Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

1:
a: 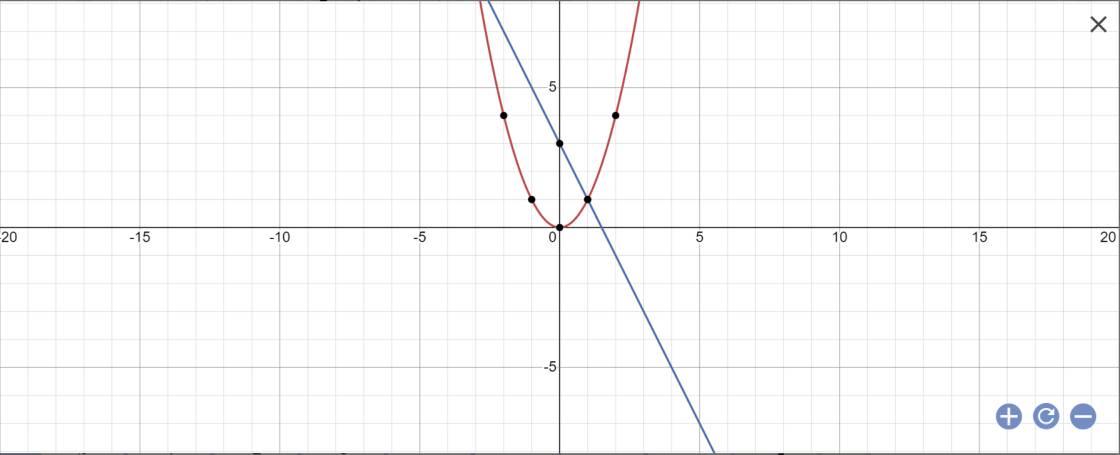
b: PTHĐGĐ là:
x^2+2x-3=0
=>(x+3)(x-1)=0
=>x=-3 hoặc x=1
=>y=9 hoặc y=1

Bạn tự vẽ nhé.
\(a,\) 2 đồ thị hàm số \(y=2x,y=-3x+5\) giao nhau khi và chỉ khi :
\(2x=-3x+5\\ \Leftrightarrow5x=5\\ \Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Thay \(x=1\) vào \(y=2x\Leftrightarrow y=2\)
Vậy giao điểm của 2 đồ thị là \(\left(1;2\right)\)
\(b,\) 2 đồ thị hàm số \(y=3x+2,y=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+1\) giao nhau khi và chỉ khi :
\(3x+2=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+1\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{7}{2}x=-1\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{2}{7}\)
Thay \(x=-\dfrac{2}{7}\) vào \(y=3x+2\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{8}{7}\)
Vậy giao điểm của 2 đồ thị là \(\left(-\dfrac{2}{7};\dfrac{8}{7}\right)\)
\(c,\) 2 đồ thị hàm số \(y=\dfrac{3}{2}x-2,y=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+2\) giao nhau khi và chỉ khi :
\(\dfrac{3}{2}x-2=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+2\\ \Leftrightarrow2x=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Thay \(x=2\) vào \(y=\dfrac{3}{2}x-2\Rightarrow y=1\)
Vậy giao điểm của 2 đồ thị là \(\left(2;1\right)\)
\(d,\) 2 đồ thị hàm số \(y=-2x+5,y=x+2\) giao nhau khi và chỉ khi :
\(-2x+5=x+2\\ \Leftrightarrow-3x=-3\\ \Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Thay \(x=1\) vào \(y=x+2\Rightarrow y=3\)
Vậy giao điểm của 2 đồ thị là \(\left(1;3\right)\)

b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(\dfrac{-1}{2}x^2-4x+16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}+4x-16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+8x-32=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)^2=48\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\sqrt{3}-4\\x=-4\sqrt{3}-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi \(x=4\sqrt{3}-4\) thì \(y=\dfrac{-1}{2}\cdot\left(4\sqrt{3}-4\right)^2=-32+16\sqrt{3}\)
Khi \(x=-4\sqrt{3}-4\) thì \(y=\dfrac{-1}{2}\left(-4\sqrt{3}-4\right)^2=-32-16\sqrt{3}\)
b: Để hai đường song song thì
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-1=-1\\m+3< >1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow m=0\)
a) Vẽ:
(d): \(y=\dfrac{3}{2}x-1\)
(d'): \(y=\dfrac{2}{3}x+1\)
b) Tìm tọa độ giao điểm A của (d) và (d')

b: Tọa độ giao điểm là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{2}x-1=\dfrac{2}{3}x+1\\y=\dfrac{2}{3}x+1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{12}{5}\\y=\dfrac{13}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a, bạn tự vẽ
b, Hoành độ giao điểm tm pt
\(\dfrac{x^2}{2}=\dfrac{x}{2}+3\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-6=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=3;x=-2\)
hay \(x_A=3;x_B=-2\)
\(\Rightarrow y_A=\dfrac{9}{2};y_B=2\)
Vậy (P) cắt (d) tại A(3;9/2) ; B(-2;2)
c, Ta có \(AB=\sqrt{\left(x_A-x_B\right)^2+\left(y_A-y_B\right)^2}=\dfrac{5\sqrt{5}}{2}\)
Theo Pytago ta có \(OA=\sqrt{\left(\dfrac{9}{2}\right)^2+3^2}=\dfrac{3\sqrt{13}}{2}\)
Theo Pytago ta có \(OB=\sqrt{2^2+2^2}=2\sqrt{2}\)
Chu vi tam giác ABC là
\(AB+OA+OB=\dfrac{5\sqrt{5}+3\sqrt{13}+4\sqrt{2}}{2}\)

Lời giải:
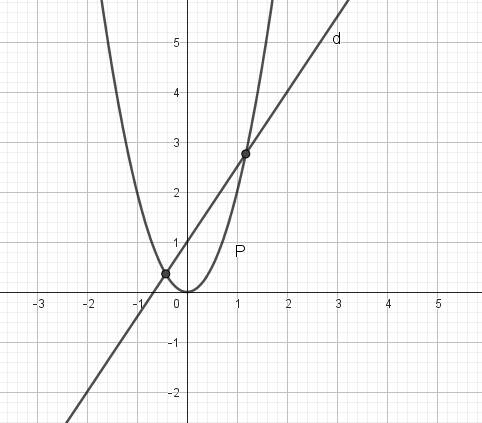
b. PT hoành độ giao điểm:
$2x^2=\frac{3}{2}x+1$
$\Leftrightarrow 4x^2-3x-2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{3\pm \sqrt{41}}{8}$
$x=\frac{3+\sqrt{41}}{8}\Rightarrow y=\frac{3}{2}x+1=\frac{25+3\sqrt{41}}{16}$. Ta có giao điểm $(\frac{3+\sqrt{41}}{8}; \frac{25+3\sqrt{41}}{16})$
$x=\frac{3-\sqrt{41}}{8}\Rightarrow y=\frac{25-3\sqrt{41}}{16}$. Ta có giao điểm $(\frac{3-\sqrt{41}}{8}; \frac{25-3\sqrt{41}}{16})$

\(\text{PT hoành độ giao điểm: }-\dfrac{2}{3}x+1=\dfrac{3}{2}x-3\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{13}{6}x=4\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{24}{13}\Leftrightarrow y=-\dfrac{3}{13}\Leftrightarrow A\left(\dfrac{24}{13};-\dfrac{3}{13}\right)\\ \text{Vậy giao điểm 2 đths là }A\left(\dfrac{24}{13};-\dfrac{3}{13}\right)\)

PT hoành độ giao điểm: \(-2x+3=\dfrac{1}{2}x-3\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5}{2}x=6\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{12}{5}\Leftrightarrow y=-\dfrac{9}{5}\Leftrightarrow A\left(\dfrac{12}{5};-\dfrac{9}{5}\right)\)
Vậy \(A\left(\dfrac{12}{5};-\dfrac{9}{5}\right)\) là giao điểm 2 đths
Xét ptr hoành độ của `(P)` và `(D)` có:
`x^2/3=2x-3`
`<=>x^2=6x-9`
`<=>x^2-6x+9=0`
`<=>(x-3)^2=0`
`<=>x-3=0<=>x=3`
`=>y=2.3-3=3`
Vậy tọa độ giao điểm của `(P)` và `(D)` là: `(3;3)`