
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



Đặt x^2 + 2x = a ta có:
a^2 - 9a + 20 = (a - 4)(a - 5)
Thay ngược lại ta có: (x^2 + 2x - 4)(x^2 + 2x - 5)


pt⇔y2(x2−7)=(x+y)2(1)
Phương trình đã cho có nghiệm x=y=0x=y=0
Xét x,y\ne0x,y≠0, từ (1)(1) suy ra x^2-7x2−7 là một số chính phương
Đặt x^2-7=a^2x2−7=a2 ta có:
\left(x-a\right)\left(x+a\right)=7(x−a)(x+a)=7 từ đây tìm được x
Vậy (x,y)=(0,0);(4,-1);(4,2);(-4,1);(-4;-2)(x,y)=(0,0);(4,−1);(4,2);(−4,1);(−4;−2)

\(\left|2x-3\right|=3-2x\)
\(ĐK:x\le\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-3=3-2x\\3-2x=3-2x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\0=0\left(đúng\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{x\in R;x=\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)

\(E=22x-23-5x+2-3x+1\)
\(=14x-20\)
\(=14\cdot\dfrac{-2}{3}-20=\dfrac{-28}{3}-\dfrac{60}{3}=-\dfrac{88}{3}\)

Bài 5 hình 1: (tự vẽ hình nhé bạn)
a) Xét ΔABD và ΔACB ta có:
\(\widehat{BAD}\)= \(\widehat{BAC}\) (góc chung)
\(\widehat{ABD}\)= \(\widehat{ACB}\) (gt)
=> ΔABD ~ ΔACB (g-g)
=> \(\dfrac{AB}{AC}\) = \(\dfrac{BD}{CB}\) = \(\dfrac{AD}{AB}\) (tsđd)
b) Ta có: \(\dfrac{AB}{AC}\) = \(\dfrac{AD}{AB}\) (cm a)
=> \(AB^2\) = AD.AC
=> \(2^2\) = AD.4
=> AD = 1 (cm)
Ta có: AC = AD + DC (D thuộc AC)
=> 4 = 1 + DC
=> DC = 3 (cm)
c) Xét ΔABH và ΔADE ta có:
\(\widehat{AHB}\) = \(\widehat{AED}\) (=\(90^0\))
\(\widehat{ADB}\) = \(\widehat{ABH}\) (ΔABD ~ ΔACB)
=> ΔABH ~ ΔADE
=> \(\dfrac{AB}{AD}\) = \(\dfrac{AH}{AE}\) = \(\dfrac{BH}{DE}\) (tsdd)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{S_{ABH}}{S_{ADE}}\) = \(\left(\dfrac{AB}{AD}\right)^2\)= \(\left(\dfrac{2}{1}\right)^2\)= 4
=> đpcm
Tiếp bài 5 hình 2 (tự vẽ hình)
a) Xét ΔABC vuông tại A ta có:
\(BC^2\) = \(AB^2\) + \(AC^2\)
\(BC^2\) = \(21^2\) + \(28^2\)
BC = 35 (cm)
b) Xét ΔABC và ΔHBA ta có:
\(\widehat{BAC}\) = \(\widehat{AHB}\) ( =\(90^0\))
\(\widehat{ABC}\) = \(\widehat{ABH}\) (góc chung)
=> ΔABC ~ ΔHBA (g-g)
=> \(\dfrac{AB}{BH}\) = \(\dfrac{BC}{AB}\) (tsdd)
=> \(AB^2\) = BH.BC
=> \(21^2\) = 35.BH
=> BH = 12,6 (cm)
c) Xét ΔABC ta có:
BD là đường p/g (gt)
=> \(\dfrac{AD}{DC}\) = \(\dfrac{AB}{BC}\) (t/c đường p/g)
Xét ΔABH ta có:
BE là đường p/g (gt)
=> \(\dfrac{HE}{AE}\) = \(\dfrac{BH}{AB}\) (t/c đường p/g)
Mà: \(\dfrac{AB}{BC}\) = \(\dfrac{BH}{AB}\) (cm b)
=> đpcm
d) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\widehat{HBE}+\widehat{BEH}=90^0\\\widehat{ABD}+\widehat{ADB=90^0}\\\widehat{HBE}=\widehat{ABD}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=> \(\widehat{BEH}=\widehat{ADB}\)
Mà \(\widehat{BEH}=\widehat{AED}\) (2 góc dd)
Nên \(\widehat{ADB}=\widehat{AED}\)
=> đpcm

\(a.A=\left(\dfrac{x}{x^2-4}+\dfrac{1}{x+2}-\dfrac{2}{x-2}\right):\left(1-\dfrac{x}{x+2}\right)\left(đk:x\ne\pm2\right)\)
\(=\left[\dfrac{x}{x^2-4}+\dfrac{x-2}{x^2-4}-\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)}{x^2-4}\right]:\left(\dfrac{x+2}{x+2}-\dfrac{x}{x+2}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{x+x-2-2x-4}{x^2-4}:\dfrac{x+2-x}{x+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{-6}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}.\dfrac{x+2}{2}\)
\(=\dfrac{-3}{x-2}\left(1\right)\)
\(b.\) Thay x = 2023 vào (1), ta được:
\(\dfrac{-3}{2023-2}=-\dfrac{3}{2021}\)
\(c.\) Để A là một số nguyên thì \(x-2\inƯ_{\left(-3\right)}\)
Vậy x - 2 có các giá trị sau:
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=1\\x-2=-1\\x-2=3\\x-2=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=1\\x=5\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)

Vì \(AB//CD\) nên \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\widehat{B}+\widehat{C}=180^0\\\widehat{A}+\widehat{D}=180^0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\widehat{B}=\left(180^0+40^0\right):2=110^0\\3\widehat{D}=180^0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\widehat{C}=180^0-110^0=70^0\\\widehat{D}=60^0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\widehat{A}=120^0\)
\(\widehat{B}=110^0\)
\(\widehat{C}=70^0\)
\(\widehat{A}=120^0\)
\(\widehat{D}=60^0\)
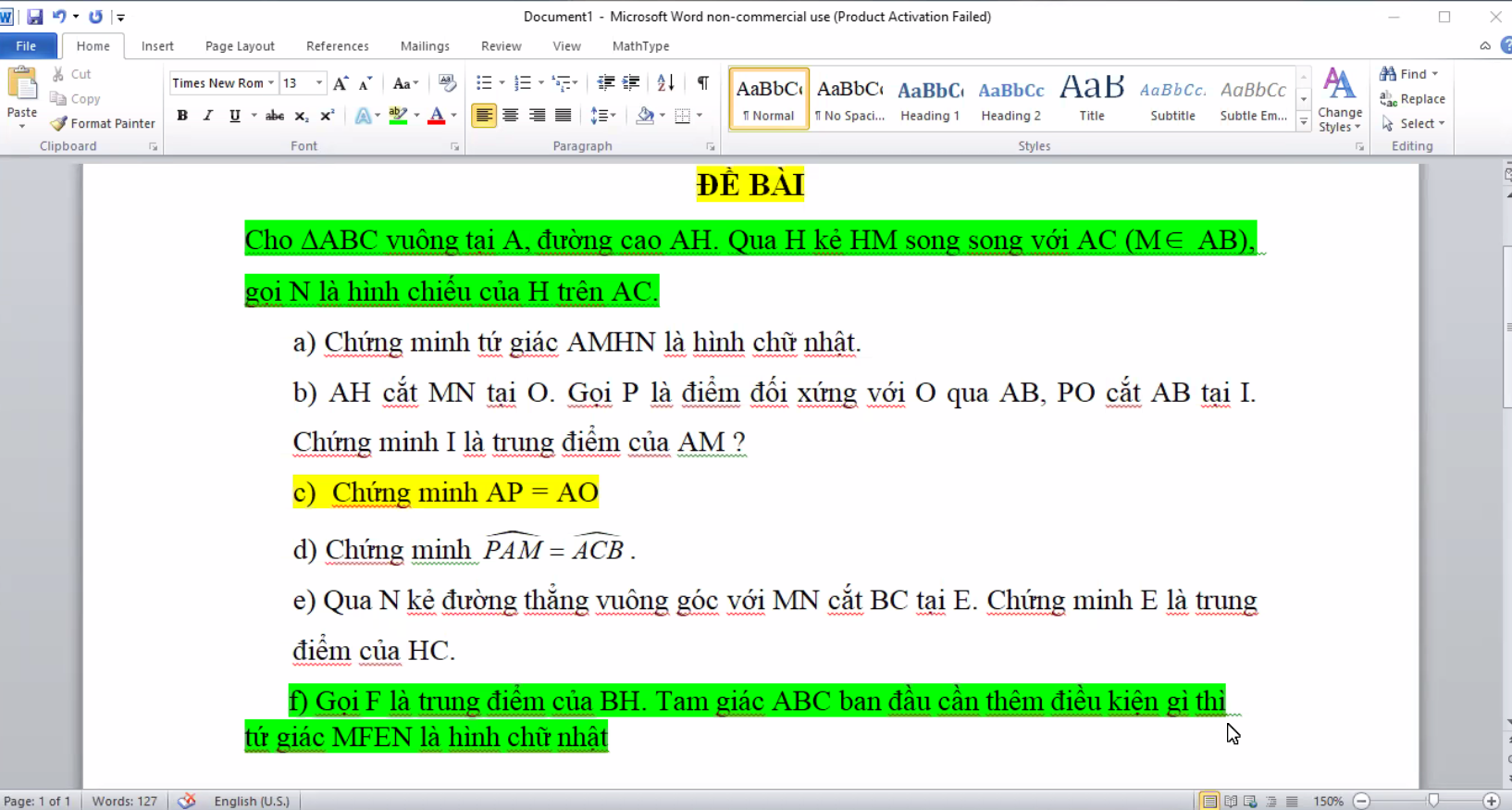
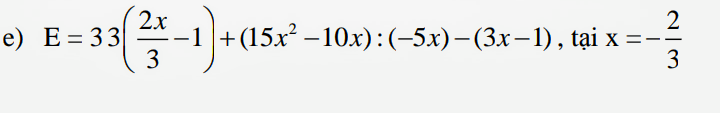
 giải hộ mình mấy bài này vs ạ !
giải hộ mình mấy bài này vs ạ !
 giúp mình bài 3 vs mn ơi ko phải thi chỉ là đề ôn thôi ạ
giúp mình bài 3 vs mn ơi ko phải thi chỉ là đề ôn thôi ạ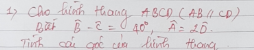
\(P=\left(x^2+4xy+4y^2\right)+\left(y^2+8y+16\right)+16\\ P=\left(x+2y\right)^2+\left(y+4\right)^2+16\ge16\\ P_{min}=16\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-2y=8\\y=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
thanh kìu :))))))))