
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 1:
\(A=\log_380=\log_3(2^4.5)=\log_3(2^4)+\log_3(5)\)
\(=4\log_32+\log_35=4a+b\)
\(B=\log_3(37,5)=\log_3(2^{-1}.75)=\log_3(2^{-1}.3.5^2)\)
\(=\log_3(2^{-1})+\log_33+\log_3(5^2)=-\log_32+1+2\log_35\)
\(=-a+1+2b\)
Bài 2:
\(\log_{30}8=\frac{\log 8}{\log 30}=\frac{\log (2^3)}{\log (10.3)}=\frac{3\log2}{\log 10+\log 3}\)
\(=\frac{3\log (\frac{10}{5})}{1+\log 3}=\frac{3(\log 10-\log 5)}{1+\log 3}=\frac{3(1-b)}{1+a}\)

Bạn sử dụng công cụ gõ công thức có sẵn này ở chỗ khoanh đỏ viết lại đề được không, sử dụng rất đơn giản

Chứ đề thế này không thể dịch nổi

Đáp án D.
Ta có
log 6125 7 = log 6125 + log 7 = log 7 2 . 125 + 1 2 log 7
= 5 2 log 7 + log 5 3 = 5 2 n + 3 log 5 = 5 2 n + 3 1 - log 2
= 5 2 n + 3 - 3 m .

bài 1 mk o bt lm ; nên mk lm câu 2 thôi nha .
bài 2) ta có : \(\log_x\left(x-\dfrac{1}{4}\right)\ge2\Leftrightarrow x-\dfrac{1}{4}\ge x^2\Leftrightarrow x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\le0\)
mà ta có : \(\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow0\le\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\le0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
vậy \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)

Lời giải:
a) ĐKXĐ:......
Ta có: \(\log_{2x+1}(3-x^2)=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 3-x^2=(2x+1)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 5x^2+4x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-2+\sqrt{14}}{5}\\x=\dfrac{-2-\sqrt{14}}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Kết hợp với đkxđ suy ra \(x=\frac{-2+\sqrt{14}}{5}\) là nghiệm
b) ĐKXĐ:....
Đặt \(2-x=a\Rightarrow \log_2(2a+1)=a\) (\(a>\frac{-1}{2}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow 2a+1=2^a\)
Xét hàm \(y(a)=2^a-2a-1\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=\ln 2.2^a-2=0\Leftrightarrow a=\log_2\left(\frac{2}{\ln 2}\right)\)
Lập bảng biến thiên của $y(a)$ với $a>\frac{-1}{2}$ ta thấy đồ thì của $y(a)$ cắt đường thẳng \(y=0\) tại hai điểm, tức là pt có hai nghiệm. Trong đó một nghiệm thuộc \((-\frac{1}{2}; \log_2\left(\frac{2}{\ln 2}\right))\) và nghiệm khác thuộc \((\log_2\left(\frac{2}{\ln 2}\right);+\infty)\)
Thực hiện shift-solve ta thu được \(a=0\) hoặc \(a\approx 2,66\)
Câu c)
ĐKXĐ: \(x>-1\)
Ta có: \(\log_2(x+1)=4-3x\Leftrightarrow x+1=2^{4-3x}\)
Ta thấy:
\((x+1)'=1>0\) nên hàm vế trái đồng biến trên KXĐ
\((2^{4-3x})'=-3.\ln 2.2^{4-3x}<0\) nên hàm vế phải nghịch biến trên KXĐ
Do đó, PT chỉ có thể có duy nhất một nghiệm
Thấy \(x=1\) thỏa mãn nên $x=1$ là nghiệm duy nhất của phương trình

ĐKXĐ: \(x>0\)
\(log_{a^4}x-log_{a^2}x+log_ax=\frac{3}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{1}{4}log_ax-\frac{1}{2}log_ax+log_ax=\frac{3}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{3}{4}log_ax=\frac{3}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_ax=1\)
\(\Rightarrow x=a\)

Lời giải:
\(\log_2(x^2-4)+x=\log_2[8(x+2)]\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \log_2[(x-2)(x+2)]+x=\log_2[8(x+2)]\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \log_2(x-2)+\log_2(x+2)+x=\log_28+\log_2(x+2)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \log_2(x-2)+x=3\)
Đặt \(\log_2(x-2)=t\Rightarrow x-2=2^t\Rightarrow x=2^t+2\). PT trở thành:
\(t+2^t+2=3\Leftrightarrow 2^t+t=1\)
Nếu $t>0$ thì \(2^t+t>2^0+0\Leftrightarrow 2^t+t>1\) (loại)
Nếu $t=0$ thì thỏa mãn
Nếu \(t< 0\Rightarrow 2^t+t< 2^0+0\Leftrightarrow 2^t+t< 1\) (loại)
Vậy \(t=0\Rightarrow x=2^0+2=3\)
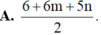
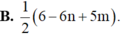
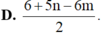
Đáp án C