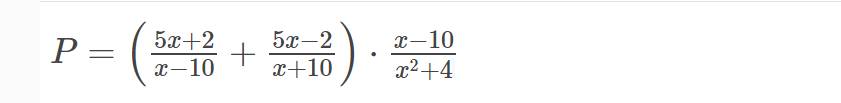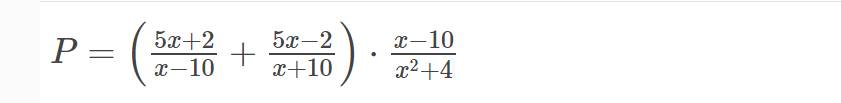Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Bài 1: ĐKXĐ:`x + 3 ne 0` và `x^2+ x-6 ne 0 ; 2-x ne 0`
`<=> x ne -3 ; (x-2)(x+3) ne 0 ; x ne2`
`<=>x ne -3 ; x ne 2`
b) Với `x ne - 3 ; x ne 2` ta có:
`P= (x+2)/(x+3) - 5/(x^2 +x -6) + 1/(2-x)`
`P = (x+2)/(x+3) - 5/[(x-2)(x+3)] + 1/(2-x)`
`= [(x+2)(x-2)]/[(x-2)(x+3)] - 5/[(x-2)(x+3)] - (x+3)/[(x-2)(x+3)]`
`= (x^2 -4)/[(x-2)(x+3)] - 5/[(x-2)(x+3)] - (x+3)/[(x-2)(x+3)]`
`=(x^2 - 4 - 5 - x-3)/[(x-2)(x+3)]`
`= (x^2 - x-12)/[(x-2)(x+3)]`
`= [(x-4)(x+3)]/[(x-2)(x+3)]`
`= (x-4)/(x-2)`
Vậy `P= (x-4)/(x-2)` với `x ne -3 ; x ne 2`
c) Để `P = -3/4`
`=> (x-4)/(x-2) = -3/4`
`=> 4(x-4) = -3(x-2)`
`<=>4x -16 = -3x + 6`
`<=> 4x + 3x = 6 + 16`
`<=> 7x = 22`
`<=> x= 22/7` (thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
Vậy `x = 22/7` thì `P = -3/4`
d) Ta có: `P= (x-4)/(x-2)`
`P= (x-2-2)/(x-2)`
`P= 1 - 2/(x-2)`
Để P nguyên thì `2/(x-2)` nguyên
`=> 2 vdots x-2`
`=> x -2 in Ư(2) ={ 1 ;2 ;-1;-2}`
+) Với `x -2 =1 => x= 3` (thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
+) Với `x -2 =2 => x= 4` (thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
+) Với `x -2 = -1=> x= 1` (thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
+) Với `x -2 = -2 => x= 0`(thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
Vậy `x in{ 3 ;4; 1; 0}` thì `P` nguyên
e) Từ `x^2 -9 =0`
`<=> (x-3)(x+3)=0`
`<=> x= 3` hoặc `x= -3`
+) Với `x=3` (thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ) thì:
`P = (3-4)/(3-2)`
`P= -1/1`
`P=-1`
+) Với `x= -3` thì không thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ
Vậy với x= 3 thì `P= -1`

a) đk x khác 0;2
P = \(\dfrac{1}{x\left(x-2\right)}.\left(\dfrac{x^2+4}{x}-4\right)+1\)
= \(\dfrac{1}{x\left(x-2\right)}.\dfrac{x^2-4x+4}{x}+1\)
= \(\dfrac{1}{x\left(x-2\right)}.\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)^2}{x}+1\)
= \(\dfrac{x-2}{x^2}+1\)
= \(\dfrac{x^2+x-2}{x^2}\)
b) Để \(\left|2+x\right|=1\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}2+x=1< =>x=-1\left(tm\right)\\2+x=-1< =>x=-3\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
TH1: x = -1
Thay x = -1 vào P, ta có:
\(P=\dfrac{\left(-1\right)^2-1-2}{\left(-1\right)^2}=-2\)
TH2: x = -3
Thay x = -3 vào P, ta có:
\(P=\dfrac{\left(-3\right)^2-3-2}{\left(-3\right)^2}=\dfrac{4}{9}\)
c) P = \(1+\dfrac{x-2}{x^2}\)
Xét \(\dfrac{x^2}{x-2}=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)^2+4\left(x-2\right)+4}{x-2}\)
= \(\left(x-2\right)+\dfrac{4}{x-2}+4\)
Áp dụng bdt co-si, ta có:
\(\left(x-2\right)+\dfrac{4}{x-2}\ge2\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)\dfrac{4}{x-2}}=4\)
<=> \(\dfrac{x^2}{x-2}\ge4+4=8\)
<=> \(\dfrac{x-2}{x^2}\le\dfrac{1}{8}\)
<=> A \(\le\dfrac{9}{8}\)
Dấu "=" <=> x = 4

a: \(A=\left(\dfrac{x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{2}{x-2}+\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right)\cdot\dfrac{x+2}{6}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-2x-4+x-2}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x+2}{6}=\dfrac{-6}{6}\cdot\dfrac{1}{x-2}=\dfrac{-1}{x-2}\)
b: x=2 ko thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ
=>Loại
Khi x=3 thì A=-1/(3-2)=-1
c: A=2
=>x-2=-1/2
=>x=3/2

a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\pm10\)
b) \(P=\left(\dfrac{5x+2}{x-10}+\dfrac{5x-2}{x+10}\right)\cdot\dfrac{x-10}{x^2+4}\left(x\ne\pm10\right)\)
\(=\left[\dfrac{\left(5x+2\right)\left(x+10\right)}{\left(x-10\right)\left(x+10\right)}+\dfrac{\left(5x-2\right)\left(x-10\right)}{\left(x-10\right)\left(x+10\right)}\right]\cdot\dfrac{x-10}{x^2+4}\)
\(=\dfrac{5x^2+52x+20+5x^2-52x+20}{\left(x-10\right)\left(x+10\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x-10}{x^2+4}\)
\(=\dfrac{10x^2+40}{x+10}\cdot\dfrac{1}{x^2+4}\)
\(=\dfrac{10\left(x^2+4\right)}{\left(x+10\right)\left(x^2+4\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{10}{x+10}\)
c) Thay \(x=\dfrac{2}{5}\) vào \(P\), ta được:
\(P=\dfrac{10}{\dfrac{2}{5}+10}=\dfrac{25}{26}\)
\(\text{#}Toru\)

Bài 2
a) ĐKXĐ: x - 10 0 và x + 10 0
*) x - 10 0
x 10
*) x + 10 0
x 10
Vậy ĐKXĐ: x -10; x 10
b) P = [(5x + 2)(x + 10) + (5x - 2)(x - 10)]/[(x - 10)(x + 10)] . (x - 10)/(x² + 4)
= (5x² + 50x + 2x + 20 + 5x² - 50x - 2x + 20)/[(x + 10)(x² + 4)]
= (10x² + 40)/[(x + 10)(x² + 4)]
= 10(x² + 4)/[(x + 10)(x² + 4)]
= 10/(x + 10)
c) Khi x = 2/5 ta có:
P = 10.(2/5 + 10)
= 4 + 100
= 104

Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(P=1+\dfrac{3}{x^2+5x+6}:\left(\dfrac{8x^2}{4x^3-8x^2}-\dfrac{3x}{3x^2-12}-\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right)\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\left(\dfrac{8x^2}{4x^2\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{3x}{3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right)\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\left(\dfrac{4}{x-2}-\dfrac{x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right)\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\dfrac{4\left(x+2\right)-x-\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{4x+8-x-x+2}\)
\(=1+3\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)+3\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2+10x+6x+30+3x-6}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2+19x-6}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)

a: \(P=\dfrac{x^2+x-x^2+x+2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2}{x-1}\)