Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(x+2=x\sqrt{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\cdot\left(1-\sqrt{3}\right)=-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\sqrt{3}+1\)
Thay \(x=\sqrt{3}+1\) vào (d'), ta được:
\(y=\sqrt{3}\left(\sqrt{3}+1\right)=3+\sqrt{3}\)

a)
\(\left(P\right):y=x^2\)
Ta có bảng
| x | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| y | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 |
Vậy đồ thị hàm số \(y=x^2\) là một parabol lần lượt đi qua các điểm
\(\left(-2;4\right),\left(-1;1\right),\left(0;0\right),\left(1;1\right),\left(2;4\right)\)
Bạn tự vẽ nhé
\(\left(d\right):y=-2x+3\)
Cho \(y=0\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}\Rightarrow A\left(\dfrac{3}{2};0\right)\in Ox\)
Cho \(x=0\Rightarrow y=3\Rightarrow B\left(0;3\right)\in Oy\)
Vẽ đường thẳng AB ta được đths \(y=-2x+3\)
Bạn tự bổ sung vào hình vẽ nhé
b) Xét PTHĐGĐ của \(\left(P\right),\left(d\right)\) là nghiệm của phương trình
\(x^2=-2x+3\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-3=0\)
Xét \(a+b+c=1+2-3=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Với `x=1 => y=x^2 = 1`
Với `x=2 => y=x^2 = 4`
Vậy tọa độ giao điểm của \(\left(P\right),\left(d\right)\) là 2 điểm \(\left(1;1\right)\) và \(\left(2;4\right)\)

\(a,-1< 0\Leftrightarrow\left(d'\right)\text{ nghịch biến trên }R\\ b,\text{PT hoành độ giao điểm: }x=-x+2\Leftrightarrow x=1\Leftrightarrow y=1\Leftrightarrow A\left(1;1\right)\\ \text{Vậy }A\left(1;1\right)\text{ là giao 2 đths}\\ c,\text{3 đt đồng quy }\Leftrightarrow A\left(1;1\right)\in\left(d''\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow m-1+2m=1\\ \Leftrightarrow3m=2\Leftrightarrow m=\dfrac{2}{3}\)

a: 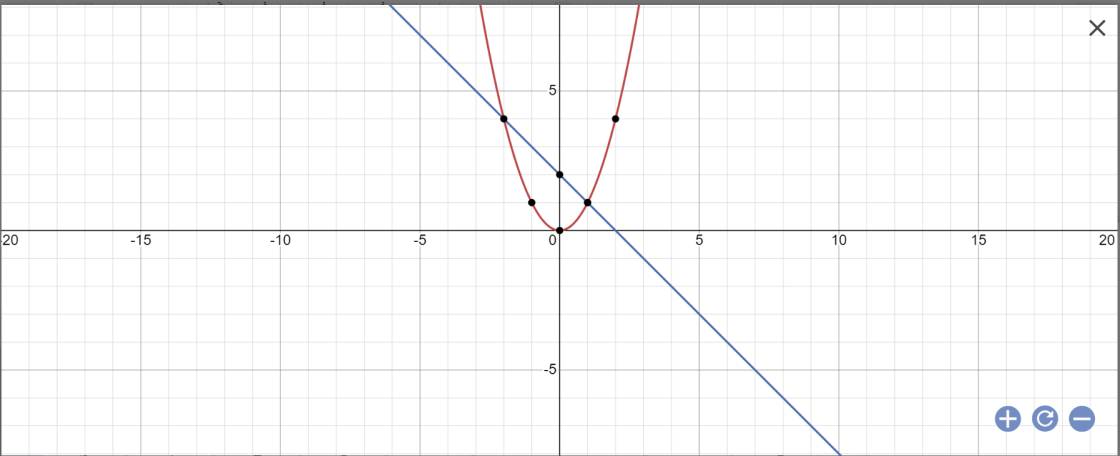
b: PTHĐGĐ là:
x^2+x-2=0
=>(x+2)(x-1)=0
=>x=-2 hoặc x=1
=>y=4 hoặc y=1

a) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(d\right):y=-2x-5\\\left(d'\right):y=-x\end{matrix}\right.\)
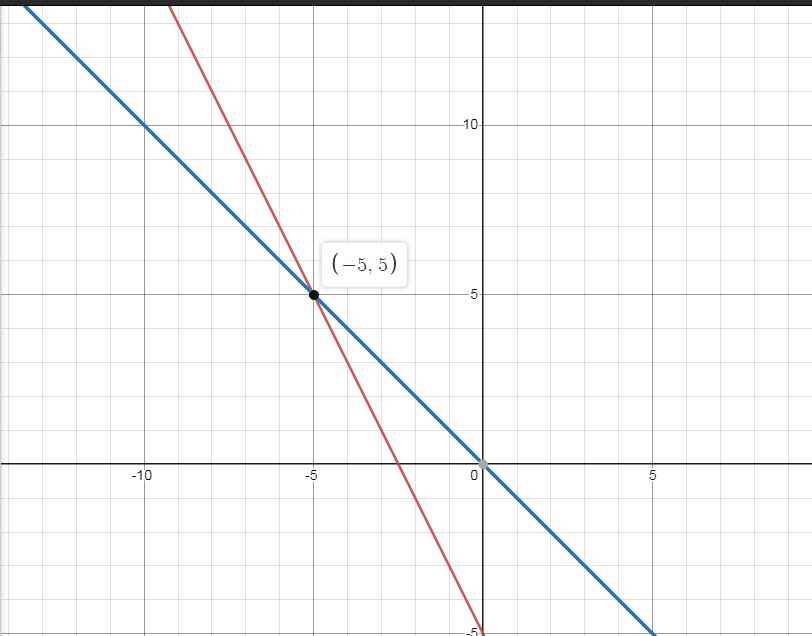
b) \(\left(d\right)\cap\left(d'\right)=M\left(x;y\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-2x-5\\y=-x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x=-2x-5\\y=-x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-5\\y=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow M\left(-5;5\right)\)
c) Gọi \(\widehat{M}=sđ\left(d;d'\right)\)
\(\left(d\right):y=-2x-5\Rightarrow k_1-2\)
\(\left(d'\right):y=-x\Rightarrow k_1-1\)
\(tan\widehat{M}=\left|\dfrac{k_1-k_2}{1+k_1.k_2}\right|=\left|\dfrac{-2+1}{1+\left(-2\right).\left(-1\right)}\right|=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{M}\sim18^o\)
d) \(\left(d\right)\cap Oy=A\left(0;y\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y=-2.0-5=-5\)
\(\Rightarrow A\left(0;-5\right)\)
\(OA=\sqrt[]{0^2+\left(-5\right)^2}=5\left(cm\right)\)
\(OM=\sqrt[]{5^2+5^2}=5\sqrt[]{2}\left(cm\right)\)
\(MA=\sqrt[]{5^2+10^2}=5\sqrt[]{5}\left(cm\right)\)
Chu vi \(\Delta MOA:\)
\(C=OA+OB+MA=5+5\sqrt[]{2}+5\sqrt[]{5}=5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}\right)\left(cm\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow p=\dfrac{C}{2}=\dfrac{5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{2}\left(cm\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}p-OA=\dfrac{5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{2}-5=\dfrac{5\left(\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}-1\right)}{2}\\p-OB=\dfrac{5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{2}-5\sqrt[]{2}=\dfrac{5\left(-\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}+1\right)}{2}\\p-MA=\dfrac{5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{2}-5\sqrt[]{5}=\dfrac{5\left(\sqrt[]{2}-\sqrt[]{5}+1\right)}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(p\left(p-MA\right)=\dfrac{5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{2}.\dfrac{5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}-\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow p\left(p-MA\right)=\dfrac{25\left[\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}\right)^2-5\right]}{4}=\dfrac{25.2\left(\sqrt[]{2}-1\right)}{4}=\dfrac{25\left(\sqrt[]{2}-1\right)}{2}\)
\(\left(p-OA\right)\left(p-OB\right)=\dfrac{25\left[5-\left(\sqrt[]{2}-1\right)^2\right]}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(p-OA\right)\left(p-OB\right)=\dfrac{25.2\left(\sqrt[]{2}+1\right)}{4}=\dfrac{25\left(\sqrt[]{2}+1\right)}{4}\)
Diện tích \(\Delta MOA:\)
\(S=\sqrt[]{p\left(p-OA\right)\left(p-OB\right)\left(p-MA\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow S=\sqrt[]{\dfrac{25\left(\sqrt[]{2}-1\right)}{2}.\dfrac{25\left(\sqrt[]{2}+1\right)}{2}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow S=\sqrt[]{\dfrac{25^2}{2^2}}=\dfrac{25}{2}=12,5\left(cm^2\right)\)

1: Để (d)//(d') thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-3=1\\2\ne-5\left(đúng\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>m-3=1
=>m=4
Thay m=4 vào (d), ta được:
\(y=\left(4-3\right)x+2=x+2\)
Vẽ đồ thị:
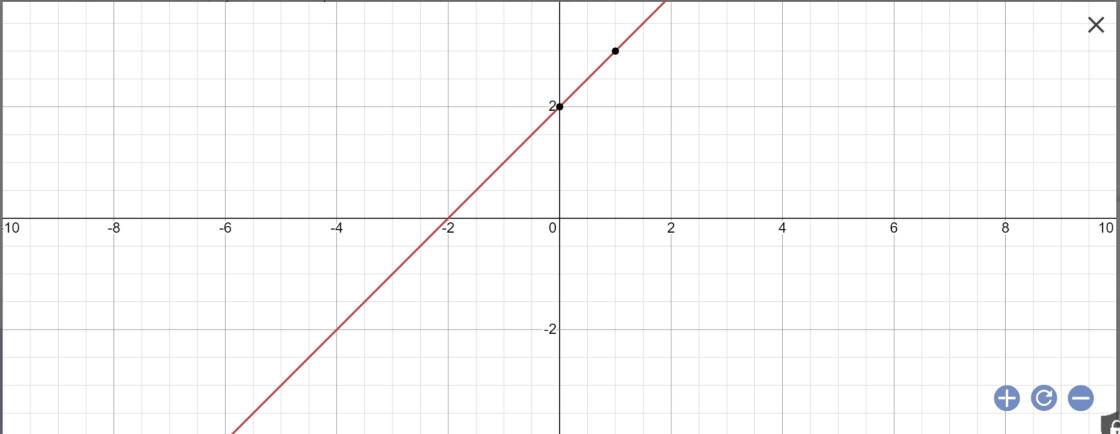
2: Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\left(m-3\right)x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x\left(m-3\right)=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{2}{m-3}\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(A\left(-\dfrac{2}{m-3};0\right)\)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=\left(m-3\right)\cdot x+2=0\left(m-3\right)+2=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy: B(0;2)
\(OA=\sqrt{\left(-\dfrac{2}{m-3}-0\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}\)
\(=\sqrt{\left(-\dfrac{2}{m-3}\right)^2+0^2}=\dfrac{2}{\left|m-3\right|}\)
\(OB=\sqrt{\left(0-0\right)^2+\left(2-0\right)^2}=2\)
Vì Ox\(\perp\)Oy
nên OA\(\perp\)OB
=>ΔOAB vuông tại O
=>\(S_{OBA}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot OA\cdot OB=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot2\cdot\dfrac{2}{\left|m-3\right|}=\dfrac{2}{\left|m-3\right|}\)
Để \(S_{OAB}=2\) thì \(\dfrac{2}{\left|m-3\right|}=2\)
=>|m-3|=1
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}m-3=1\\m-3=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=4\\m=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
t học lớp 8 bạn ei :)