Chứng minh đẳng thức: cos (\(\dfrac{\Pi}{2}\)- a) sin (\(\dfrac{\Pi}{2}-b\)) - sin(a - b) = cos a. sin b
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Câu a)
Từ \(\tan a=3\Leftrightarrow \frac{\sin a}{\cos a}=3\Rightarrow \sin a=3\cos a\)
Do đó:
\(\frac{\sin a\cos a+\cos ^2a}{2\sin ^2a-\cos ^2a}=\frac{3\cos a\cos a+\cos ^2a}{2(3\cos a)^2-\cos ^2a}\)
\(=\frac{\cos ^2a(3+1)}{\cos ^2a(18-1)}=\frac{4}{17}\)
Câu b)
Có: \(\cot \left(\frac{\pi}{2}-x\right)=\tan x=\frac{\sin x}{\cos x}\)
\(\cos\left(\frac{\pi}{2}+x\right)=-\sin x\)
\(\Rightarrow \cot \left(\frac{\pi}{2}-x\right)\cos \left(\frac{\pi}{2}+x\right)=\frac{-\sin ^2x}{\cos x}\)
Và:
\(\frac{\sin (\pi-x)\cot x}{1-\sin ^2x}=\frac{\sin x\cot x}{\cos^2x}=\frac{\sin x.\frac{\cos x}{\sin x}}{\cos^2x}=\frac{1}{\cos x}\)
Do đó:
\(\Rightarrow \cot \left(\frac{\pi}{2}-x\right)\cos \left(\frac{\pi}{2}+x\right)+\frac{\sin (\pi-x)\cot x}{1-\sin ^2x}=\frac{1-\sin ^2x}{\cos x}=\frac{\cos ^2x}{\cos x}=\cos x\)
Ta có đpcm.

a: \(2\cdot cot\left(\dfrac{pi}{2}-x\right)+tan\left(pi-x\right)\)
\(=2\cdot tanx-tanx\)
=tan x
b: \(sin\left(\dfrac{5}{2}pi-x\right)+cos\left(13pi+x\right)-sin\left(x-5pi\right)\)
\(=sin\left(\dfrac{pi}{2}-x\right)+cos\left(pi+x\right)+sin\left(pi-x\right)\)
\(=cosx-cosx+sinx=sinx\)

Áp dụng công thức biến tích thành tổng:
\(cos\left(a+b\right).cos\left(a-b\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(cos2a+cos2b\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(2cos^2a-1+1-2sin^2b\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(2cos^2a-2sin^2b\right)\)
\(=cos^2a-sin^2b\)
\(cos\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}+a\right).cos\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}-a\right)+\dfrac{1}{2}sin^2a=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(cos\dfrac{\pi}{2}+cos2a\right)+\dfrac{1}{2}sin^2a\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}cos2a+\dfrac{1}{2}sin^2a=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(cos^2a-sin^2a\right)+\dfrac{1}{2}sin^2a\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}cos^2a\)

rút gọn biểu thức:
E=cos(\(\dfrac{3\pi}{3}-\alpha\))-sin(\(\dfrac{3\pi}{2}-\alpha\))+sin(\(\alpha+4\pi\))

\(VT=\dfrac{-tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}-a\right)cos\left(2\pi-\dfrac{\pi}{2}+a\right)-sin^3\left(4\pi-\dfrac{\pi}{2}-a\right)}{cos\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}-a\right)tan\left(2\pi-\dfrac{\pi}{2}+a\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-cota.sina+sin^3\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}+a\right)}{sina.\left(-cota\right)}=\dfrac{-cosa+cos^3a}{-cosa}=1-cos^2a=sin^2a\)

a) \(sin\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)=cos\left[\dfrac{\pi}{2}-\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)\right]=cos\left(-x\right)=cosx\)
a : Đúng.
b) \(cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)=sin\left[\dfrac{\pi}{2}-\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)\right]=sin\left(-x\right)=-cosx\)
b: Sai.
c) \(sin\left(x-\pi\right)=-sin\left(\pi-x\right)=-sinx\).
d: Sai.
d) \(cos\left(x-\pi\right)=cos\left(\pi-x\right)=cosx\)
c: Đúng.

Để chứng minh các định lượng đẳng cấp, ta sẽ sử dụng các công thức định lượng giác cơ bản và các quy tắc biến đổi đẳng thức. a) Bắt đầu với phương trình ban đầu: 1 - cos^2(π/2 - x) / (1 - sin^2(π/2 - x)) = -cot(π/2 - x) * tan( π/2 - x) Ta biết rằng: cos^2(π/2 - x) = sin^2(x) (công thức lượng giác) sin^2(π/2 - x) = cos^2(x) (công thức lượng giác) Thay vào phương trình ban đầu, ta có: 1 - sin^2(x) / (1 - cos^2(x)) = -cot(π/2 - x) * tan(π/ 2 - x) Tiếp theo, ta sẽ tính toán một số lượng giác: cot(π/2 - x) = cos(π/2 - x) / sin(π/2 - x) = sin(x) / cos(x) = tan(x) (công thức lượng giác) tan(π/2 - x) = sin(π/2 - x) / cos(π/2 - x) = cos(x) / sin(x) = 1 / tan(x) (công thức lượng giác) Thay vào phương trình, ta có: 1 - sin^2(x) / (1 - cos^2(x)) = -tan(x) * (1/tan(x)) = -1 Vì vậy, ta đã chứng minh là đúng. b) Bắt đầu với phương thức ban đầu: (1/cos^2(x) + 1) * tan(x) = tan^2(x) Tiếp tục chuyển đổi phép tính: 1/cos^2(x) + 1 = tan^2(x) / tan(x) = tan(x) Tiếp theo, ta sẽ tính toán một số giá trị lượng giác: 1/cos^2(x) = sec^2(x) (công thức) lượng giác) sec^2(x) + 1 = tan^2(x) + 1 = sin^2(x)/cos^2(x) + 1 = (sin^2(x) + cos^2(x) ))/cos^2(x) = 1/cos^2(x) Thay thế vào phương trình ban đầu, ta có: 1/cos^2(x) + 1 = 1/cos^2(x) Do đó, ta đã chứng minh được b)đúng.
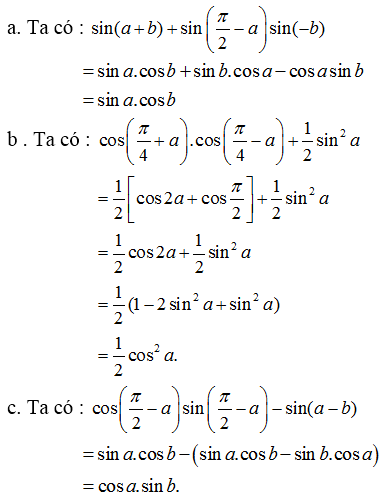
\(VT=\sin a.\cos b-sin\left(a-b\right)\)
\(\sin a.\cos b-\sin a\cos b+\cos a\sin b=\cos a\sin b\)
=>ĐPCM