
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



Lời giải:
1. $|x-1|-|5-x|=0$
$\Leftrightarrow |x-1|=|5-x|$
$\Leftrightarrow x-1=5-x$ hoặc $x-1=x-5$
$\Leftrightarrow x=3$ hoặc $1=5$ (vô lý)
Vậy $x=3$
---------------------------
2.
Nếu $x\geq 4$ thì pt trở thành:
$x-4+x-\frac{3}{2}=5$
$\Leftrightarrow x=5,25$ (thỏa mãn)
Nếu $\frac{3}{2}\leq x< 4$ thì:
$4-x+x-\frac{3}{2}=5\Leftrightarrow \frac{5}{2}=5$ (vô lý)
Nếu $x< \frac{3}{2}$ thì:
$4-x+\frac{3}{2}-x=5$
$\Leftrightarrow x=0,25$ (thỏa mãn)

cậu cho mk xin link facebook của jonathan galindo đi rồi mk sẽ trả lời câu hỏi của cậu

a)
`4(x-2)^2 =4`
`<=>(x-2)^2 =1`
`<=>x-2=1` hoặc `x-2=-1`
`<=>x=3` hoặc `x=1`
b)
`5(x^2 -6x+9)=5`
`<=>(x-3)^2 =1`
`<=>x-3=1`hoặc `x-3=-1`
`<=>x=4` hoặc `x=2`
c)
`4x^2 +4x+1=0`
`<=>(2x+1)^2 =0`
`<=>2x+1=0`
`<=>x=-1/2`
d)
`9x^2 +6x+1=2`
`<=>(3x+1)^2 =2`
\(< =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+1=\sqrt{2}\\3x+1=-\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{3}\\x=\dfrac{-\sqrt{2}-1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(a,\Leftrightarrow x-1=4\Leftrightarrow x=5\\ b,\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\\3x+1=4x-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\\x=4\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=4\\ c,ĐK:x\ge-5\\ PT\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{x+5}-3\sqrt{x+5}+4\sqrt{x+5}=6\\ \Leftrightarrow3\sqrt{x+5}=6\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x+5}=3\\ \Leftrightarrow x+5=9\\ \Leftrightarrow x=4\left(tm\right)\)
\(d,\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)^2}=\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{5}+1\right)^2}\\ \Leftrightarrow\left|x-2\right|=\sqrt{5}+1\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=\sqrt{5}+1\\2-x=\sqrt{5}+1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{5}+3\\x=1-\sqrt{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(R=\left(\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+2}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}-\dfrac{3x-5\sqrt{x}}{4-x}\right):\left(\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}-2}-1\right)\left(ĐK:x\ge0,x\ne4\right)\\ =\left(\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+2}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}+\dfrac{3x-5\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}^2-2^2}\right):\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}-1-\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)+\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)+3x-5\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}.\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{2\sqrt{x}-1-\sqrt{x}+2}\\ =\dfrac{3x-6\sqrt{x}+x+2\sqrt{x}+3x-5\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+2}.\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{7x-9\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
Bạn xem lại đề nhé, rút gọn thường ra kết quả rất đẹp chứ không dài như kết quả này đâu ạ.

ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne1\)
\(x^2+\frac{x^2}{\left(x-1\right)^2}=\frac{5}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x^2\left(x-1\right)^2+x^2}{\left(x-1\right)^2}=\frac{5}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x^4-2x^3+2x^2}{x^2-2x+1}=\frac{5}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x^4-2x^3+2x^2\right).4=5\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^4-8x^3+8x^2-\left(5x^2-10x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^4-8x^3+3x^2+10x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^3\left(x+1\right)-12x^2\left(x+1\right)+15x\left(x+1\right)-5\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(4x^3-12x^2+15x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left[2x^2\left(2x-1\right)-5x\left(2x-1\right)+5\left(2x-1\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x^2-5x+5\right)=0\)
Mà \(2x^2-5x+5=2\left(x-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2+\frac{30}{16}>0\forall x\)
Do đó: \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=0\\2x-1=0\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-1\\x=\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}}\)
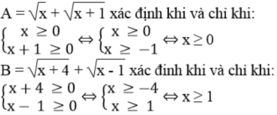
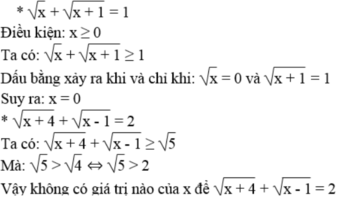
Ta có: 1 - 4 x + 4 x 2 = 5 ⇔ 1 - 2 x 2 = 5
⇔ |1 - 2x| = 5 (3)
* Trường hơp 1: 1 - 2x ≥ 0 ⇔ 2x ≤ 1 ⇔ x ≤ 1/2 ⇒ |1 - 2x| = 1 - 2x
Suy ra: 1 - 2x = 5 ⇔ -2x = 5 - 1 ⇔ x = -2
Giá trị x = -2 thỏa mãn điều kiện x ≤ 1/2
Vậy x = -2 là nghiệm của phương trình (3).
* Trường hợp 2: 1 - 2x < 0 ⇔ 2x > 1 ⇔ x > 12 ⇒ |1 - 2x| = 2x - 1
Suy ra: 2x - 1 = 5 ⇔ 2x = 5 + 1 ⇔ x = 3
Giá trị x = 3 thỏa mãn điều kiện x > 1/2
Vậy x = 3 là nghiệm của phương trình (3).
Vậy x = -2 và x = 3.