Giải phương trình : \(|\)3x^2 - 3x + 1 \(|\)= 1- 2x.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(a,2x\left(x-5\right)+4\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(2x+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\2x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\2x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{5;-2\right\}\)
\(b,3x-15=2x\left(x-5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow3\left(x-5\right)-2x\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(-2x+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\-2x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\2x=3\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{5;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
\(c,\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)=\left(5x-8\right)\left(2x+1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)-\left(5x-8\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2-5x+8\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(-2x+6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=0\\-2x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=-1\\2x=6\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};3\right\}\)
Câu d xem lại đề

Điều kiện xác định: x ≠ 1; x ≠ 2; x ≠ 3.
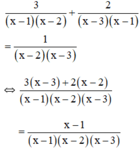
⇒ 3(x – 3) + 2(x – 2) = x – 1
⇔ 3x – 9 + 2x – 4 = x – 1
⇔ 3x + 2x – x = 9 + 4 – 1
⇔ 4x = 12
⇔ x = 3 (không thỏa mãn điều kiện xác định)
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm.

Bạn coi lại đề xem có sai không chứ nghiệm giải ra xấu cực. Và phương trình không rút gọn hết nghe cũng rất vô lý.
dạ vâng,em cx không bt có sai ko do đây là đề của thầy em đưa,chắc cx có sai sót mong thầy bỏ qua

a: =>3x=-9
hay x=-3
b: =>3x=2
hay x=2/3
c: =>2x=4
hay x=2
d: =>-2x=-6
hay x=3
e: =>0,5x=1
hay x=2
f: =>0,6x=3,6
hay x=6
g: =>2/3x=4/3
hay x=2
h: =>-3x+3=6x+2
=>-9x=-1
hay x=1/9
i: =>4x-2x=1+3
=>2x=4
hay x=2
\(A.3x+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=-9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)
\(B.3x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(C.4-2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4=2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
\(D.-2x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6=2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
\(E.0,5x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0,5x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
\(F.3,6-0,6x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3,6=0,6x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=6\)
\(G.\dfrac{2}{3}x-1=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2}{3}x=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
\(H.-\dfrac{1}{3}x+1=\dfrac{2}{3}x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4=x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=4\)
\(I.4x-3=2x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)

Đặt \(2x^2-3x+1=t\Rightarrow2x^2-3x-9=t-10\)
Phương trình trở thành:
\(t\left(t-10\right)=-9\Leftrightarrow t^2-10t+9=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=1\\t=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x^2-3x+1=1\\2x^2-3x+1=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x^2-3x=0\\2x^2-3x-8=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\) (bấm máy)

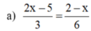
![]()
⇔ 4x - 10 = 2 - x
⇔ 4x + x = 2 + 10 ⇔ 5x = 12 ⇔ x = 12/5
Vậy: S = {12/5}
b) (3x + 1) = (3x + 1)2
⇔ (3x + 1)2 - (3x + 1) = 0
⇔ (3x + 1)[(3x + 1) - 1] = 0
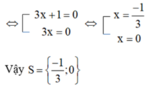
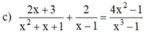
ĐKXĐ:x ≠ 1
Quy đồng mẫu hai vế của phương trình ta được:
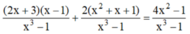
Khử mẫu hai vế, ta được:
(2x + 3)(x - 1) + 2(x2 + x + 1) = 4x2 - 1
⇔ 2x2 + x - 3 + 2x2 + 2x + 2 = 4x2 - 1
⇔ 3x - 1 = -1
⇔ 3x = 0 ⇔ x = 0 (thỏa mãn điều kiện)
Vậy: S = {0}

1/ ( x-1) (2x+1) =0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\2x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-0,5\end{matrix}\right.\)
2/ x (2x-1) (3x+15) =0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\2x-1=0\\3x+15=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=0,5\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
3/ (2x-6) (3x+4).x=0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-6=0\\3x+4=0\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
4/ (2x-10)(x2+1)=0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-10=0\\x^2+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x^2=-1\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
5/ (x2+3) (2x-1) =0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2+3=0\\2x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2=-3\left(loại\right)\\x=0,5\end{matrix}\right.\)
6/ (3x-1) (2x2 +1)=0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=0\\2x^2+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\x^2=-0,5\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
1: Ta có: \(\left(x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\2x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
2: Ta có: \(x\left(2x-1\right)\left(3x+15\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\2x-1=0\\3x+15=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
3: Ta có: \(\left(2x-6\right)\left(3x+4\right)x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-6=0\\3x+4=0\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)

Di chuyển tất cả các số hạng sang vế trái và đặt = 0. Sau đó đặt mỗi nhân tử = 0 (như cách tìm nghiệm)
\(\Rightarrow x=2;-\frac{17}{6};-\frac{5-i\sqrt{831}}{12};-\frac{5+i\sqrt{831}}{12}\)

Nhận thấy :
\(3x^2-3x+1=3\left(x^2-x\right)+1=3\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2-\frac{3}{4}+1=3\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{1}{4}>0\)
Nên phương trình trên
<=> \(3x^2-3x+1=1-2x\)
<=> \(3x^2-x=0\)
<=> \(x\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy .................
Để phương trình trên có nghiệm thì \(1-2x\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\le\frac{1}{2}\)
Ta có: \(3x^2-3x+1=3\left(x^2-x+\frac{1}{4}\right)+\frac{1}{4}=3\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{1}{4}\ge\frac{1}{4}>0\)
Vậy nên \(\left|3x^2-3x+1\right|=3x^2-3x+1\)
Phương trình trở thành:
\(3x^2-3x+1=1-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\3x-1=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}\left(tmđk\right)\)
Vậy phương trình có 2 nghiệm x = 0 hoặc \(x=\frac{1}{3}.\)