Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(f\left(x\right)=\frac{x^2+2x+1-x^2}{x^2\left(x+1\right)^2}=\frac{\left(x+1\right)^2-x^2}{x^2\left(x+1\right)^2}=\frac{1}{x^2}-\frac{1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(1\right)+f\left(2\right)+....+f\left(x\right)=1-\frac{1}{2^2}+\frac{1}{2^2}-....-\frac{1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{2y\left(x+1\right)^3-1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}-19+x=\frac{x\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2y\left(x+1\right)^3-1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}-19+x=\frac{2y\left(x+1\right)^3-1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}-20+\left(x+1\right)=\frac{x\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
Dat:\(x+1=a\Rightarrow\frac{\left(2y+1\right)a^3-20a^2-1}{a^2}=\frac{a^2-1}{a^2}\Leftrightarrow\left(2y+1\right)a^3-20a^2-1=a^2-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2y+1\right)a^3-20a^2=a^2\Leftrightarrow\left(2ay+a\right)-20=1\left(coi:x=-1cophailanghiemko\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2ay+a=21\Leftrightarrow a\left(2y+1\right)=21\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(2y+1\right)=21\)

a) \(f\left(x\right)-g\left(x\right)+h\left(x\right)\)
\(=x^3-2x^2+3x+1-\left(x^3+x-1\right)+\left(2x^2-1\right)\)
\(=x^3-2x^2+3x+1-x^3-x+1+2x^2-1\)
\(=2x+1\)
b) \(f\left(x\right)-g\left(x\right)+h\left(x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(2x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(x=-\frac{1}{2}\)

Ta có \(f\left(1\right)=g\left(2\right)\)
hay \(2.1^2+a.1+4=2^2-5.2-b\)
\(2+a+4\) \(=4-10-b\)
\(6+a\) \(=-6-b\)
\(a+b\) \(=-6-6\)
\(a+b\) \(=-12\) \(\left(1\right)\)
Lại có \(f\left(-1\right)=g\left(5\right)\)
hay \(2.\left(-1\right)^2+a.\left(-1\right)+4=5^2-5.5-b\)
\(2-a+4\) \(=25-25-b\)
\(6-a\) \(=-b\)
\(-a+b\) \(=-6\)
\(b-a\) \(=-6\)
\(b\) \(=-b+a\) \(\left(2\right)\)
Thay \(\left(2\right)\) vào \(\left(1\right)\) ta được:
\(a+\left(-6+a\right)=-12\)
\(a-6+a\) \(=-12\)
\(a+a\) \(=-12+6\)
\(2a\) \(=-6\)
\(a\) \(=-6:2\)
\(a\) \(=-3\)
Mà \(a=-3\)
⇒ \(b=-6+\left(-3\right)=-9\)
Vậy \(a=3\) và \(b=-9\)
Cái Vậy \(a=3\) và \(b=-9\) bạn ghi là \(a=-3\) và \(b=-9\) nha mk quên ghi dấu " \(-\) "

a) (x-1):2/3=-2/5
=>x-1=-4/15
=>x=11/15
b) |x-1/2|-1/3=0
=>|x-1/2|=1/3
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{5}{6}\\x=-\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{1}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) Tương Tự câu B

\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+9-4x^2-4x-1-2\left(x^2+x-2\right)=3\left(x-3\right)-\left(4x^2+8x-x-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x^2-10x+8-2x^2-2x+4=3\left(x-3\right)-4x^2-7x+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-5x^2-12x+12=3x-9-4x^2-7x+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-5x^2-12x+12=-4x^2-4x-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x^2-4x-7+5x^2+12x-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+8x-19=0\)
\(\text{Δ}=8^2-4\cdot1\cdot\left(-19\right)=76+64=140\)
Vì Δ>0 nên phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-8-2\sqrt{35}}{2}=-4-\sqrt{35}\\x_2=-4+\sqrt{35}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a, \(f\left(x\right)=2x^2\left(x-1\right)-5\left(x+2\right)-2x\left(x-2\right)\)
\(=2x^3-2x^2-5x-10-2x^2+4x=2x^3-4x^2-x-10\)
b, \(g\left(x\right)=x^2\left(2x-3\right)-x\left(x+1\right)-\left(3x-2\right)\)
\(=2x^3-3x^2-x^2-x-3x+2=2x^3+2-4x^2-4x\)
b, Ta có : \(H\left(x\right)=F\left(x\right)-G\left(x\right)=2x^3-4x^2-x-10-2x^3+4x^2+4x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-12=0\Leftrightarrow x=4\)
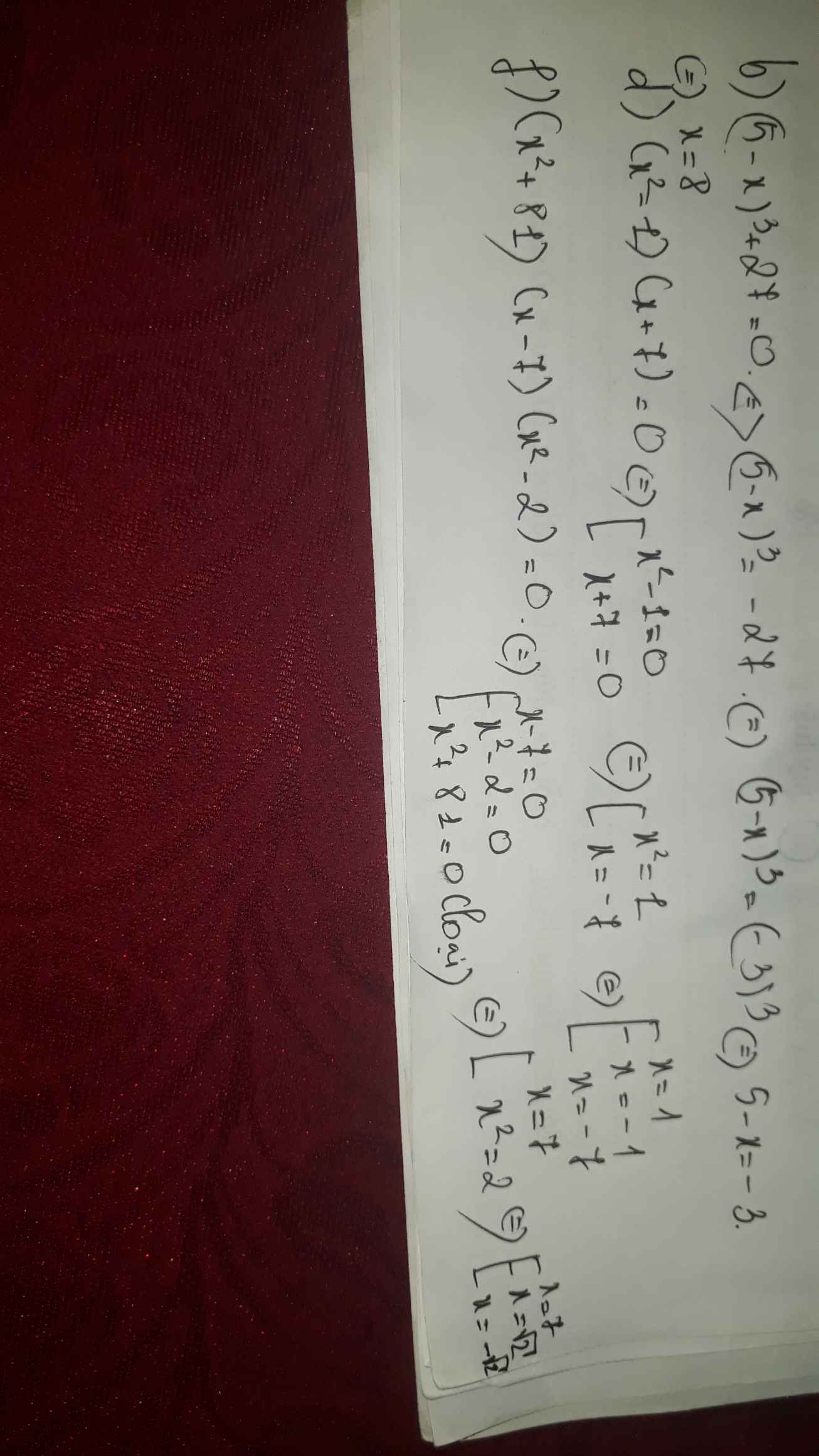
d, \(\left|2x+1\right|=\left|x-1\right|\)
TH1 : 2x + 1 = x - 1 <=> x = -2
TH2 : 2x + 1 = 1 - x <=> 3x = 0 <=> x = 0
f, | x - 1 | - 1 = 50 - 2 | x - 1 |
<=> 3 | x - 1 | = 51 <=> | x - 1 | = 17
TH1 : x - 1 = 17 <=> x = 18
TH2 : x - 1 = -17 <=> x = -16
thanks