
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Câu 4:
a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{\dfrac{1}{2};-\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
b: \(A=\dfrac{1-2x}{1-4x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{1-2x}{\left(1-2x\right)\left(1+2x\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2x+1}\)
c: Để A là số nguyên thì \(2x+1\inƯ\left(1\right)\)
=>\(2x+1\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
=>\(2x\in\left\{0;-2\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{0;-1\right\}\)
Câu 3:
a: \(A=\dfrac{3x-2}{x}-\dfrac{x-7}{x-5}-\dfrac{10}{x^2-5x}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x-2}{x}-\dfrac{x-7}{x-5}-\dfrac{10}{x\left(x-5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(3x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)-x\cdot\left(x-7\right)-10}{x\left(x-5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x^2-17x+10-x^2+7x-10}{x\left(x-5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2-10x}{x\left(x-5\right)}=\dfrac{2x\left(x-5\right)}{x\left(x-5\right)}=2\)


a) \(A=x^4+4x+7=\left(x^2+4x+4\right)+3=\left(x+2\right)^2+3\ge3\)
\(minA=3\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)
b) \(B=x^2-x+1=\left(x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)+\dfrac{3}{4}=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(minB=\dfrac{3}{4}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
c) \(C=4x-x^2+3=-\left(x^2-4x+4\right)+7=-\left(x-2\right)^2+7\le7\)
\(maxC=7\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
d) \(D=2x-2x^2-5=-2\left(x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)-\dfrac{9}{2}=-2\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2-\dfrac{9}{2}\le-\dfrac{9}{2}\)
\(maxD=-\dfrac{9}{2}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)

\(1,\\ a,=6x^4y^4-x^3y^3+\dfrac{1}{2}x^4y^2\\ b,=4x^3+5x^2-8x^2-10x+12x+15\\ =4x^3-3x^2+2x+15\\ 2,\\ a,=7\left(x^2-6x+9\right)=7\left(x-3\right)^2\\ b,=\left(x-y\right)^2-36=\left(x-y-6\right)\left(x-y+6\right)\\ 3,\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2-0,36\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x-0,6\right)\left(x+0,6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=0,6\\x=-0,6\end{matrix}\right.\)

a: =>(3x+1)(3x-1)-(3x+1)(2x-3)=0
=>(3x+1)(3x-1-2x+3)=0
=>(3x+1)(x+2)=0
=>x=-1/3 hoặc x=-2
b: =>(3x+1)(6x+2)-(3x+1)(x-2)=0
=>(3x+1)(6x+2-x+2)=0
=>(3x+1)(5x+4)=0
=>x=-1/3 hoặc x=-4/5

Câu 2:
a: *Vẽ đồ thị
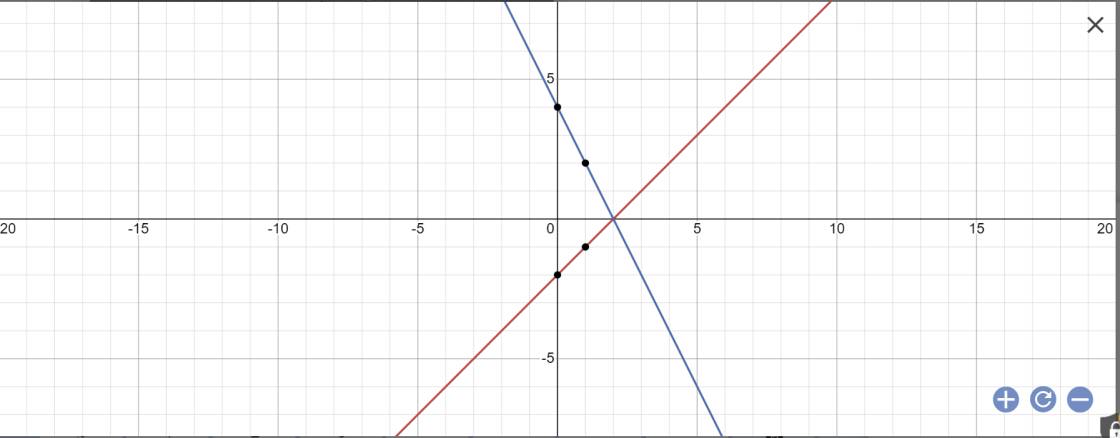
*Tìm giao điểm:
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
x-2=-2x+4
=>x+2x=4+2
=>3x=6
=>x=2
Thay x=2 vào y=x-2, ta được:
y=2-2=0
Vậy: (d1):y=x-2 cắt (d2): y=-2x+4 tại A(2;0)
b: *Vẽ đồ thị
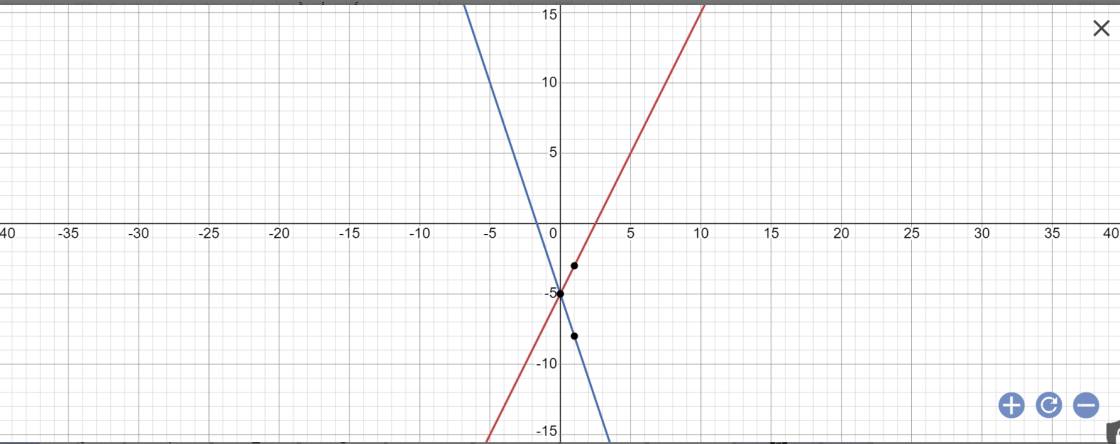
*Tìm giao điểm
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
2x-5=-3x-5
=>2x+3x=-5+5=0
=>5x=0
=>x=0
Thay x=0 vào y=2x-5, ta được:
\(y=2\cdot0-5=-5\)
Vậy: (d1): y=2x-5 cắt (d2):y=-3x-5 tại A(0;-5)
c: *Vẽ đồ thị
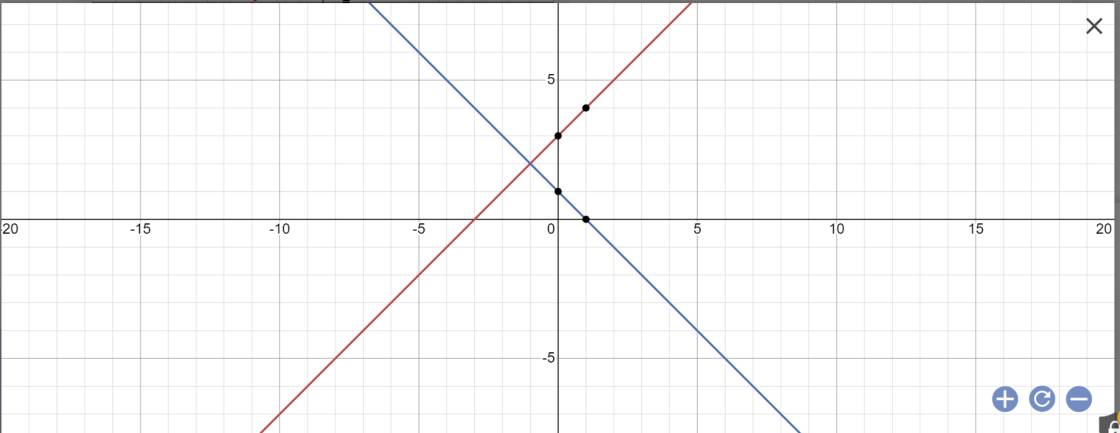
*Tìm giao điểm
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
x+3=-x+1
=>x+x=1-3
=>2x=-2
=>x=-1
Thay x=-1 vào y=x+3, ta được:
y=-1+3=2
vậy: (d1): y=x+3 và (d2): y=-x+1 cắt nhau tại C(-1;2)

Câu 1. B
Câu 2. C
Câu 3. C
Câu 4. A
Câu 5. B
Câu 6. C
Câu 7. A
Câu 8. D

1:
a: ĐKXĐ: x<>0; x<>5; x<>-5
\(A=\dfrac{x^2-5x+5x+25+10x}{\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x-5}{x}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+10x+25}{x+5}\cdot\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{x+5}{x}\)
b: Để A>0 và A nguyên thì 5 chia hết cho x và x>0
=>x=1

 Giúp em câu này vs ạ
Giúp em câu này vs ạ giúp em 2 câu này vs ạ
giúp em 2 câu này vs ạ
 giúp em bài này vs ạ em cảm ơn trc ạ
giúp em bài này vs ạ em cảm ơn trc ạ ai giải giúp em mấy bài toán này vs ạ giải chi tiết giúp em ạ
ai giải giúp em mấy bài toán này vs ạ giải chi tiết giúp em ạ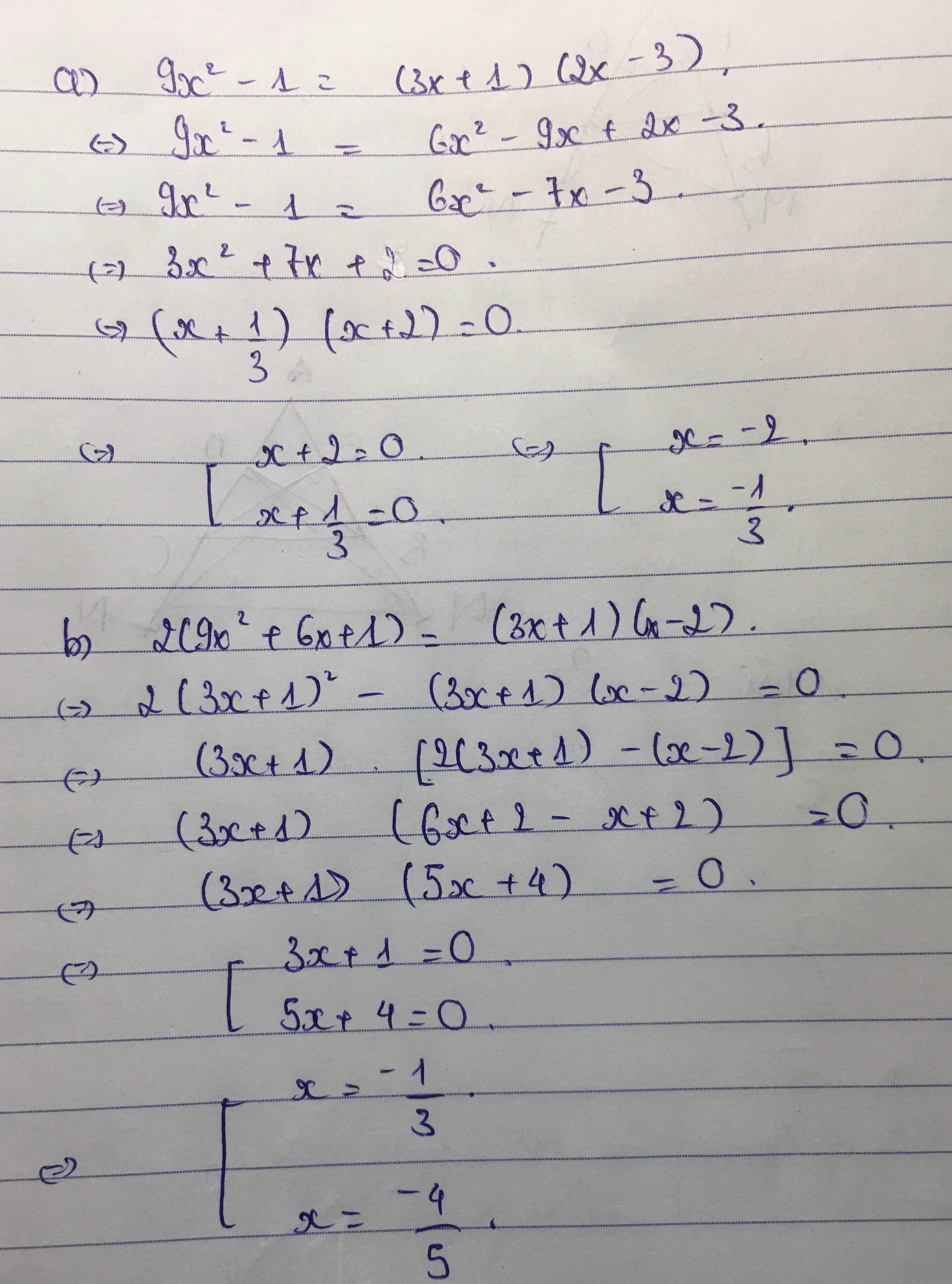
 cứu em 2 câu này vs ạ
cứu em 2 câu này vs ạ
 giúp em mấy bài này vs ạ
giúp em mấy bài này vs ạ
\(=12,7\left(85+15\right)=12,7\cdot100=1270\)