
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Ta có:\(6A=\dfrac{6\sqrt{x}}{6\sqrt{x}+1}=\dfrac{6\sqrt{x}+1-1}{6\sqrt{x}+1}=1-\dfrac{1}{6\sqrt{x}+1}\)
Để \(A\in Z\) thì \(\dfrac{1}{6\sqrt{x}+1}=1\Leftrightarrow6\sqrt{x}+1=1\Leftrightarrow6\sqrt{x}=0\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
Với x=0 => A=0

\(A=4\left(x-1\right)+\dfrac{25}{x-1}+4\ge2\sqrt{\dfrac{100\left(x-1\right)}{x-1}}+4=24\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(x=\dfrac{7}{2}\)
Anh ơi giúp em vc này https://hoc24.vn/cau-hoi/admin-oi-xu-ly-ho-em-avt-cua-ban-nay-aban-theo-doi-em-nen-em-vao-xem-thu-trang-ca-nhan-va-tot-nhat-admin-nen-xem-se-hieuhttpshoc24vnviptienganhlamontu.330703432754

a) \(P=\left(3-\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x}-1}\right):\left(\dfrac{x+2}{x+\sqrt{x}-2}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+2}\right)\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{3\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)-3}{\sqrt{x}-1}\right):\left[\dfrac{x+2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x+2}\right)}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+2}\right]\)
\(=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}-3-3}{\sqrt{x}-1}:\dfrac{x+2-\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}-6}{\sqrt{x}-1}:\dfrac{x+2-x+\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}-6}{\sqrt{x}-1}:\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}-6}{\sqrt{x}-1}:\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}-6}{\sqrt{x}-1}.\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\)
\(=3\sqrt{x}-6\)
b) \(P=\dfrac{4\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\sqrt{x}-6=\dfrac{4\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}}\) (1)
ĐKXĐ: \(x>0\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow3x-6\sqrt{x}=4\sqrt{x}-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-6\sqrt{x}-4\sqrt{x}+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-10\sqrt{x}+1=0\) (2)
Đặt \(t=\sqrt{x}\ge0\)
\(\left(2\right)\Leftrightarrow3t^2-10t+1=0\)
\(\Delta'=25-4=22\)
Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt:
\(t_1=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{22}}{3}\) (nhận)
\(t_2=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{22}}{3}\) (nhận)
Với \(t=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{22}}{3}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{22}}{3}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{47+10\sqrt{22}}{9}\) (nhận)
Với \(t=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{22}}{3}\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{22}}{3}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{47-10\sqrt{22}}{9}\) (nhận)
Vậy \(x=\dfrac{47+10\sqrt{22}}{9};x=\dfrac{47-10\sqrt{22}}{9}\) thì \(P=\dfrac{4\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}}\)
a: \(P=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}-3-3}{\sqrt{x}-1}:\dfrac{x+2-x+\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}{\sqrt{x}+2}=3\sqrt{x}-6\)
b: P=(4căn x-1)/căn x
=>3x-6căn x-4căn x+1=0
=>3x-10căn x+1=0
=>x=(47+10căn 22)/9 hoặc x=(47-10căn 22)/9

a, Th1 : \(m-1=0\Rightarrow m=1\)
\(\Rightarrow-x+3=0\\ \Rightarrow x=3\)
Th2 : \(m\ne1\)
\(\Delta=\left(-1\right)^2-4.\left(m-1\right).3\\ =1-12m+12\\=13-12m \)
phương trình có nghiệm \(\Delta\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow13-12m\ge0\\ \Rightarrow m\le\dfrac{13}{12}\)
b, Áp dụng hệ thức vi ét : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=\dfrac{1}{m-1}\\x_1x_1=\dfrac{3}{m-1}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tổng bình phương hai nghiệm bằng 12 \(\Rightarrow x^2_1+x^2_2=12\)
\(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=12\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{1}{m-1}\right)^2-2.\left(\dfrac{3}{m-1}\right)=12\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{\left(m-1\right)^2}-\dfrac{6}{m-1}=12\\ \Leftrightarrow1-6\left(m-1\right)=12\left(m-1\right)^2\\ \Leftrightarrow1-6m+6=12\left(m^2-2m+1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow7-6m-12m^2+24m-12=0\\ \Leftrightarrow-12m^2+18m-5=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=\dfrac{9-\sqrt{21}}{12}\\m=\dfrac{9+\sqrt{21}}{12}\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow m=\dfrac{9+\sqrt{21}}{12}\)

Giao điểm của 2 đồ thị 1 và 2 là:
-x+3m=2x-(m+6) <=> 3x=4m+6 => \(x_1=\frac{4m+6}{3}\); \(y_1=-\frac{4m+6}{3}+3m=\frac{5m-6}{3}\)
Để giao điểm nằm trên đồ thì y=x+1 thì x1 và y1 phải là nghiệm của PT: y=x+1
=> \(\frac{5m-6}{3}=\frac{4m+6}{3}+1\) <=> 5m-6=4m+6+3 => m=15
Đáp số: m=15

ĐKXĐ : \(x>0\)
Áp dụng bất đẳng thức Cauchy cho 2 số dương \(\sqrt{x};\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{x}}\) ta có
\(P=\sqrt{x}+\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{x}}\ge2\sqrt{\sqrt{x}.\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{x}}}=4\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(\sqrt{x}=\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{x}}\Leftrightarrow x=4\)
\(P=\sqrt[]{x}+\dfrac{4}{\sqrt[]{x}}\left(x>0\right)\)
\(P=\dfrac{x+4}{\sqrt[]{x}}=\dfrac{x+4}{\sqrt[]{x}}\)
Vì \(x>0;x+4>4\)
\(\Rightarrow P=\dfrac{x+4}{\sqrt[]{x}}>4\)
⇒ Không có giá trị nhỏ nhất

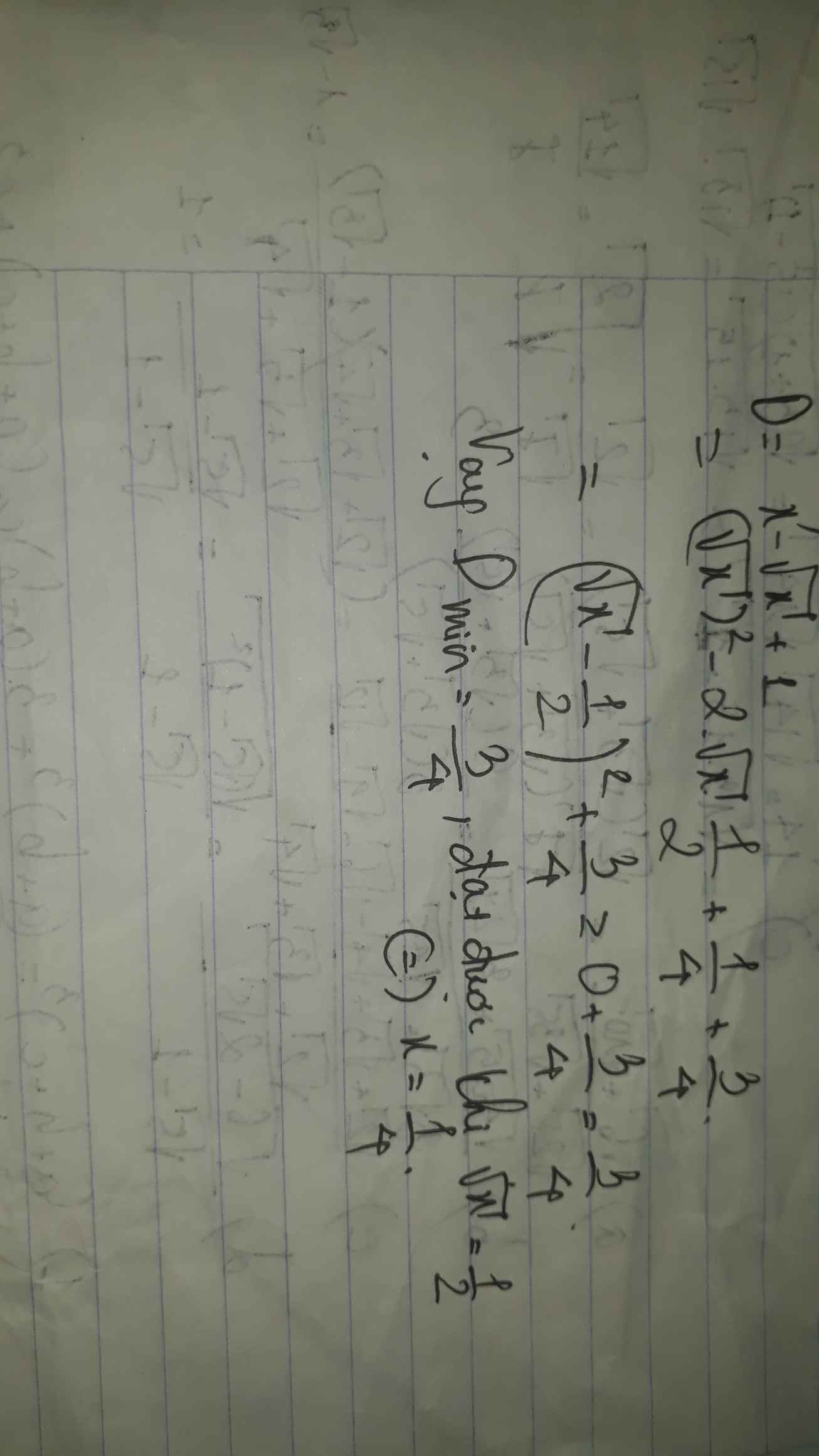
`4x^2=13`
`<=>x^2=13/4`
`<=>x=[+-\sqrt{13}]/2`
Vậy `S={[+-\sqrt{13}]/2}`
`4x^2 = 13`.
`=> x^2 = 13/4`.
`=> x = (sqrt 13)/(sqrt 4)`
`=> x = (+-sqrt 13)/2`.
Vậy `S = (+-sqrt 13)/2`.