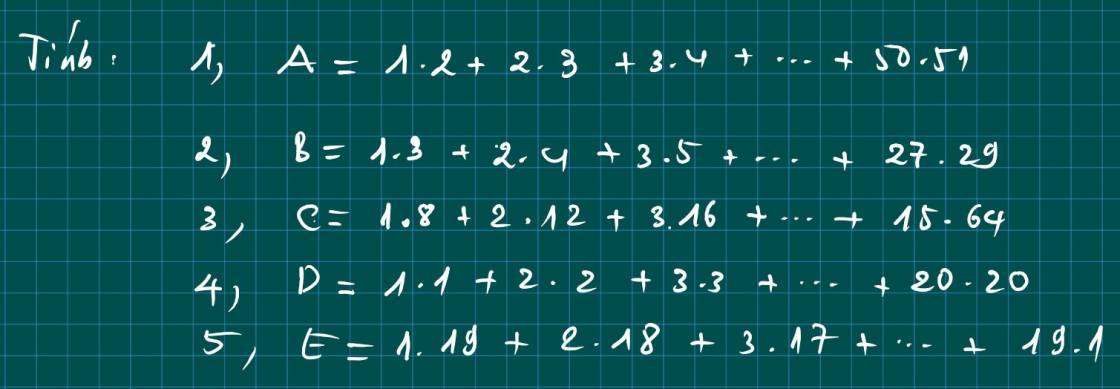
GIẢI GÚP EM CHI TIẾT VỚI Ạ
EM CẢM ƠN
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Gọi số sản phẩm dự định là a (sản phẩm ) (a là số tự nhiên khác 0)
Vì theo dự định mỗi ngày sản xuất 50 sản phẩm nên số ngày theo dự định là \(\dfrac{a}{50}\)
Nhưng thực tế , đội đã sản xuất theeo được 30 sản phẩm do mỗi ngày vượt mức 10 sản phẩm (nghĩa là sản xuất 60 sản phẩm) , nên số ngày thực tế là \(\dfrac{a+30}{60}\)
Vì thực tế sớm hơn dự định 2 ngày nên ta có phương trình :
\(\dfrac{a}{50}=\dfrac{a+30}{60}+2\\ \Leftrightarrow6a=5\left(a+30+120\right)\\\Leftrightarrow a=750\left(t.m\right) \)
Vậy số sản phẩm dự định là 750 sản phẩm
Bài 3:
Gọi số sản phẩm đội phải sản xuất theo kế hoạch là x( sản phẩm, x\(\in N\)*)
Thời gian đội sản xuất theo kế hoạch là: \(\dfrac{x}{50}\) (ngày)
Số ngày làm thực tế là: \(\dfrac{x+30}{50+10}=\dfrac{x+30}{60}\) (ngày)
Theo bài ra, ta có phương trình:
\(\dfrac{x}{50}-\dfrac{x+30}{60}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{60x-50\left(x+30\right)}{50.60}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow60x-50x-1500=6000\Leftrightarrow x=750\)(thoả mãn)
Vậy theo kế hoạch đội phải sản xuất 750 sản phẩm

a, Xét tứ giác ADHE có ^ADH = ^AEH = ^DAE = 900
=> tứ giác ADHE là hcn
=> AH = DE (2 đường chéo bằng nhau)
b, Xét tam giác AHB và tam giác CHA ta có
^AHB = ^CHA = 900
^HAB = ^HCA ( cùng phụ ^HAC )
Vậy tam giác AHB~ tam giác CHA (g.g)
\(\dfrac{AH}{CH}=\dfrac{HB}{AH}\Rightarrow AH^2=BH.CH\)
c, Xét tam giác AHD và tam giác ABH có
^ADH = ^AHB = 900
^A _ chung
Vậy tam giác AHD ~ tam giác ABH (g.g)
\(\dfrac{AH}{AB}=\dfrac{AD}{AH}\Rightarrow AH^2=AD.AB\)(1)
tương tự tam giác AEH ~ tam giác AHC (g.g)
\(\dfrac{AE}{AH}=\dfrac{AH}{AC}\Rightarrow AH^2=AE.AC\left(2\right)\)
Từ (1) ; (2) suy ra \(AD.AB=AE.AC\Rightarrow\dfrac{AD}{AC}=\dfrac{AE}{AB}\)
Xét tam giác ADE và tam giác ACB
^A _ chung
\(\dfrac{AD}{AC}=\dfrac{AE}{AB}\left(cmt\right)\)
Vậy tam giác ADE ~ tam giác ACB (c.g.c)


a) \(I_1=\int\dfrac{dx}{x^2+2x+3}\)
\(=\int\dfrac{dx}{\left(x+1\right)^2+2}=\int\dfrac{d\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)^2+\left(\sqrt{2}\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}arctan\left(\dfrac{x+1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)+C\)
b) \(I_2=\int\dfrac{dx}{4x^2+4x+2}\)
\(=\int\dfrac{dx}{\left(2x+1\right)^2+1}=\dfrac{1}{2}\int\dfrac{d\left(2x+1\right)}{\left(2x+1\right)^2+1^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}arctan\left(2x+1\right)+C\)

a) \(I_4=\int\dfrac{3x+5}{2x^2+x+10}dx\)
\(=\int\dfrac{\dfrac{3}{4}\left(4x+1\right)+\dfrac{17}{4}}{2x^2+x+10}dx=\dfrac{3}{4}\int\dfrac{\left(4x+1\right)dx}{2x^2+x+10}+\dfrac{17}{4}\int\dfrac{dx}{2x^2+x+10}\)
\(=\dfrac{3}{4}\int\dfrac{d\left(2x^2+x+10\right)}{2x^2+x+10}+\dfrac{17}{8}\int\dfrac{dx}{x^2+\dfrac{x}{2}+5}\)
\(=\dfrac{3}{4}\ln\left(2x^2+x+10\right)+\dfrac{17}{8}\int\dfrac{dx}{\left(x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{79}{16}}\)
\(=\dfrac{3}{4}\ln\left(2x^2+x+10\right)+\dfrac{17}{8}\int\dfrac{dx}{\left(x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{79}{16}}\)
\(=\dfrac{3}{4}\ln\left(2x^2+x+10\right)+\dfrac{17}{8}\int\dfrac{d\left(x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)}{\left(x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{79}}{4}\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{3}{4}\ln\left(2x^2+x+10\right)+\dfrac{17}{8}.\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{79}}arctan\left(\dfrac{4x+1}{\sqrt{79}}\right)+C\)
\(=\dfrac{3}{4}\ln\left(2x^2+x+10\right)+\dfrac{17}{2\sqrt{79}}arctan\left(\dfrac{4x+1}{\sqrt{79}}\right)+C\)
b) \(I_5=\int\dfrac{4x-1}{6x^2+9x+4}dx\)
\(=\int\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{3}\left(12x+9\right)-4}{6x^2+9x+4}dx\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{3}\int\dfrac{\left(12x+9\right)dx}{6x^2+9x+4}-4\int\dfrac{dx}{6x^2+9x+4}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{3}\int\dfrac{d\left(6x^2+9x+4\right)}{6x^2+9x+4}-4\int\dfrac{dx}{\left(3x+1\right)^2+3}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{3}\ln\left(6x^2+9x+4\right)-\dfrac{4}{3}\int\dfrac{d\left(3x+1\right)}{\left(3x+1\right)^2+\left(\sqrt{3}\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{3}\ln\left(6x^2+9x+4\right)-\dfrac{4}{3}.\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}arctan\left(\dfrac{3x+1}{\sqrt{3}}\right)+C\)

\(n_{Fe}=\dfrac{11,2}{56}=0,2\left(mol\right)\\ n_S=\dfrac{3,2}{32}=0,1\left(mol\right)\\ PTHH:Fe+S\underrightarrow{t^o}FeS\left(1\right)\\ LTL:0,2>0,1\Leftrightarrow Fe.dư\)
\(Theo.pt\left(1\right):n_{Fe\left(pư\right)}=n_{FeS}=0,1\left(mol\right)\\ n_{FeS\left(dư\right)}=0,2-0,1=0,1\left(mol\right)\)
\(PTHH:FeS+H_2SO_4\rightarrow FeSO_4+H_2S\uparrow\left(2\right)\\ Fe+2H_2SO_4\rightarrow FeSO_4+SO_2\uparrow+2H_2O\left(3\right)\)
\(Theo.pt\left(2\right):n_{H_2S}=n_{FeS}=0,1\left(mol\right)\\ Theo.pt\left(3\right):n_{SO_2}=n_{Fe}=0,1\left(mol\right)\\ \%V_{H_2S}=\dfrac{0,1}{0,1+0,1}=50\%\\ \%V_{SO_2}=100\%-50\%=50\%\)
\(Theo.pt\left(2\right):n_{H_2SO_4\left(2\right)}=n_{FeS}=0,1\left(mol\right)\\ Theo.pt\left(3\right):n_{H_2SO_4\left(3\right)}=2n_{Fe}=2.0,1=0,3\left(mol\right)\\ C_{MddH_2SO_4}=\dfrac{0,3}{0,2}=1,5M\)


ĐK: \(x\ge0\)
Dễ thấy \(1-\sqrt{2\left(x^2-x+1\right)}\le1-\sqrt{2}< 0\)
Khi đó bất phương trình tương đương:
\(x-\sqrt{x}\le1-\sqrt{2\left(x^2-x+1\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}-1+\sqrt{2\left(x+\dfrac{1}{x}-1\right)}\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}-1+\sqrt{2\left(\sqrt{x}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\right)^2+2}\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t-1+\sqrt{2t^2+2}\le0\)

Bài 1:
1.2 + 2.3 + 3.4 +...+ 50.51
1.2.3 = 1.2.3 = 1.2.3
2.3.3 = 2.3.(4-1) = 2.3.4 - 1.2.3
3.4.3 = 3.4.(5-2) = 3.4.5 - 2.3.4
....................................................................
50.51.3 = 50.51.(52-49) = 50.51.52 - 49.50.51
Cộng vế với vế ta có:
1.2.3 + 2.3.3 + 3.4.3 +...+ 50.51.3= 50.51.52
3.(1.2 + 2.3 + 3.4+..+50.51) = 50.51.52
1.2 + 2.3 + 3.4 +....+ 50.51 = 50.51.52: 3 = 44200
B = 1.3 + 2.4 + 3.5 +...+ 27.29
1.3 = 1.(2+1) = 1.2 + 1
2.4 = 2.(3+1) = 2.3 + 2
...........................................
27.29 = 27.(28+1) = 27.28 + 28
cộng vế với vế ta có:
B = 1.3 + 2.4+...+27.29 = 1.2 + 2.3 +...+ 27.28 + 1 + 2+...+ 28
Đặt: A = 1.2 + 2.3+..+27.28; C= 1+2+...+28
Thì B = A + C
1.2.3 = 1.2.3
2.3.3 = 2.3.(4-1) = 2.3.4 - 1.2.3
...........................
27.28.3 = 27.28.(29-26) = 27.28.29 - 26.27.28
Cộng vế với vế ta được : 1.2.3 + 2.3.3 +...+ 27.28.3 = 27.28.29
3.(1.2 + 2.3 +...+ 27.28) = 27.28.29
1.2 + 2.3 + ...+ 27.28 = 27.28.29 : 3
A = 1.2 + 2.3 +...+ 27.28 = 7308
C = 1 + 2 + ....+ 28
Dãy số trên là dãy số cách đều với khoảng cách là: 2-1 = 1
Số số hạng của dãy số trên là: (28 - 1): 1 + 1 = 28
Tổng C = ( 28 + 1)\(\times\) 28 : 2 = 406
B = 7308 + 406 = 7714