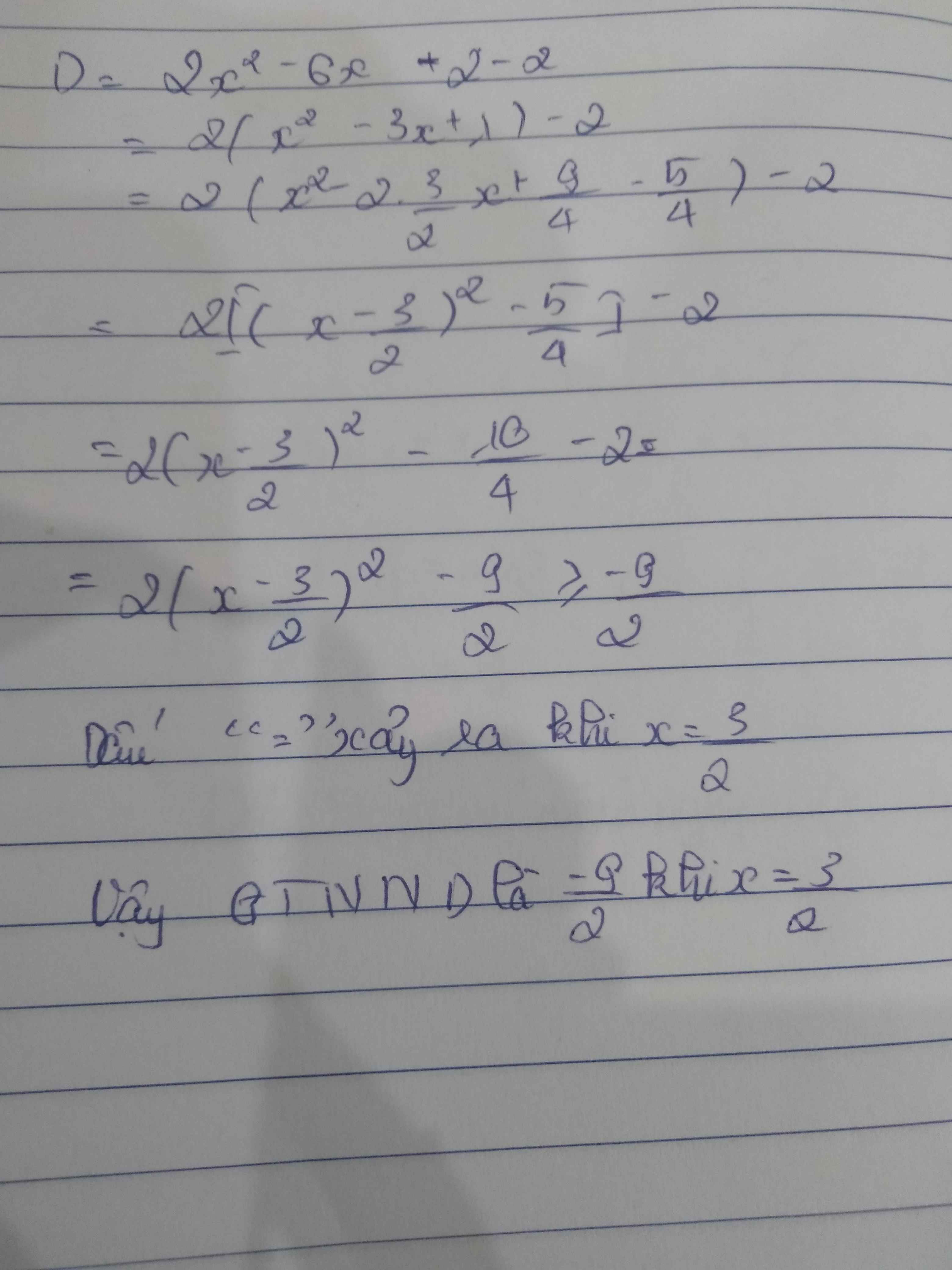Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



D= 2x2 - 6x
= 2(x2 - 3x +\(\dfrac{9}{4}\)) - \(\dfrac{9}{2}\)
= 2[x2 - 2.x.\(\dfrac{3}{2}\) + (\(\dfrac{3}{2}\))2 ] - \(\dfrac{9}{2}\)
= 2 (x - \(\dfrac{3}{2}\))2 - \(\dfrac{9}{2}\)
Ta có:
2(x - \(\dfrac{3}{2}\))2 ≥ 0 ⇒ 2 (x - \(\dfrac{3}{2}\))2 - \(\dfrac{9}{2}\) ≥ -\(\dfrac{9}{2}\)
Hay D≥ -\(\dfrac{9}{2}\)
Dấu = xảy ra ⇔ (x - \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = 0 ⇔ x = \(^{\dfrac{3}{2}}\)
Vậy MinD = - \(\dfrac{9}{2}\) ⇔ x = \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)


a) \(A+B=2x^3+x^2-4x+x^3+3+6x+3x^3-2x+x^2-5\)
\(=6x^3+2x^2-2\)
b) \(A-B=\left(2x^3+x^2-4x+x^3+3\right)-\left(6x+3x^3-2x+x^2-5\right)\)
\(=-8x+8\)
c) Đặt \(f\left(x\right)=-8x+8\)
Ta có: \(f\left(x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow-8x+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-8x=-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Vậy \(x=1\)là nghiệm của đa thức f(x).


b: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)+2\left(x-1\right)=0\)
=>x-1=0
=>x=1
c: \(\Leftrightarrow x^3+x^2+5x^2+5x+6x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+5x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-1;-3;-2\right\}\)

nghiem chung cua hai da thuc la 1
minh doan day, sai thi thoi

Bạn kham khảo tại link:
tìm Min ( x^2 + y^2 ) / xy đk x>= 2y; x,y dương? | Yahoo Hỏi & Đáp
Tìm Min:
\(x=x^2+y^2-y\)
\(\Rightarrow B=\left(x^2+y^2-y\right)-y=x^2+\left(y^2-2y+1\right)-1=x^2+\left(y-1\right)^2-1\ge-1\)
Tìm Max:
\(y=x^2+y^2-x\)
\(\Rightarrow B=x-\left(x^2+y^2-x\right)=-y^2-\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+1=-y^2-\left(x-1\right)^2+1\le1\)