
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(a,2x\left(x-5\right)+4\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(2x+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\2x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\2x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{5;-2\right\}\)
\(b,3x-15=2x\left(x-5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow3\left(x-5\right)-2x\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(-2x+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\-2x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\2x=3\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{5;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
\(c,\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)=\left(5x-8\right)\left(2x+1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)-\left(5x-8\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2-5x+8\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(-2x+6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=0\\-2x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=-1\\2x=6\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};3\right\}\)
Câu d xem lại đề

Điều kiện xác định: x ≠ 1; x ≠ 2; x ≠ 3.
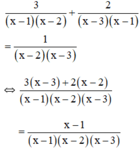
⇒ 3(x – 3) + 2(x – 2) = x – 1
⇔ 3x – 9 + 2x – 4 = x – 1
⇔ 3x + 2x – x = 9 + 4 – 1
⇔ 4x = 12
⇔ x = 3 (không thỏa mãn điều kiện xác định)
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm.

a: =>3x=-9
hay x=-3
b: =>3x=2
hay x=2/3
c: =>2x=4
hay x=2
d: =>-2x=-6
hay x=3
e: =>0,5x=1
hay x=2
f: =>0,6x=3,6
hay x=6
g: =>2/3x=4/3
hay x=2
h: =>-3x+3=6x+2
=>-9x=-1
hay x=1/9
i: =>4x-2x=1+3
=>2x=4
hay x=2
\(A.3x+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=-9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)
\(B.3x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(C.4-2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4=2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
\(D.-2x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6=2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
\(E.0,5x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0,5x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
\(F.3,6-0,6x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3,6=0,6x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=6\)
\(G.\dfrac{2}{3}x-1=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2}{3}x=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
\(H.-\dfrac{1}{3}x+1=\dfrac{2}{3}x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4=x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=4\)
\(I.4x-3=2x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)

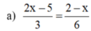
![]()
⇔ 4x - 10 = 2 - x
⇔ 4x + x = 2 + 10 ⇔ 5x = 12 ⇔ x = 12/5
Vậy: S = {12/5}
b) (3x + 1) = (3x + 1)2
⇔ (3x + 1)2 - (3x + 1) = 0
⇔ (3x + 1)[(3x + 1) - 1] = 0
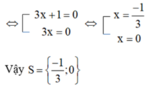
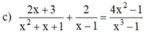
ĐKXĐ:x ≠ 1
Quy đồng mẫu hai vế của phương trình ta được:
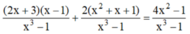
Khử mẫu hai vế, ta được:
(2x + 3)(x - 1) + 2(x2 + x + 1) = 4x2 - 1
⇔ 2x2 + x - 3 + 2x2 + 2x + 2 = 4x2 - 1
⇔ 3x - 1 = -1
⇔ 3x = 0 ⇔ x = 0 (thỏa mãn điều kiện)
Vậy: S = {0}

1/ ( x-1) (2x+1) =0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\2x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-0,5\end{matrix}\right.\)
2/ x (2x-1) (3x+15) =0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\2x-1=0\\3x+15=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=0,5\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
3/ (2x-6) (3x+4).x=0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-6=0\\3x+4=0\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
4/ (2x-10)(x2+1)=0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-10=0\\x^2+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x^2=-1\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
5/ (x2+3) (2x-1) =0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2+3=0\\2x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2=-3\left(loại\right)\\x=0,5\end{matrix}\right.\)
6/ (3x-1) (2x2 +1)=0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=0\\2x^2+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\x^2=-0,5\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
1: Ta có: \(\left(x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\2x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
2: Ta có: \(x\left(2x-1\right)\left(3x+15\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\2x-1=0\\3x+15=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
3: Ta có: \(\left(2x-6\right)\left(3x+4\right)x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-6=0\\3x+4=0\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)


Casio fx 570Vn PLUS lấy ra mà tình nghiệm
Có 1 nghiện là 0,5 tự tìm tiếp

a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-1;0\right\}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{x+3}{x+1}+\dfrac{x-2}{x}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(x+3\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
Suy ra: \(x^2+3x+x^2-3x+2=2x^2+2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+2-2x^2-2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x=-2\)
hay x=1(nhận)
Vậy: S={1}
b) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-7;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{3x-2}{x+7}=\dfrac{6x+1}{2x-3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-2\right)\left(2x-3\right)=\left(6x+1\right)\left(x+7\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-9x-4x+6=6x^2+42x+x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-13x+6-6x^2-43x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-56x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-56x=1\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{1}{56}\)(nhận)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{1}{56}\right\}\)
c) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{5}{3x+2}=2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5=\left(3x+2\right)\left(2x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-3x+4x-2-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2+x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-6x+7x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x\left(x-1\right)+7\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(6x+7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\6x+7=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\6x=-7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\left(nhận\right)\\x=-\dfrac{7}{6}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{1;-\dfrac{7}{6}\right\}\)
d) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\dfrac{2}{7}\)
Ta có: \(\left(2x+3\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{3x+8}{2-7x}+1\right)=\left(x-5\right)\left(\dfrac{3x+8}{2-7x}+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+3\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{3x+8+2-7x}{2-7x}\right)-\left(x-5\right)\left(\dfrac{3x+8+2-7x}{2-7x}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+3-x+5\right)\cdot\dfrac{-4x+6}{2-7x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+8\right)\cdot\left(-4x+6\right)=0\)(Vì \(2-7x\ne0\forall x\) thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+8=0\\-4x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-8\\-4x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-8\left(nhận\right)\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-8;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)

\(a,\dfrac{x-3}{x}=\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}\)\(\left(đk:x\ne0,-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-3}{x}-\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9-x^2+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(n\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
\(b,\dfrac{4x-3}{4}>\dfrac{3x-5}{3}-\dfrac{2x-7}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x-3}{4}-\dfrac{3x-5}{3}+\dfrac{2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(4x-3\right)-4\left(3x-5\right)+2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-9-12x+20+2x-7>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x>-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-2\)

(2x + 1)(3x – 2) = (5x – 8)(2x + 1)
⇔ (2x + 1)(3x – 2) – (5x – 8)(2x + 1) = 0
⇔ (2x + 1).[(3x – 2) – (5x – 8)] = 0
⇔ (2x + 1).(3x – 2 – 5x + 8) = 0
⇔ (2x + 1)(6 – 2x) = 0
⇔ 2x + 1 = 0 hoặc 6 – 2x = 0
+ 2x + 1 = 0 ⇔ 2x = -1 ⇔ x = -1/2.
+ 6 – 2x = 0 ⇔ 6 = 2x ⇔ x = 3.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 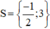
Nhận thấy :
\(3x^2-3x+1=3\left(x^2-x\right)+1=3\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2-\frac{3}{4}+1=3\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{1}{4}>0\)
Nên phương trình trên
<=> \(3x^2-3x+1=1-2x\)
<=> \(3x^2-x=0\)
<=> \(x\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy .................
Để phương trình trên có nghiệm thì \(1-2x\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\le\frac{1}{2}\)
Ta có: \(3x^2-3x+1=3\left(x^2-x+\frac{1}{4}\right)+\frac{1}{4}=3\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{1}{4}\ge\frac{1}{4}>0\)
Vậy nên \(\left|3x^2-3x+1\right|=3x^2-3x+1\)
Phương trình trở thành:
\(3x^2-3x+1=1-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\3x-1=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}\left(tmđk\right)\)
Vậy phương trình có 2 nghiệm x = 0 hoặc \(x=\frac{1}{3}.\)