
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


`A=x(x-6)+10=x^2-6x+10`
`=x^2 -2.x .3 + 3^2 + 1`
`=(x-3)^2+1 >0 forall x`
`B=x^2-2x+9y^2-6y+3`
`=(x^2-2x+1)+(9y^2-6y+1)+1`
`=(x-1)^2+(3y-1)^2+1 > 0 forall x,y`.

Đặt A=x^4-x^3+3x^2-2x+2
=(x^4+3x^2+2)-(x^3+2x)
=(x^4+x^2+2x^2+2)-x(x^2+2)
=(x^2+1)(x^2+2)-x(x^2+2)
=(x^2+2)(x^2-x+1)
Ta có x^2+2>=2>0;
x^2-x+1=(x^2-x+1/4)+3/4 =(x-1/2)^2+3/4>=3/4>0
=> A>0

a) \(x^2+x+1=x^2+x+\frac{1}{4}+\frac{3}{4}=\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}\ge\frac{3}{4}>0\forall x\)
c) \(C=4x-10-x^2=-\left(x^2-4x+10\right)\)
\(=-\left(x^2-4x+4+6\right)=-\left[\left(x-2\right)^2+6\right]\)
\(=-\left(x^2-4x+4+6\right)=-\left[\left(x-2\right)^2\right]-6\le-6< 0\forall x\)

\(a,P=5x\left(2-x\right)-\left(x+1\right)\left(x+9\right)\)
\(=10x-5x^2-\left(x^2+x+9x+9\right)\)
\(=10x-5x^2-x^2-x-9x-9\)
\(=\left(10x-x-9x\right)+\left(-5x^2-x^2\right)-9\)
\(=-6x^2-9\)
Ta thấy: \(x^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow-6x^2\le0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow-6x^2-9\le-9< 0\forall x\)
hay \(P\) luôn nhận giá trị âm với mọi giá trị của biến \(x\).
\(b,Q=3x^2+x\left(x-4y\right)-2x\left(6-2y\right)+12x+1\)
\(=3x^2+x^2-4xy-12x+4xy+12x+1\)
\(=\left(3x^2+x^2\right)+\left(-4xy+4xy\right)+\left(-12x+12x\right)+1\)
\(=4x^2+1\)
Ta thấy: \(x^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow4x^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow4x^2+1\ge1>0\forall x\)
hay \(Q\) luôn nhận giá trị dương với mọi giá trị của biến \(x\) và \(y\).
#\(Toru\)

a) \(A=x^2+2x+3=x^2+2x+1+2\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)^2+2\ge2\)
Vậy A luôn dương với mọi x
b) \(B=-x^2+4x-5=-\left(x^2-4x+5\right)\)
\(=-\left(x^2-4x+2^2\right)-1\)
\(=-\left(x-2\right)^2-1\le-1\)
Vậy B luôn âm với mọi x
a)\(x^2+2x+3=\left(x^2+2x+1\right)+2=\left(x+1\right)^2+2\ge2\)
Vậy x2 +2x+3 luôn dương.
b)\(-x^2+4x-5=-\left(x^2-4x+5\right)=-\left(x^2-4x+4+1\right)=-\left[\left(x-2\right)^2+1\right]\le-1\)
Vậy -x2 +4x-5 luôn luôn âm.

\(A=x^2+10y^2+2xy-6y+5\)
\(A=x^2+2xy+y^2+9y^2-6y+1+4\)
\(A=\left(x+y\right)^2+\left(3y+1\right)^2+4\)
Mà \(\hept{\begin{cases}\left(x+y\right)^2\ge0\\\left(3y+1\right)^2\ge0\\4>0\end{cases}}\)
=> A luôn dương với mọi x ; y
\(B=x-x^2-1\)
\(B=-\left(x^2-x+1\right)\)
\(B=-\left(x^2-x+\frac{1}{4}+\frac{3}{4}\right)\)
\(B=-\left[\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}\right]\)
\(B=-\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2-\frac{3}{4}\)
Mà \(\hept{\begin{cases}-\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\le0\\-\frac{3}{4}< 0\end{cases}}\)
=> B luôn âm với mọi x

Điều kiện x ≠ 1 và x ≠ - 1
Ta có:
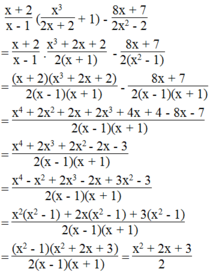
Biểu thức dương khi x 2 + 2 x + 3 > 0
Ta có: x 2 + 2 x + 3 = x 2 + 2 x + 1 + 2 = x + 1 2 + 2 > 0 với mọi giá trị của x.
Vậy giá trị của biểu thức dương với mọi giá trị x ≠ 1 và x ≠ - 1

\(1,x^2-x+1=x^2-2.x.\frac{1}{2}+\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}=\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}\)
Vì \(\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge0=>\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}\ge\frac{3}{4}>0\) (với mọi x)
Vậy ........
\(2,a,\left(x-3\right)\left(1-x\right)-2=x-x^2-3+3x-2=-x^2+4x-5=-\left(x^2-4x+5\right)\)
\(=-\left(x^2-4x+4+1\right)=-\left(x^2-2.x.2+2^2+1\right)=-\left[\left(x-2\right)^2+1\right]=-1-\left(x-2\right)^2\)
Vì \(\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0=>-\left(x-2\right)^2\le0=>-1-\left(x-2\right)^2\le-1< 0\) (với mọi x)
Vậy........
\(b,\left(x+4\right)\left(2-x\right)-10=2x-x^2+8-4x-10=-x^2-2x-2=-\left(x^2+2x+2\right)=-\left(x^2+2x+1+1\right)\)
\(=-\left(x^2+2.x.1+1^2+1\right)=-\left(x+1\right)^2+1=-1-\left(x+1\right)^2\le-1< 0\) (với mọi x)
Vậy.......

\(a,\left(x+1\right)^2+2x\left(x-2\right)=3\left(x+4\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
\(x^2+2x+1+2x^2-4x=3\left(x^2+5x+4\right)\)
\(3x^2-2x+1=3x^2+15x+12\)
\(\Rightarrow3x^2-2x+1-3x^2-15x-12=0\)
\(\Rightarrow-17x=11\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-\frac{11}{17}\)
\(b,M=x^2+12x+50\)
\(M=x^2+2.6.x+6^2+14\)
\(M=\left(x+6\right)^2+14\ge14>0\)
=> M luôn dương
\(\left(x+1\right)^2+2x\left(x-2\right)=3\left(x+4\right)\left(x+1\right).\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+1+2x^2-4x=3.(x^2+x+4x+4)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+2x^2+1=3x^2+15x+12\)
\(\left(x^2-3x^2+2x^2\right)=\left(15x+2x\right)+12-1\)
\(17x+11=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-11}{17}\)
Ta có:x4-x+1=(x4-x2+\(\dfrac{1}{4}\))+(x2-x+\(\dfrac{1}{4}\))+\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)=\(\left(x^2-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Do \(\left(x^2-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\ge0\forall x\in R\)
\(\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge0\forall x\in R\)
=>\(\left(x^2-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge0\forall x\in R\)
=>\(x^4-x+1=\left(x^2-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{1}{2}\ge\dfrac{1}{2}>0\forall x\in R\)(đpcm)
Vì x^4 có số mũ là chẵn nên cho dù x là mấy thì x^4-x+1 luôn dương với mọi x .
mk ko giải nhưng mình định hướng thôi .