
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Ta có \(x^2-7x+8=0\Leftrightarrow x^2-\dfrac{2.7}{2}x+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-7x+\dfrac{49}{4}-\dfrac{49}{4}+8=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\dfrac{7}{2}\right)^2-\dfrac{17}{4}=0\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-\dfrac{7}{2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{17}}{2}\\x-\dfrac{7}{2}=-\dfrac{\sqrt{17}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\sqrt{17}+7}{2}\\x=\dfrac{-\sqrt{17}+7}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Đặt \(x^2-7x+8=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(-7\right)^2-4\cdot1\cdot8=17>0\)
Do đó: Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{7-\sqrt{17}}{2}\\x_2=\dfrac{7+\sqrt{17}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Đặt \(x^2-7x+8=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(-7\right)^2-4\cdot1\cdot8=17>0\)
Do đó: Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{7-\sqrt{17}}{2}\\x_2=\dfrac{7+\sqrt{17}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Đặt \(-16x^2+7x+18=0\)
\(\text{Δ}=7^2-4\cdot\left(-16\right)\cdot18=1201>0\)
Do đó: Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-7-\sqrt{1201}}{-32}=\dfrac{7+\sqrt{1201}}{32}\\x_2=\dfrac{7-\sqrt{1201}}{32}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) Sắp xếp theo lũy thừa giảm dần
P(x)=x^5−3x^2+7x^4−9x^3+x^2−1/4x
=x^5+7x^4−9x^3−3x^2+x^2−1/4x
=x^5+7x^4−9x^3−2x^2−1/4x
Q(x)=5x^4−x^5+x^2−2x^3+3x^2−1/4
=−x^5+5x^4−2x^3+x^2+3x^2−1/4
=−x^5+5x^4−2x^3+4x^2−1/4
b)
P(x)+Q(x)
=(x^5+7x^4−9x^3−2x^2−1/4^x)+(−x^5+5x^4−2x^3+4x^2−1/4)
=x^5+7x^4−9x^3−2x^2−1/4x−x^5+5x^4−2x^3+4x^2−1/4
=(x^5−x^5)+(7x^4+5x^4)+(−9x^3−2x^3)+(−2x^2+4x^2)−1/4x−1/4
=12x^4−11x^3+2x^2−1/4x−1/4
P(x)−Q(x)
=(x^5+7x^4−9x^3−2x^2−1/4x)−(−x^5+5x^4−2x^3+4x^2−1/4)
=x^5+7x^4−9x^3−2x^2−1/4x+x^5−5x^4+2x^3−4x^2+1/4
=(x^5+x^5)+(7x^4−5x^4)+(−9x^3+2x^3)+(−2x^2−4x^2)−1/4x+1/4
=2x5+2x4−7x3−6x2−1/4x−1/4
c) Ta có
P(0)=0^5+7.0^4−9.0^3−2.0^2−1/4.0
⇒x=0là nghiệm của P(x).
Q(0)=−0^5+5.0^4−2.0^3+4.0^2−1/4=−1/4≠0
⇒x=0không phải là nghiệm của Q(x).
Cho 2 đa thức: f(x)= 9 - x5 + 4x - 2x3 + x2 - 7x4
g(x)= x5 - 9 + 2x2 + 7x4 + 2x3 - 3x
a) Sắp sếp các đa thức trên theo luỹ thừa giảm dần của biến
f(x)= 9 - x5 + 4x - 2x3 + x2 - 7x4
f(x) = -x5 - 7x4 - 2x3 + x2 + 4x + 9
g(x)= x5 - 9 + 2x2 + 7x4 + 2x3 - 3x
g(x) = x5 + 7x4 + 2x3 + 2x2 - 3x - 9
b) Tìm bậc, hệ số cao nhất, hệ số tự do của đa thức f(x); g(x)
f(x) = -x5 - 7x4 - 2x3 + x2 + 4x + 9
+ Bậc : 5 _ hệ số cao nhất : -1 _ hệ số tự do : 9
g(x) = x5 + 7x4 + 2x3 + 2x2 - 3x - 9
+ Bậc : 5_ hệ số cao nhất : 1 _ hệ số tự do : -9
c) Tính f(x) + g(x); f(x) - g(x)
f( x) + g(x) = ( -x5 - 7x4 - 2x3 + x2 + 4x + 9 ) +( x5 + 7x4 + 2x3 + 2x2 - 3x - 9 )
= -x5 - 7x4 - 2x3 + x2 + 4x + 9 + x5 + 7x4 + 2x3 + 2x2 - 3x - 9
= ( -x5 + x5 ) + ( -7x4 + 7x4 ) + ( -2x3 + 2x3 ) + ( x2 + 2x2 ) + ( 4x -3x ) + ( 9 - 9 )
= 3x2 + x
f( x) - g(x) = ( -x5 - 7x4 - 2x3 + x2 + 4x + 9 ) - ( x5 + 7x4 + 2x3 + 2x2 - 3x - 9 )
= -x5 - 7x4 - 2x3 + x2 + 4x + 9 - x5 - 7x4 - 2x3 - 2x2 + 3x + 9
= ( -x5 - x5 ) + ( -7x4 - 7x4 ) + ( -2x3 - 2x3 ) + ( x2 - 2x2 ) + ( 4x + 3x ) + ( 9 + 9 )
= -2x5 - 14x4 - 2x3 -x2 + 7x + 18

a, \(P\left(x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{4}{5}\)
Vậy ...
b/ \(Q\left(x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-7x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-7=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ..

\(f\left(x\right)=x2-7x+6\)
ta có f(x)=0
hay\(x2-7x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x2-7x=-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(-5\right)=-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{6}{5}\)
vậy nghiệm của đa thức f(x) là 6/5
\(f\left(x\right)=x^2-7x+6\)
\(f\left(x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x^2-7x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-6x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x.\left(x-1\right)-6.\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right).\left(x-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=0\\x-6=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}z=1\\x=6\end{cases}}\)
Vậy phương trình có 2 nghiệm \(x=\left\{1,6\right\}\)

`x^2 - 3x = 0`
`<=> x.(x-3)=0`
`<=> x = 0` hoặc `x-3=0`
`<=> x = 0 ` hoặc `x = 3`
Vậy `S = { 0;3}`
`2x^2 + 5x = 0`
`<=> x.(2x + 5)=0`
`<=> x = 0` hoặc `2x+5=0`
`<=> x = 0` hoặc `2x= -5`
`<=> x = 0` hoặc `x = -5/2`
Vậy `S = {0; -5/2}`
\(a,x^2-3x=0\\ x\left(x-3\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\\ b,2x^2+5x=0\\ x\left(2x+5\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\2x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
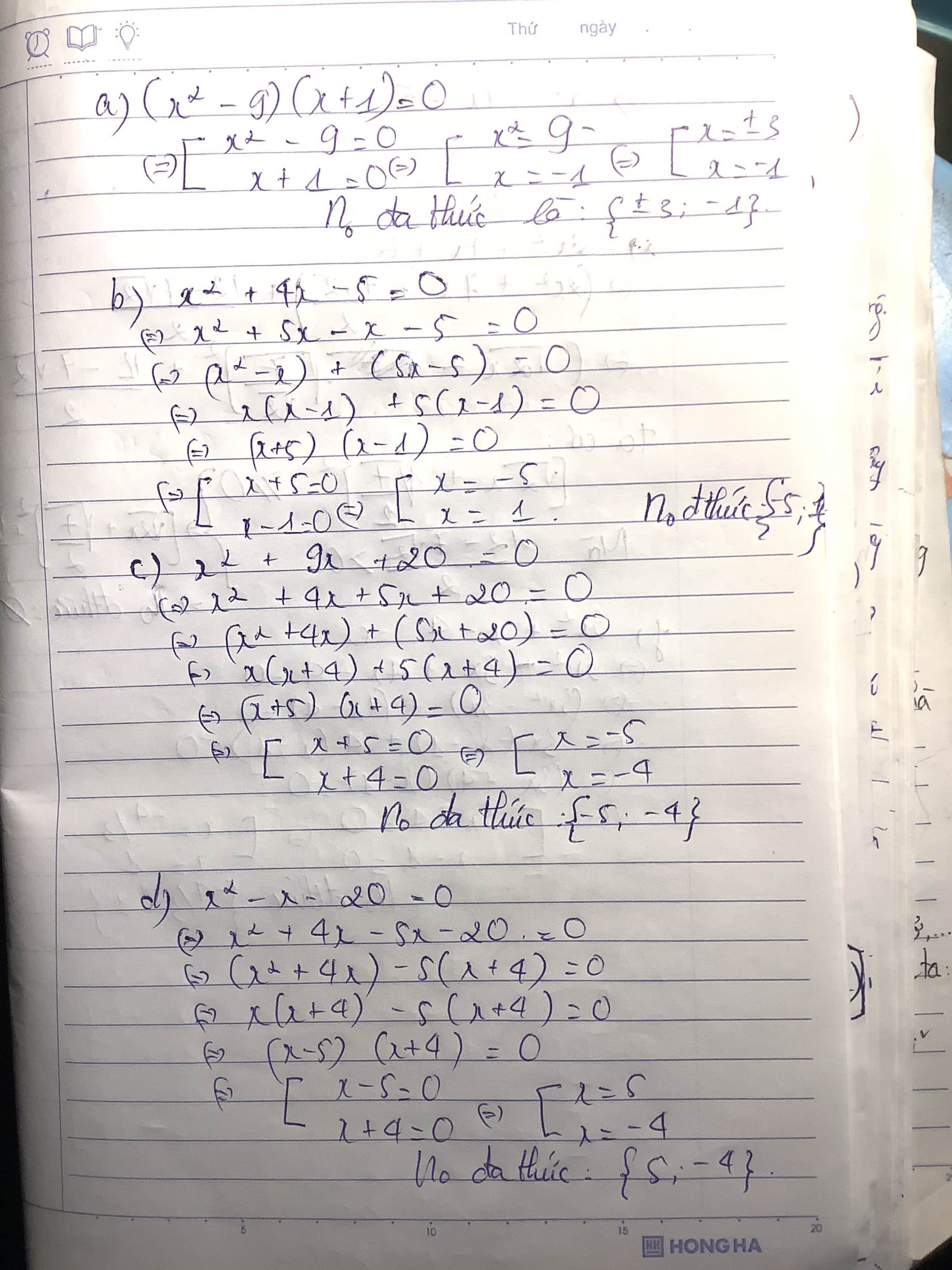

Ta có : \(x^2+5x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x.\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x+5=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=-5\end{cases}}\)
Vậy đa thức trên có 2 nghiệm là x=0 hoặc x=-5
Ta có : \(x^2+7x+12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+3,5\right)^2-0,25=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+3,5\right)^2=0,25\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+3,5=0,5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-3\)
Vậy đa thức trên có 1 nghiệm là x=-3
1) x2 + 5x
Đặt x2 + 5x = 0
=> x.(x + 5) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x+5=0\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=-5\end{cases}}\). Vậy x \(\in\){0 , -5} là nghiệm của x2 + 5x
2) x2 + 7x + 12
Đặt x2 + 7x + 12 = 0
=> x2 + 3x + 4x + 12 = 0
=> x.(x + 3) + 4(x + 3) = 0
=> (x + 3)(x + 4) = 0
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+3=0\\x+4=0\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-3\\x=-4\end{cases}}\).Vậy x \(\in\){-3 , -4} là nghiệm của x2 + 7x + 12
- Đúng 100%