Cho hàm số f x = 3 - 4 - x 4 k h i x ≠ 0 1 4 k h i x = 0 Khi đó f'(0) là kết quả nào sau đây?
A. 1 4
B. 1 16
C. 1 32
D. Không tồn tại
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

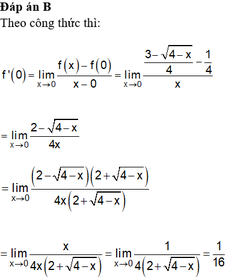

a) Parabol: \(y = a{(x - h)^2} + k\) với \(I(h;k) = \left( {\frac{5}{2}; - \frac{1}{4}} \right)\) là tọa độ đỉnh.
\( \Rightarrow y = a{\left( {x - \frac{5}{2}} \right)^2} - \frac{1}{4}\)
(P) đi qua \(A(1;2)\) nên \(2 = a{\left( {1 - \frac{5}{2}} \right)^2} - \frac{1}{4} \Rightarrow a = 1\)
\( \Rightarrow y = {\left( {x - \frac{5}{2}} \right)^2} - \frac{1}{4} \Leftrightarrow y = {x^2} - 5x + 6\)
Vậy parabol đó là \(y = {x^2} - 5x + 6\)
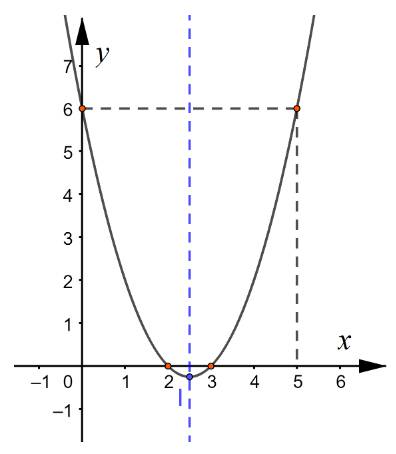
b) Vẽ parabol \(y = {x^2} - 5x + 6\)
+ Đỉnh \(I\left( {\frac{5}{2}; - \frac{1}{4}} \right)\)
+ Giao với Oy tại điểm \((0;6)\)
+ Giao với Ox tại điểm \((3;0)\) và \((2;0)\)
+ Trục đối xứng \(x = \frac{5}{2}\). Điểm đối xứng với điểm \((0;6)\) qua trục đối xứng có tọa độ \((5;6)\)
b) Hàm số đồng biến trên khoảng \(\left( { - \frac{5}{2}; + \infty } \right)\)
Hàm số nghịch biến trên khoảng \(\left( { - \infty ; - \frac{5}{2}} \right)\)
c) \(f(x) \ge 0 \Leftrightarrow {x^2} - 5x + 6 \ge 0\)
Cách 1: Quan sát đồ thị, ta thấy các điểm có\(y \ge 0\) ứng với hoành độ \(x \in ( - \infty ;2] \cup [3; + \infty )\)
Do đó tập nghiệm của BPT \(f(x) \ge 0\) là \(S = ( - \infty ;2] \cup [3; + \infty )\)
Cách 2:
\(\begin{array}{l} \Leftrightarrow {x^2} - 5x + 6 \ge 0\\ \Leftrightarrow (x - 2)(x - 3) \ge 0\end{array}\)
Do đó \(x - 2\) và \(x - 3\) cùng dấu. Mà \(x - 2 > x - 3\;\forall x \in \mathbb{R}\)
\( \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l}x - 3 \ge 0\\x - 2 \le 0\end{array} \right. \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l}x \ge 3\\x \le 2\end{array} \right.\)
Tập nghiệm của BPT là \(S = ( - \infty ;2] \cup [3; + \infty )\)

`a)TXĐ: R`
`b)TXĐ: R\\{0}`
`c)TXĐ: R\\{1}`
`d)TXĐ: (-oo;-1)uu(1;+oo)`
`e)TXĐ: (-oo;-1/2)uu(1/2;+oo)`
`f)TXĐ: (-oo;-\sqrt{2})uu(\sqrt{2};+oo)`
`h)TXĐ: (-oo;0) uu(2;+oo)`
`k)TXĐ: R\\{1/2}`
`l)ĐK: {(x^2-1 > 0),(x-2 > 0),(x-1 ne 0):}`
`<=>{([(x > 1),(x < -1):}),(x > 2),(x ne 1):}`
`<=>x > 2`
`=>TXĐ: (2;+oo)`
câu l) $x^2-1 > 0$ thì giải ra 2 nghiệm $x < -1, x > 1$ mới đúng chứ nhỉ?

3.
\(f\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)=cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)\Rightarrow f'\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)=-sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)\)
\(f'\left(x-\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=-sin\left(x-\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\)
\(f'\left(0\right)=-sin\left(0\right)=0\)
\(2f'\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right).f'\left(x-\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=2sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)sin\left(x-\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\)
\(=cos\left(\frac{\pi}{2}\right)-cos\left(2x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=-cos\left(2x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\)
\(f'\left(0\right)-f\left(2x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=0-cos\left(2x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=-cos\left(2x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow2f'\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)f'\left(x-\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=f'\left(0\right)-f\left(2x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\) (đpcm)
4.
\(y=3\left(sin^4x+cos^4x\right)-2\left(sin^6x+cos^6x\right)\)
\(=3\left(sin^2x+cos^2x\right)^2-6sin^2x.cos^2x-2\left(sin^2x+cos^2x\right)^3+6sin^2x.cos^2x\left(sin^2x+cos^2x\right)\)
\(=3-2=1\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=0\) ; \(\forall x\)
5.
\(y=\left(\frac{sinx}{1+cosx}\right)^3=\left(\frac{sinx\left(1-cosx\right)}{1-cos^2x}\right)^3=\left(\frac{sinx\left(1-cosx\right)}{sin^2x}\right)^3=\left(\frac{1-cosx}{sinx}\right)^3\)
\(y'=3\left(\frac{1-cosx}{sinx}\right)^2\left(\frac{sin^2x-cosx\left(1-cosx\right)}{sin^2x}\right)=3\left(\frac{1-cosx}{sinx}\right)^2\left(\frac{1-cosx}{sin^2x}\right)=\frac{3\left(1-cosx\right)^3}{sin^4x}\)
\(\Rightarrow y'.sinx-3y=\frac{3\left(1-cosx\right)^3}{sin^3x}-3\left(\frac{1-cosx}{sinx}\right)^3=0\) (đpcm)

Lời giải:
$f'(x)=5(\sin ^23x-4)'(\sin ^23x-4)^4=5.2.\sin 3x (\sin 3x)'.(\sin ^23x-4)^4$
$=30\sin 3x\cos 3x(\sin ^23x-4)^4$
$\Rightarrow k=30$

a, \(\Rightarrow x-2\inƯ\left(-3\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm3\right\}\)
| x-2 | 1 | -1 | 3 | -3 |
| x | 3 | 1 | 5 | -1 |
b, \(3\left(x-2\right)+13⋮x-2\Rightarrow x-2\inƯ\left(13\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm13\right\}\)
| x-2 | 1 | -1 | 13 | -13 |
| x | 3 | 1 | 15 | -11 |
c, \(x\left(x+7\right)+2⋮x+7\Rightarrow x+7\inƯ\left(2\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm2\right\}\)
| x+7 | 1 | -1 | 2 | -2 |
| x | -6 | -8 | -5 | -9 |

c. x^2-5x +6 = 0
<=> x^2 - 5x = -6
<=> - 4x = -6
<=> x= -6/-4
Mình chỉ phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử thôi , phần còn lại bạn tự tính nha keo dài lắm
A) 2x2(x+3) - x(x+3) = 0 <=> x(x - 3)(2x-1)=0
B) (2x+5)2 - (x+2)2=0 <=> (x+3)(3x+7)=0
C) (x2-2x) - (3x-6)=0 <=> (x-2)(x-3)=0
D) (2x-7)(2x-7-6x+18)=0 <=> (2x-7)(-4x+11)=0
E) (x-2)(x+1) - (x-2)(x+2)=0 <=> (x-2)*(-1)=0 <=> x-2=0
G) (2x-3)(2x+2-5x)=0 <=> (2x-3)(-3x+2)=0
H) (1-x)(5x+3+3x-7)=0 <=> (1-x)(8x-4)=0
F) (x+6)*3x=0
I) (x-3)(4x-1-5x-2)=0 <=> (x-3)(-x-3)=0
K) (x+4)(5x+8)=0
H) (x+3)(4x-9)=0