
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: \(x^2+x+1=x^2+x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(=\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}>=\dfrac{3}{4}>0\forall x\)
b: \(4y^2+2y+1\)
\(=4\left(y^2+\dfrac{1}{2}y+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)\)
\(=4\left(y^2+2\cdot y\cdot\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{16}+\dfrac{3}{16}\right)\)
\(=4\left(y+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}>=\dfrac{3}{4}>0\forall y\)
c: \(-2x^2+6x-10\)
\(=-2\left(x^2-3x+5\right)\)
\(=-2\left(x^2-3x+\dfrac{9}{4}+\dfrac{11}{4}\right)\)
\(=-2\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2-\dfrac{11}{2}< =-\dfrac{11}{2}< 0\forall x\)
`#3107.101107`
a)
`x^2 + x + 1`
`= (x^2 + 2*x*1/2 + 1/4) + 3/4`
`= (x + 1/2)^2 + 3/4`
Vì `(x + 1/2)^2 \ge 0` `AA` `x`
`=> (x + 1/2)^2 + 3/4 \ge 3/4` `AA` `x`
Vậy, `x^2 + x + 1 > 0` `AA` `x`
b)
`4y^2 + 2y + 1`
`= [(2y)^2 + 2*2y*1/2 + 1/4] + 3/4`
`= (2y + 1/2)^2 + 3/4`
Vì `(2y + 1/2)^2 \ge 0` `AA` `y`
`=> (2y + 1/2)^2 + 3/4 \ge 3/4` `AA` `y`
Vậy, `4y^2 + 2y + 1 > 0` `AA` `y`
c)
`-2x^2 + 6x - 10`
`= -(2x^2 - 6x + 10)`
`= -2(x^2 - 3x + 5)`
`= -2[ (x^2 - 2*x*3/2 + 9/4) + 11/4]`
`= -2[ (x - 3/2)^2 + 11/4]`
`= -2(x - 3/2)^2 - 11/2`
Vì `-2(x - 3/2)^2 \le 0` `AA` `x`
`=> -2(x - 3/2)^2 - 11/2 \le 11/2` `AA` `x`
Vậy, `-2x^2 + 6x - 10 < 0` `AA `x.`

\(A=\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)+2=x^2-4x+3+2=\left(x^2-4x+4\right)+1=\left(x-2\right)^2+1\ge1>0\forall x\)

\(a,x^2-6xy+9y^2+1=\left(x-3y\right)^2+1\ge1>0\\ b,-25x^2+5x-1=-\left(25x^2+2\cdot5\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)-\dfrac{3}{4}=-\left(5x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2-\dfrac{3}{4}\le-\dfrac{3}{4}< 0\)

\(x-x^2-1=-\left(x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)-\dfrac{3}{4}=-\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2-\dfrac{3}{4}\le-\dfrac{3}{4}< 0\forall x\)
hằng đẳng thức 2= (x-1)2-1<0
GTLN của (x-1)2chỉ có thể là 0 nên với mọi x ta có x-x2-1<0


\(A=x^2+x+1\)
\(A=x^2+x+\dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{1}{4}+1\)
\(A=\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\)
mà \(\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}>\dfrac{3}{4}>0\) với mọi x
\(\Rightarrow Dpcm\)

Ta có:
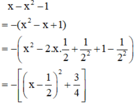
Ta có: 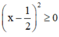 với mọi số thực x
với mọi số thực x
⇒ 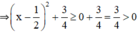 với mọi số thực x
với mọi số thực x
⇒ 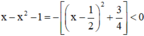 với mọi số thực (ĐPCM)
với mọi số thực (ĐPCM)

Câu a :
\(x^2+x+1=x^2+x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}=\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Vậy biểu thức trên luôn lớn hơn 0 với mọi x
Làm Full cho you nhé,bạn kia sai r:
\(linh_1=x^2+x+1=x^2+x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}=\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}>0\left(đpcm\right)\)
\(linh_2=-4x^2-4x-2=-1\left(4x^2+4x+2\right)=-1\left(4x^2+4x+1+1\right)=-1\left(4x^2+4x+1\right)-1=-1\left(2x+1\right)^2-1< 0\left(đpcm\right)\)

a) \(x^2-2x+3=\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+2=\left(x-1\right)^2+2\)
Vì: \(\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0,\forall x\)
=> \(\left(x-1\right)^2+2>0,\forall x\)
=>đpcm
b) \(x^2+7x+13=\left(x^2+7x+\frac{49}{4}\right)+\frac{3}{4}=\left(x+\frac{7}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}\)
Vì: \(\left(x+\frac{7}{2}\right)^2\ge0,\forall x\)
=> \(\left(x+\frac{7}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}>0,\forall x\)
=>đpcm
c) \(x-x^2-1=-\left(x^2-x+\frac{1}{4}\right)-\frac{3}{4}=-\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2-\frac{3}{4}\)
Vì: \(-\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\le0,\forall x\)
=> \(-\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2-\frac{3}{4}< 0,\forall x\)
=>đpcm
ng đầu tiên trên hoc24 nắm chắc kiến thức toán học là cj đó
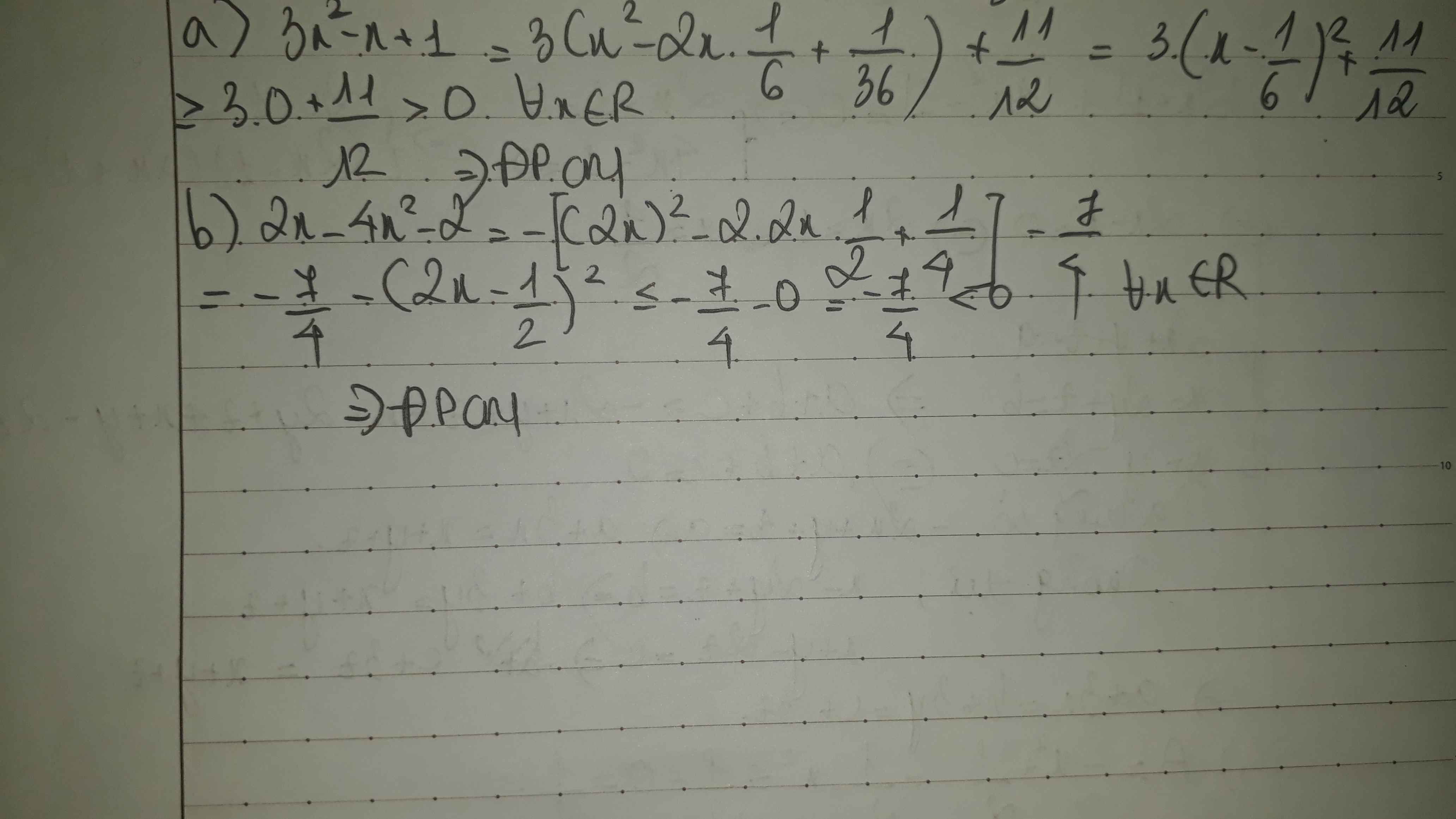
Ta xet 3 truong hop
TH1 : x la so nguyen duong
Co 2x^8 + 2x^7 + 1 = duong + duong + duong = duong
Ma so duong luon lon hon 0
=> 2x^8 + 2x^7 + 1 > 0 voi x la so nguyen duong
TH2 : x la so nguyen am
Co 2x^8 + 2x^7 + 1 = duong + am + duong .
Do 2x^8 > 2x^7 nen tong tren mang dau duong
Ma so duong luon lon hon 0
=> 2x^8 + 2x^7 + 1 > 0 voi x la so nguyen am
TH3 : x = 0
Voi x = 0 ta co 2x^8 + 2x^7 + 1 = 0 + 0 + 1 = 1
Ma 1 > 0
=> 2x^8 + 2x^7 + 1 > 0 voi x = 0
Vay 2x^8 + 2x^7 + 1 > 0 voi moi x