Với giá trị nào của \(x\) thì :
a) Giá trị phân thức \(\dfrac{5-2x}{6}\) lớn hớn giá trị phân thức \(\dfrac{5x-2}{3}\) ?
b) Giá trị phân thức \(\dfrac{1,5-x}{5}\) nhỏ hơn giá trị phân thức \(\dfrac{4x+5}{2}\) ?
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a: \(\dfrac{2x-3}{35}+\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{7}\le\dfrac{x^2}{7}-\dfrac{2x-3}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-3+5x\left(x-2\right)\le5x^2-7\left(2x-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-3+5x^2-10x< =5x^2-14x+21\)
=>-8x-3<=-14x+21
=>6x<=24
hay x<=4
b: \(\dfrac{6x+1}{18}+\dfrac{x+3}{12}>=\dfrac{5x+3}{6}+\dfrac{12-5x}{9}\)
=>2(6x+1)+3(x+3)>=6(5x+3)+4(12-5x)
=>12x+2+3x+9>=30x+18+48-20x
=>15x+11>=10x+66
=>5x>=55
hay x>=11

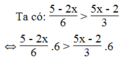
⇔ 5 – 2x > 10x – 4
⇔ -2x – 10x > -4 – 5⇔ -12x > -9⇔ x < 3/4
Vậy với x < 3/4 thì giá trị phân thức (5 - 2x)/6 lớn hơn giá trị phân thức (5x - 2)/3

a: ĐKXĐ: x<>0; x<>-1
b: E=5(x+1)/2x(x+1)=5/2x
b: Để E=1 thì 5/2x=1
=>2x=5
=>x=5/2

x đầu ở đa thức A là x^3 chăng?
a/ \(A=x^3-5x^2+8x-4\)
\(=\left(x^3-x^2\right)+\left(-4x^2+4\right)+\left(8x-8\right)\)
\(=x^2\left(x-1\right)-4\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)+8\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-4x-4\right)=\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)^2\)
b/ \(B=\dfrac{x^5}{30}-\dfrac{x^3}{6}+\dfrac{2x}{15}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^5}{30}-\dfrac{5x^3}{30}+\dfrac{4x}{30}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x^4-5x^2+4\right)}{30}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x^4-x^2-4x^2+4\right)}{30}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}{30}\)

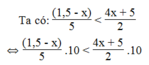
⇔ 3 – 2x < 20x + 25⇔ -2x – 20x < 25 – 3
⇔ -22x < 22⇔ x > -1
Vậy với x > -1 thì giá trị phân thức (1,5 - x)/5 nhỏ hơn giá trị phân thức 4x + 5)/2 .

Ta có: \(\dfrac{10x-5}{18}+\dfrac{x+3}{12}\ge\dfrac{7x+3}{6}-\dfrac{12-x}{9}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\left(10x-5\right)}{36}+\dfrac{3\left(x+3\right)}{36}\ge\dfrac{6\left(7x+3\right)}{36}-\dfrac{4\left(12-x\right)}{36}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow20x-10+3x+9\ge43x+9-48+4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow23x-1-47x+39\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-24x+38\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-24x\ge-38\)
hay \(x\le\dfrac{19}{12}\)
Vậy: S={x|\(x\le\dfrac{19}{12}\)}

a: Để \(\dfrac{3x-2}{4}\) không nhỏ hơn \(\dfrac{3x+3}{6}\) thì \(\dfrac{3x-2}{4}>=\dfrac{3x+3}{6}\)
=>\(\dfrac{6\left(3x-2\right)}{24}>=\dfrac{4\left(3x+3\right)}{24}\)
=>18x-12>=12x+12
=>6x>=24
=>x>=4
b: Để \(\left(x+1\right)^2\) nhỏ hơn \(\left(x-1\right)^2\) thì \(\left(x+1\right)^2< \left(x-1\right)^2\)
=>\(x^2+2x+1< x^2-2x+1\)
=>4x<0
=>x<0
c: Để \(\dfrac{2x-3}{35}+\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{7}\) không lớn hơn \(\dfrac{x^2}{7}-\dfrac{2x-3}{5}\) thì
\(\dfrac{2x-3}{35}+\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{7}< =\dfrac{x^2}{7}-\dfrac{2x-3}{5}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x-3+5x\left(x-2\right)}{35}< =\dfrac{5x^2-7\cdot\left(2x-3\right)}{35}\)
=>\(2x-3+5x^2-10x< =5x^2-14x+21\)
=>-8x-3<=-14x+21
=>6x<=24
=>x<=4

a. \(x\ne5\) là ĐKXĐ của biểu thức P
b. P =\(\dfrac{\left(x-5\right)^2}{x-5}\)=\(x-5\)
c. P = -1 <=> x-5 =-1 <=> x=4
a) \(\dfrac{5-2x}{6}>\dfrac{5x-2}{3}\\ < =>\dfrac{5-2x}{6}>\dfrac{10x-4}{6}\\ < =>5-2x>10x-4\\ < =>-2x-10x>-4-5\\ < =>-12x>-9\\ =>x< \dfrac{-9}{-12}\\ < =>x< \dfrac{3}{4}\)
Vậy: Tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là S= \(\left\{x|x< \dfrac{3}{4}\right\}\)
b) \(\dfrac{1,5-x}{5}< \dfrac{4x+5}{2}\\ < =>\dfrac{3-2x}{10}< \dfrac{20x+25}{10}\\ < =>3-2x< 20x+25\\ < =>-2x-20x< 25-3\\ < =>-22x< 22\\ =>x>\dfrac{22}{-22}\\ < =>x>-1\)
Vậy: tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là S= \(\left\{x|x>-1\right\}\)