
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(xy^2-2xy+x+y^2=6\Leftrightarrow x\left(y^2-2y+1\right)+y^2-1=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(y-1\right)^2+\left(y-1\right)\left(y+1\right)=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(y-1\right)\left(xy-x+y+1\right)=5\)
\(Ư\left(5\right)=\left(-5;-1;1;5\right)\)
| y-1 | -5 | -1 | 1 | 5 |
| y | -4 | 0 | 2 | 6 |
| xy-x+y+1 | -1 | -5 | 5 | 1 |
| x | -2/5 | 6 | 2 | -6/5 |
Vì \(x;y\in Z\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left(x;y\right)=\left(6;0\right)\\\left(x;y\right)=\left(2;2\right)\end{matrix}\right. \)

ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne2;x\ne-2\)
\(\Rightarrow x-2+5\left(x+2\right)=2x-12\Leftrightarrow x-2+5x+10=2x-12\Leftrightarrow6x+8-2x=-12\Leftrightarrow4x+8=-12\Leftrightarrow4x=-20\Leftrightarrow x=-5\left(TM\right)\)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\pm2\)
\(\dfrac{1}{x+2}+\dfrac{5}{x-2}=\dfrac{2x-12}{x^2-4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-2}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{5\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{2x-12}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2+5x+10=2x-12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-12-x+2-5x-10=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x-20=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-5\)
Vậy...

\(xy^2\) - \(2xy\) + \(x\) + \(y^2\) = 6
\(x\)( \(y^2\) - \(2y\) + 1 ) + \(y^2\) - 1 = 5
\(x\) ( \(y-1\) ) 2 + ( \(y-1\))(\(y+1\)) = 5
(\(y-1\))( \(xy-x\) + y + 1) = 5
Ư(5) ={ -5; -1; 1; 5)
ta có bảng :
| y- 1 | -5 | -1 | 1 | 5 |
| y | -4 | 0 | 2 | 6 |
| xy-x+y+1 | -1 | -5 | 5 | 1 |
| x | -2/5 | 6 | 2 | -6/5 |
Vì x, y \(\in\) Z nên (x, y ) = ( 0; 6); ( 2; 2)

ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\pm1\)
\(\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x^3+3}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2-\left(x-1\right)^2=x^3+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=x^3+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-4x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-x^2+x^2-x-3x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)+x\left(x-1\right)-3\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\left(loại\right)\\x^2+x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-1\pm\sqrt{13}}{2}\)

Ta có: \(x^2\left(x^3-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2=0\\x^3-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{0}=0\\x=\sqrt[3]{1}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy x=1 và x=1
Mình chỉ đưa hướng thôi, còn bạn tự giải nhé (mình để VP=0 do bạn không nói gì)
\(x^2\left(x^3-1\right)=0\left(1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=0\left(1a\right)\)
Do \(x^2+x+1=\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ge0\left(\forall x\in R\right)\) nên... bạn tự suy ra tiếp nhé ![]()
Chúc bạn học tốt!



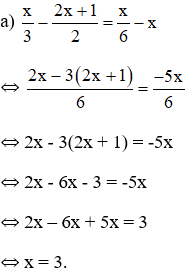

a, \(\left(x-3\right)^2< x^2-5x+4\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)^2< \left(x-4\right)\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)^2-\left(x-4\right)\left(x-1\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+9-x^2+5x-4< 0\Leftrightarrow5-x< 0\Leftrightarrow x>5\)
b, \(\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=\left(x+2\right)^2+3\Leftrightarrow x^2-9=x^2+4x+4+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+7=-9\Leftrightarrow4x=-16\Leftrightarrow x=-4\)
c, \(\frac{x-2}{x^2+1}>0\Rightarrow x-2>0\Leftrightarrow x>2\)
d, \(\frac{x^2+4x+4}{x-5}\ge0\Leftrightarrow\frac{\left(x+2\right)^2}{x-5}\ge0\Rightarrow x-5\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\ge5\)