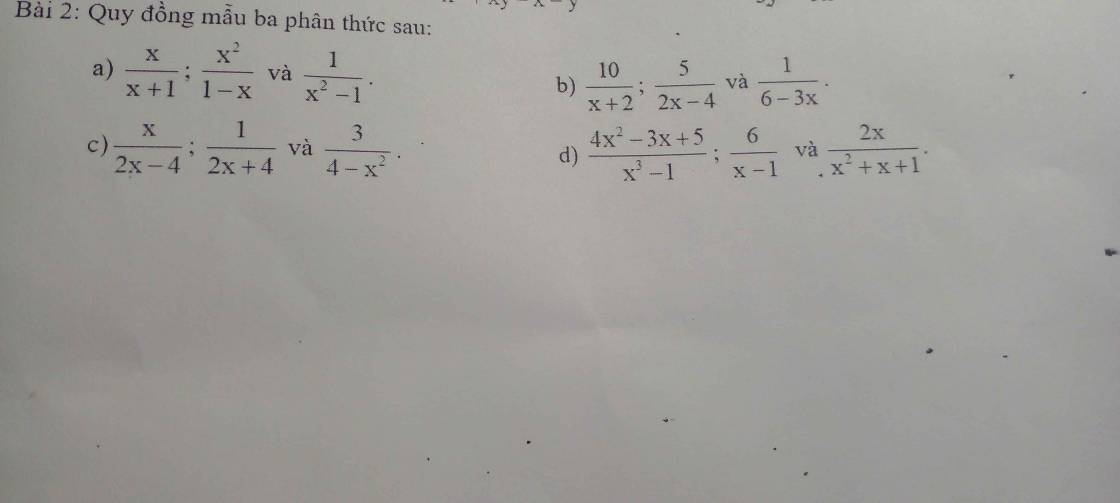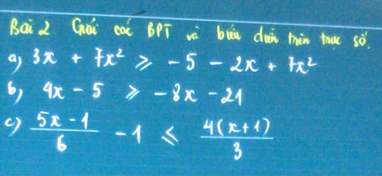Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Hướng dẫn: A đạt GTLN khi \(\dfrac{1}{A}\) đạt GTNN
Ta có: \(x^2+2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{1}{x^2+2}\le\dfrac{1}{2}\forall x\)
Vậy GTLN của A là 1/2
=> A

Mik cần lời giải á, các bạn toàn cho mik đáp án hoặc là cho mỗi câu 123 (Q▪︎Q)


câu a, \(\dfrac{x}{x+1}\); \(\dfrac{x^2}{1-x}\); \(\dfrac{1}{x^2-1}\) (đk \(x\)≠ -1; 1)
\(x^2\) - 1 = ( \(x\) - 1).(\(x\) + 1)
\(\dfrac{x}{x+1}\) = \(\dfrac{x.\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+1\right).\left(x-1\right)}\);
\(\dfrac{x^2}{1-x}\) = \(\dfrac{-x^2}{x-1}\)= \(\dfrac{-x^2.\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{x^2-1}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
b, \(\dfrac{10}{x+2}\); \(\dfrac{5}{2x-4}\); \(\dfrac{1}{6-3x}\) (đk \(x\) ≠ -2; 2)
2\(x-4\) = 2.(\(x\) - 2); 6 - 3\(x\) = - 3.(\(x\) - 2)
\(\dfrac{10}{x+2}\) = \(\dfrac{10.2.3\left(x-2\right)}{2.3\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{60\left(x-2\right)}{6\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{5}{2x-4}\) = \(\dfrac{5.3\left(x+2\right)}{2.3\left(x-2\right).\left(x+2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{15.\left(x+2\right)}{6.\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{6-3x}\) = \(\dfrac{-1}{3.\left(x-2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{-1.\left(x+2\right)}{3.2.\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{-2.\left(x+2\right)}{6.\left(x-2\right).\left(x+2\right)}\)
c, \(\dfrac{x}{2x-4}\); \(\dfrac{1}{2x+4}\) và \(\dfrac{3}{4-x^2}\) đk \(x\) ≠ 2; -2
\(\dfrac{x}{2x-4}\) = \(\dfrac{x}{2.\left(x-2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{x.\left(x+2\right)}{2.\left(x-2\right).\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{2x+4}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2.\left(x+2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)}{2.\left(x+2\right).\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{3}{4-x^2}\) = \(\dfrac{-3}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{-6}{2.\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)

Gọi quãng đường AB là x ( x > 0 )
Theo bài ra ta có pt \(\dfrac{x}{60}-\dfrac{x}{65}=\dfrac{12}{60}=\dfrac{1}{5}\Rightarrow x=156\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy ...
na ná á
Xét ΔABC có BD là phân giác
nên AB/AD=BC/CD
=>AB/4=BC/5
Đặt AB/4=BC/5=k
=>AB=4k; BC=5k
Theo đề, ta có: AB2+AC2=BC2AB2+AC2=BC2
⇔9k2=81⇔9k2=81
=>k=3
=>AB=12; BC=15

b: ĐKXĐ: x>=2/3
PT=>(x-1)(x-2)+(x-1)*căn 3x-2=0
=>căn 3x-2+x-2=0
=>căn 3x-2=-x+2
=>x<=2 và 3x-2=x^2-4x+4
=>x^2-4x+4-3x+2=0 và x<=2
=>x=1
c: =>x+3+x-4-2căn (x^2-x-12)=1
=>2*căn x^2-x-12=2x-1-1=2x-2
=>căn x^2-x-12=x-1
=>x>=1 và x^2-x-12=x^2-2x+1
=>x=13

a, \(3x+7x^2+5+2x-7x^2\ge0\Leftrightarrow5x+5\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\ge-1\)
b, \(12x\ge-16\Leftrightarrow x\ge-\dfrac{4}{3}\)
c, \(\dfrac{5x-1-6}{6}-\dfrac{4\left(x+1\right)}{3}\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5x-7-8\left(x+1\right)}{6}\le0\Rightarrow-3x-15\le0\Leftrightarrow x\le-5\)

Câu 1: A
Câu 2: B
Câu 3: D
Câu 4: A
Câu 5: C
Câu 6: B
Câu 7: A
Câu 9: B