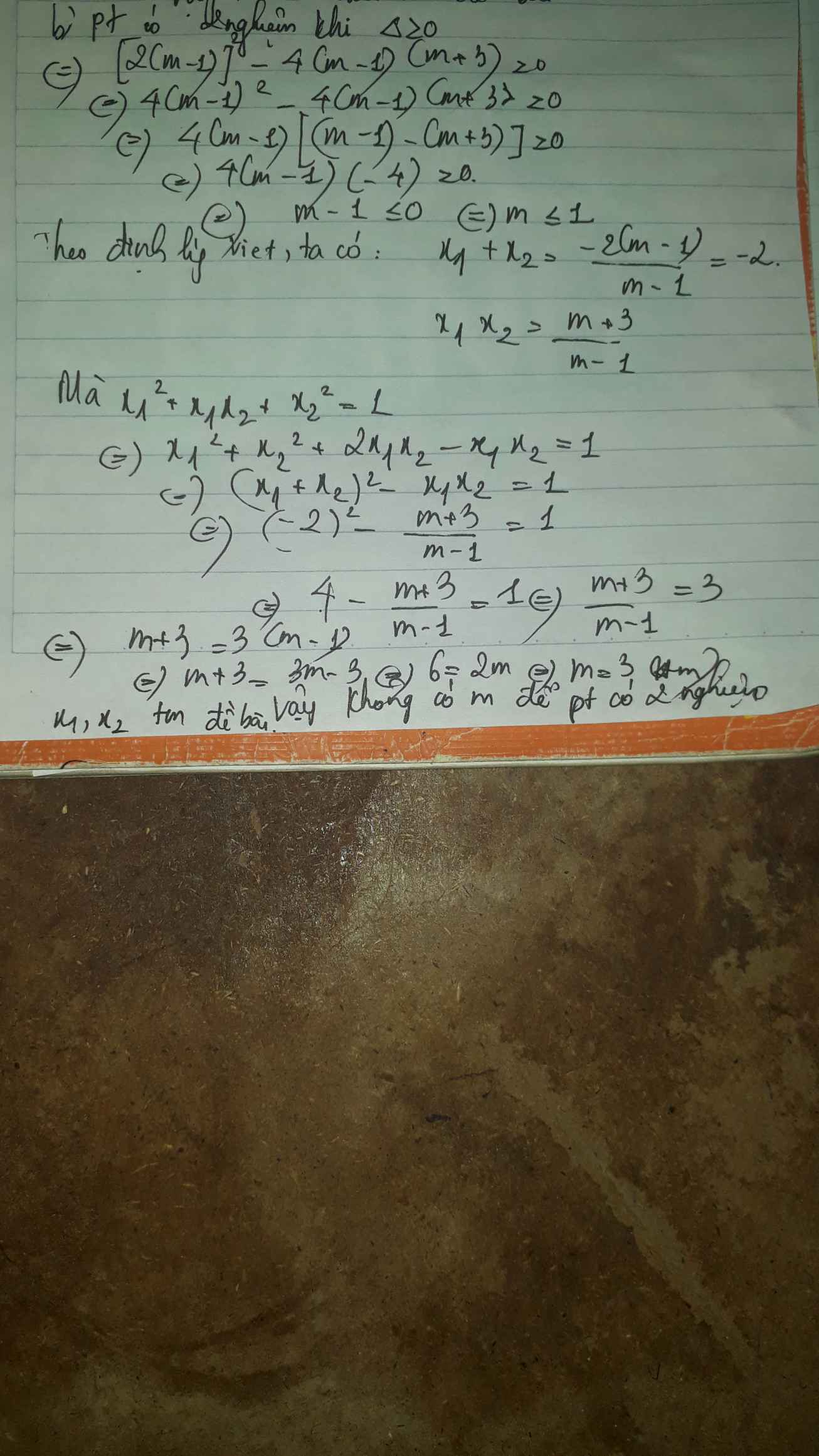Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

b) phương trình có 2 nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m-1\right)^2-\left(m-1\right)\left(m+3\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-2m+1-m^2-3m+m+3\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4m+4\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\le1\)
Ta có: \(x_1^2+x_1x_2+x_2^2=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=1\)
Theo viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=2\left(m-1\right)\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=m+3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[-2\left(m-1\right)^2\right]-2\left(m+3\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-8m+4-2m-6-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-10m-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m_1=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{37}}{4}\left(ktm\right)\\m_2=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{37}}{4}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow m=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{37}}{4}\)

a) Thay m=-2 vào phương trình, ta được:
\(x^2-\left(-x\right)-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-2=0\)
a=1; b=1; c=-2
Vì a+b+c=0 nên phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(x_1=1;x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=\dfrac{-2}{1}=-2\)

Để pt có hai nghiệm pb \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta>0\)\(\Leftrightarrow4-4\left(m-1\right)>0\)\(\Leftrightarrow2>m\)
Theo viet có:\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\\x_1x_2=m-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Có \(x_1^2+x_2^2-3x_1x_2=2m^2+\left|m-3\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-5x_1x_2=2m^2+\left|m-3\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4-5\left(m-1\right)=2m^2+\left|m-3\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m^2+\left|m-3\right|-9+5m=0\) (1)
TH1: \(m\ge3\)
PT (1) \(\Leftrightarrow2m^2+m-3-9+5m=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m^2+6m-12=0\)
Do \(m\ge3\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6m-12\ge6>0\\2m^2>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow2m^2+6m-12>0\)
=>Pt vô nghiệm
TH2: \(m< 3\)
PT (1)\(\Leftrightarrow2m^2-\left(m-3\right)-9+5m=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m^2+4m-6=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow2m^2-2m+6m-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m\left(m-1\right)+6\left(m-1\right)=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m+6\right)\left(m-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=-3\\m=1\end{matrix}\right.\) (Thỏa)
Vậy...

b: \(\text{Δ}=\left(2m-2\right)^2-4\left(2m-5\right)\)
\(=4m^2-8m+4-8m+20\)
\(=4m^2-16m+24\)
\(=4\left(m^2-4m+6\right)>0\)
Do đó: Phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt
Áp dụng hệ thức Vi-et, ta được:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m-1\right)\\x_1x_2=2m-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Theo đề, ta có: \(\left(\sqrt{x_1}-\sqrt{x_2}\right)^2=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1+x_2-2\sqrt{x_1x_2}=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m-2-2\sqrt{2m-5}=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{2m-5}=2m-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2m-5}=m-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m>=3\\m^2-6m+9-2m+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m>=3\\m^2-8m+14=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đến đây thì dễ rồi, bạn chỉ cần giải pt bậc hai rồi đối chiếu với đk là xong

a: Thay m=3 vào pt, ta được:
\(x^2-4x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=5\)
hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{5}+2\\x=-\sqrt{5}+2\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\text{Δ}=\left(-4\right)^2-4\left(-2m+5\right)\)
\(=16+8m-20=8m-4\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm thì 8m-4>=0
hay m>=1/2
Theo đề, ta có: \(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2+3x_1x_2-3\left(x_1+x_2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4^2-3\cdot4+3\left(-2m+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4-6m+15=0\)
=>-6m+19=0
hay m=19/6(nhận)