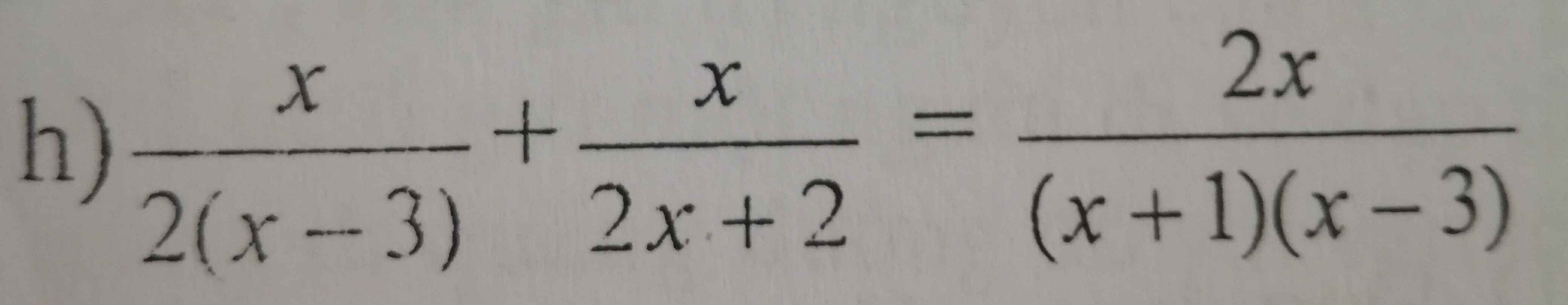GIẢI PHUƠNG TRINH NGIỆM NGUYÊN 1) \(x^2y^2-xy=x^2+2y^2\) 2) \(\left(x^2+y\right)\left(y^2+x\right)=x\left(x-y\right)^2\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



Ta có: 2xy - x - y = 1
=> x(2y-1) - y =1 => 2x(2y-1) - 2y = 2 => 2x(2y-1) - (2y-1) = 3
=> (2y-1)(2x-1) = 3
Ta có bảng:
| 2y-1 | 1 | -1 | 3 | -3 |
| 2x-1 | 3 | -3 | 1 | -1 |
| x | 2 | -1 | 1 | -1 |
| y | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 |

`h)x/(2(x-3))+x/(2x+2)=(2x)/((x+1)(x-3))(x ne -1,3)`
`<=>x(1/(2(x-3))+1/(2(x+1))-2/((x+1)(x-3)))=0`
`+)x=0`
`+)1/(2(x-3))+1/(2(x+1))-2/((x+1)(x-3))=0`
`<=>x+1+x-3-4=0` `<=>2x-6=0` `<=>x=3(l)`
Vậy `x=0`




\(3\left(x^2+\dfrac{1}{x^2}\right)-13\left(x+\dfrac{1}{x}\right)+16=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[3\left(x^2+\dfrac{1}{x^2}\right)+6\right]-13\left(x+\dfrac{1}{x}\right)+10=0\\ \Leftrightarrow3\left(x+\dfrac{1}{x}\right)^2-13\left(x+\dfrac{1}{x}\right)+10=0\\ \text{Đặt }x+\dfrac{1}{x}=y\\ \Leftrightarrow3y^2-13y+10=0\\ \Leftrightarrow3y^2-10y-3y+10=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3y^2-10y\right)-\left(3y-10\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow y\left(3y-10\right)-\left(3y-10\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(y-1\right)\left(3y-10\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+\dfrac{1}{x}-1\right)\left(3x+\dfrac{3}{x}-10\right)=0\\ \text{Ta thấy : }x=0\text{ không phải là nghiệm của phương trình }\\ nên\text{ nhân 2 vế cho }x^2\ne0\\ \text{ Ta được 1 phương trình tuơng đương }:x^2\left(x+\dfrac{1}{x}-1\right)\left(3x+\dfrac{3}{x}-10\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+1-x\right)\left(3x^2+3-10x\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}\right)\left(3x^2-9x-x+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[\left(x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)+\dfrac{3}{4}\right]\left[\left(3x^2-9x\right)-\left(x-3\right)\right]=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\right]\left[3x\left(x-3\right)-\left(x-3\right)\right]=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\left(Vì\text{ }\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ne0\right)\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x=1\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\\ \text{Vậy }S=\left\{\dfrac{1}{3};3\right\}\\ \)
cảm ơn bạn đã trả lời giúp mình câu hỏi này, nhưng là nhân với x không phải là x\(^2\) nhé

\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-xy+4xy-2y^2=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2y\right)\left(2x-y\right)=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+2y=1\\2x-y=7\end{cases}}\)hoặc \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+2y=-1\\2x-y=-7\end{cases}}\)hoặc \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+2y=7\\2x-y=1\end{cases}}\)hoặc \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+2y=-7\\2x-y=-1\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\y=-1\end{cases}}\) hoặc \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-3\\y=1\end{cases}}\) hoặc\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{9}{5}\\y=\frac{13}{5}\end{cases}}\)hoặc (loại) \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{-9}{5}\\y=\frac{-13}{5}\end{cases}}\)(loại)
vậy, phương trình có nghiệm nguyên (x;y)=(3;-1);(-3;1)