\13\sqrt{y}=65.\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x}=2.\\\sqrt{y}=5.\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=4.\\y=25.\end{matrix}\right.\) (TM).
2) \(HPT.\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3\left|x\right|+12\left|y\right|=54.\\3\left|x\right|+\left|y\right|=10.\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|x\right|+4\left|y\right|=18.\\\left|y\right|=4.\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|x\right|=2.\\\left|y\right|=4.\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2.\\x=-2.\end{matrix}\right.\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=4.\\y=-4.\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)

Câu 3:
2: Xét tứ giác OKEH có
\(\widehat{OKE}=\widehat{OHE}=\widehat{KOH}=90^0\)
Do đó: OKEH là hình chữ nhật
mà đường chéo OE là tia phân giác của \(\widehat{KOH}\)
nên OKEH là hình vuông

a/ ĐKXĐ: 2x - 1 >= 0 <=> 2x > 1 <=> x>= 1/2
\(\sqrt{2x-1}=\sqrt{5}\Leftrightarrow2x-1=5\Leftrightarrow2x=6\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(tm\right)\)
b/ ĐKXĐ: x - 10 >= 0 <=> x >= 10
Biểu thức trong căn luôn nhận giá trị dương => vô nghiệm
c/ ĐKXĐ: x - 5 >=0 <=> x >= 5
\(\sqrt{x-5}=3\Leftrightarrow x-5=9\Leftrightarrow x=14\left(tm\right)\)
a) \(\sqrt{2x-1}=\sqrt{5}\) (ĐK: \(x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-1=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(tm\right)\)
b) \(\sqrt{x-10}=-2\)
⇒ Giá trị của biểu thức trong căn luôn dương nên phương trình vô nghiệm
c) \(\sqrt{\left(x-5\right)^2}=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x-5\right|=3\)
TH1: \(\left|x-5\right|=x-5\) với \(x-5\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\ge5\)
Pt trở thành:
\(x-5=3\) (ĐK: \(x\ge5\))
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=8\left(tm\right)\)
TH2: \(\left|x-5\right|=-\left(x-5\right)\) với \(x-5< 0\Leftrightarrow x< 0\)
Pt trở thành:
\(-\left(x-5\right)=3\) (ĐK: \(x< 5\))
\(\Leftrightarrow-x+5=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x=-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{2;8\right\}\)


\(C=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)-\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)+6\sqrt{x}}{x-4}.\left(x-4\right)=2\sqrt{x}\)


\(\dfrac{AB^2}{AC^2}=\dfrac{BH}{CH}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{AB}{AC}=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{BD}{CD}=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
hay BD=100(cm)
Suy ra: HD=BD-BH=112-100=12(cm)
\(AD=\sqrt{AH^2+HD^2}=\sqrt{84^2+12^2}=60\sqrt{2}\left(cm\right)\)
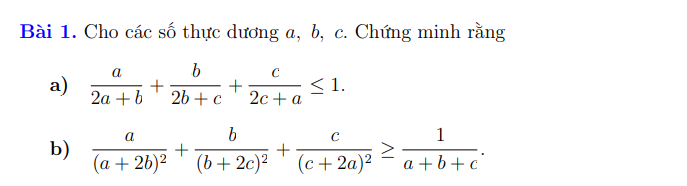



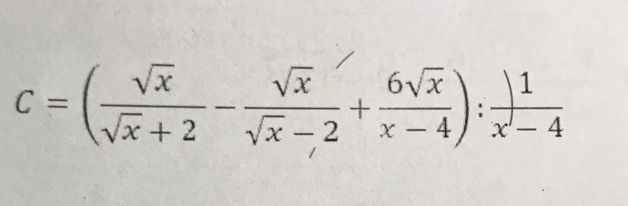
 mọi người giải giúp em câu này vs ạ
mọi người giải giúp em câu này vs ạ

a.
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2a}{2a+b}+\dfrac{2b}{2b+c}+\dfrac{2c}{2c+a}\le2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2a}{2a+b}-1+\dfrac{2b}{2b+c}-1+\dfrac{2c}{2c+a}-1\le-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{b}{2a+b}+\dfrac{c}{2b+c}+\dfrac{a}{2c+a}\ge1\)
Thật vậy, ta có:
\(VT=\dfrac{b^2}{2ab+b^2}+\dfrac{c^2}{2bc+c^2}+\dfrac{a^2}{2ca+a^2}\ge\dfrac{\left(a+b+c\right)^2}{a^2+b^2+c^2+2ab+2bc+2ca}=1\) (đpcm)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(a=b=c\)
b.
Chuẩn hóa \(a+b+c=1\), BĐT cần chứng minh trở thành:
\(\dfrac{a}{\left(a+2b\right)^2}+\dfrac{b}{\left(b+2c\right)^2}+\dfrac{c}{\left(c+2a\right)^2}\ge1\)
Ta có:
\(\dfrac{a}{\left(a+2b\right)^2}+a\left(a+2b\right)+a\left(a+2b\right)\ge3a\)
Tương tự:
\(\dfrac{b}{\left(b+2c\right)^2}+b\left(b+2c\right)+b\left(b+2c\right)\ge3b\)
\(\dfrac{c}{\left(c+2a\right)^2}+c\left(c+2a\right)+c\left(c+2a\right)\ge3c\)
Cộng vế:
\(VT+2\left(a+b+c\right)^2\ge3\left(a+b+c\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow VT+2\ge3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow VT\ge1\) (đpcm)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(a=b=c\)