Cho phương trình log 2 2 x - 2 log 2 x - m + log 2 x = m * . Có bao nhiêu giá trị nguyên của tham số m ∈ - 2019 ; 2019 để phương trình (*) có nghiệm?
A.2021
B.2019
C.4038
D.2020
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

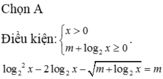
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
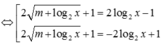
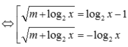

Đáp án D
Điều kiện 40 < x < 60
Vậy x cần tìm theo yêu cầu đề là các số nguyên dương chạy từ 41 đến 59; trừ giá trị 50. Có tất cả 18 giá trị thỏa mãn.

Khoảng giá trị của x mà đồ thị hàm số \(y=log_2x\) nằm phía trên đường thẳng y = 2 là \(\left(4;+\infty\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Tập nghiệm của bất phương trình \(log_2x>2\) là \(\left(4;+\infty\right)\)

a) Với \(x = 1\) thì \(y = {\log _2}1 = 0\)
Với \(x = 2\) thì \(y = {\log _2}2 = 1\)
Với \(x = 4\) thì \(y = {\log _2}4 = 2\)
b) Biểu thức \(y = {\log _2}x\) có nghĩa khi x > 0.

\(log\left(5\left(x^2+1\right)\right)\ge log\left(mx^2+4x+m\right)\)
- BPT đúng \(\forall x\Rightarrow log\left(mx^2+4x+m\right)\) xác định \(\forall x\in R\)
\(\Rightarrow mx^2+4x+m>0\) \(\forall x\in R\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=m>0\\\Delta'=4-m^2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow m>2\) (1)
- Lại có \(x^2+1\ge1\) \(\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow5\left(x^2+1\right)\ge mx^2+4x+m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5\left(x^2+1\right)-4x\ge m\left(x^2+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5-\dfrac{4x}{x^2+1}\ge m\)
Đặt \(f\left(x\right)=5-\dfrac{4x}{x^2+1}\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\ge m\) \(\forall x\Leftrightarrow m\le min\left(f\left(x\right)\right)\)
Ta có \(f\left(x\right)=3+2-\dfrac{4x}{x^2+1}=3+\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)^2}{x^2+1}\ge3\)
\(\Rightarrow min\left(f\left(x\right)\right)=3\Rightarrow m\le3\) (2)
Kết hợp (1), (2) \(\Rightarrow2< m\le3\Rightarrow m=3\)
Vậy có 1 giá trị nguyên duy nhất của m để BPT đúng với mọi x
Đáp án B

ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne y\)
\(log_xy=\frac{1}{log_xy}\Leftrightarrow log_x^2y=1\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}log_xy=1\\log_xy=-1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=y\left(l\right)\\x=\frac{1}{y}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=log_{x^{-1}}\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=-log_x\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-\frac{1}{x^2}=1\Leftrightarrow x^4-x^2-1=0\Rightarrow x^2=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\Rightarrow y^2=\frac{1}{x^2}=\frac{-1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+xy+y^2=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}+1+\frac{-1+\sqrt{5}}{2}=\sqrt{5}+1\)

\(log_xy=log_yx=\frac{1}{log_xy}\Rightarrow\left(log_xy\right)^2=1\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}log_xy=1\\log_xy=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=y\\x=\frac{1}{y}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do \(log_x\left(x-y\right)\) tồn tại \(\Rightarrow x-y\ne0\Rightarrow x\ne y\Rightarrow x=\frac{1}{y}\)
\(log_x\left(x-y\right)=log_y\left(x+1\right)\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=-log_x\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_x\left[\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+1\right)\right]=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+1\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=x\Leftrightarrow x^3+x^2-2x-1=0\)
Pt này nghiệm xấu, đề bài có vấn đề