2x+1 cong 2x = 96
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.




Xét cấp số cộng 1, 6, 11, ..., 96.
Ta có: 96 = 1 + 5(n − 1) ⇒ n = 20
Suy ra
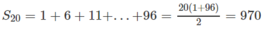
Và 2x.20 + 970 = 1010
Từ đó x = 1

2x + 2x + 1 = 96
2x + 2x . 2 = 96
2x . (1 + 2) = 96
2x . 3 = 96
2x = 96 : 3
2x = 32
2x = 25
x = 5

a)16.4x=48
\(4^2.4^x=4^{8^{ }}\)
\(4^x=4^{8^{ }}:4^2\)
\(4^x=4^{6^{ }}\)
\(x=6\)
b)(X-2)(X-5)=0
\(\Rightarrow x-2=0\rightarrow x=2\)
\(x-5=0\rightarrow x=5\)
Vậy x∈ {2;5}
c)2x+2x+1=96
\(2^x.1+2^{x^{ }}.2\)
\(2^x.\left(1+2\right)=96\)
\(2^x.3=96\)
\(2^x=96:3\)
\(2^x=32\)
\(2^x=2^5\)
\(x=5\)
\(Zzz\) 😪
chị giúp em đc mấy bài trong trang của em mới đăng đc ko ạ?

\(y'=6x^2-4x-4\)
\(y'\left(0\right)=-4\)
\(y\left(0\right)=1\)
Do đó pt tiếp tuyến tại điểm có hoành độ x=0 là:
\(y=-4\left(x-0\right)+1\Leftrightarrow y=-4x+1\)

a: =>12x-64=32
=>12x=96
=>x=8
b: =>x-1=5
=>x=6
c: =>2^x*3=96
=>2^x=32
=>x=5

9) Ta có: \(\dfrac{2x+5}{x+3}+1=\dfrac{4}{x^2+2x-3}-\dfrac{3x-1}{1-x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)+x^2+2x-3=4+\left(3x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-2x+5x-5+x^2+2x-3-4-3x^2-10x+x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x=9\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{9}{4}\)
10) Ta có: \(\dfrac{x-1}{x+3}-\dfrac{x}{x-3}=\dfrac{7x-3}{9-x^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}-\dfrac{x\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{3-7x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
Suy ra: \(x^2-4x+3-x^2-3x-3+7x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x=0\)(luôn đúng)
Vậy: S={x|\(x\notin\left\{3;-3\right\}\)}
11) Ta có: \(\dfrac{5+9x}{x^2-16}=\dfrac{2x-1}{x+4}+\dfrac{3x-1}{x-4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(2x-1\right)\left(x-4\right)}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)}+\dfrac{\left(3x-1\right)\left(x+4\right)}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)}=\dfrac{9x+5}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+5\right)}\)
Suy ra: \(2x^2-9x+4+3x^2+12x-x-4-9x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x^2-7x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(5x-7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{7}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
12) Ta có: \(\dfrac{2x}{2x-1}+\dfrac{x}{2x+1}=1+\dfrac{4}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x\left(2x+1\right)}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}+\dfrac{x\left(2x-1\right)}{\left(2x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)}=\dfrac{4x^2-1+4}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}\)
Suy ra: \(4x^2+2x+2x^2-x-4x^2-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+3x-2x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+3\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
2x+1+2x=96
2x.2+2x=96
2x(2+1)=96
2x=96:3
2x=32
=> x=5
Vậy x=5
2x+1 + 2x = 96
<=> 2x.(2 + 1) = 96
=> 2x . 3 = 96
=> 2x = 32 = 25
Vậy x = 5