
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(A=\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+4=\left(x-1\right)^2+4\ge4\\ A_{min}=4\Leftrightarrow x=1\\ B=2\left(x^2-3x\right)=2\left(x^2-2\cdot\dfrac{3}{2}x+\dfrac{9}{4}\right)-\dfrac{9}{2}\\ B=2\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2-\dfrac{9}{2}\ge-\dfrac{9}{2}\\ B_{min}=-\dfrac{9}{2}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\ C=-\left(x^2-4x+4\right)+7=-\left(x-2\right)^2+7\le7\\ C_{max}=7\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
a,\(A=x^2-2x+5=\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+4=\left(x-1\right)^2+4\ge4\)
Dấu "=" \(\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
b,\(B=2\left(x^2-3x\right)=2\left(x^2-3x+\dfrac{9}{4}\right)-\dfrac{9}{2}=2\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2-\dfrac{9}{2}\ge-\dfrac{9}{2}\)
Dấu "=" \(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
c,\(=C=-\left(x^2-4x-3\right)=-\left[\left(x^2-4x+4\right)-7\right]=-\left(x-2\right)^2+7\le7\)
Dấu "=" \(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)

1, Ta có: 3-x2+2x=-(x2-2x+1)+4=-(x-1)2+4
vì (x-1)2 luôn lớn hơn hoặc bằng không với mọi x-->-(x-1)2 nhỏ hơn hoặc bằng 0 với mọi x
vậy giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức 3-x2+2x là 4
các bài giá trị nhỏ nhất còn lại làm tương tự bạn nhé
chỉ cần đưa về nhân tử chung hoặc hằng đẳng thức là được

A = x2 - 2x + 9 = ( x2 - 2x + 1 ) + 8 = ( x - 1 )2 + 8 ≥ 8 ∀ x
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x = 1
=> MinA = 8 <=> x = 1
B = x2 + 6x - 3 = ( x2 + 6x + 9 ) - 12 = ( x + 3 )2 - 12 ≥ -12 ∀ x
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x = -3
=> MinB = -12 <=> x = -3
C = ( x - 1 )( x - 3 ) + 9 = x2 - 4x + 3 + 9 = ( x2 - 4x + 4 ) + 8 = ( x - 2 )2 + 8 ≥ 8 ∀ x
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x = 2
=> MinC = 8 <=> x = 2
D = -x2 - 4x + 7 = -( x2 + 4x + 4 ) + 11 = -( x + 2 )2 + 11 ≤ 11 ∀ x
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x = -2
=> MaxD = 11 <=> x = -2

a, \(A=-x^2-2x+3=-\left(x^2+2x-3\right)=-\left(x^2+2x+1-4\right)\)
\(=-\left(x+1\right)^2+4\le4\)
Dấu ''='' xảy ra khi x = -1
Vậy GTLN là 4 khi x = -1
b, \(B=-4x^2+4x-3=-\left(4x^2-4x+3\right)=-\left(4x^2-4x+1+2\right)\)
\(=-\left(2x-1\right)^2-2\le-2\)
Dấu ''='' xảy ra khi x = 1/2
Vậy GTLN B là -2 khi x = 1/2
c, \(C=-x^2+6x-15=-\left(x^2-2x+15\right)=-\left(x^2-2x+1+14\right)\)
\(=-\left(x-1\right)^2-14\le-14\)
Vâỵ GTLN C là -14 khi x = 1
Bài 8 :
b, \(B=x^2-6x+11=x^2-6x+9+2=\left(x-3\right)^2+2\ge2\)
Dấu ''='' xảy ra khi x = 3
Vậy GTNN B là 2 khi x = 3
c, \(x^2-x+1=x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Dấu ''='' xảy ra khi x = 1/2
Vậy ...
c, \(x^2-12x+2=x^2-12x+36-34=\left(x-6\right)^2-34\ge-34\)
Dấu ''='' xảy ra khi x = 6
Vậy ...

\(1.\)
\(-17-\left(x-3\right)^2\)
Ta có: \(\left(x-3\right)^2\ge0\)với \(\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(x-3\right)^2\le0\)với \(\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow17-\left(x-3\right)^2\le17\)với \(\forall x\)
Dấu '' = '' xảy ra khi:
\(\left(x-3\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
Vậy \(Max=-17\)khi \(x=3\)
\(2.\)
\(A=x\left(x+1\right)+\frac{3}{2}\)
\(A=x^2+x+\frac{3}{2}\)
\(A=\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{5}{4}\)
\(\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{5}{4}\ge\frac{5}{4}\)với \(\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{5}{4}\ge\frac{5}{4}\)với \(\forall x\)
Vậy \(Max=\frac{5}{4}\)khi \(x=\frac{-1}{2}\)

\(a,x^2+3x+9\)
\(=x^2+2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{3}{2}+\left(\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{27}{4}\)
\(=\left(x+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{27}{4}\)
Ta thấy: \(\left(x+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{27}{4}\ge\dfrac{27}{4}\forall x\)
Dấu \("="\) xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow x+\dfrac{3}{2}=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(b,2x^2-5x+10\)
\(=2x^2-5x+\dfrac{25}{8}+\dfrac{55}{8}\)
\(=2\left(x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{5}{4}+\dfrac{25}{16}\right)+\dfrac{55}{8}\)
\(=2\left(x-\dfrac{5}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{55}{8}\)
Ta có: \(2\left(x-\dfrac{5}{4}\right)^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow2\left(x-\dfrac{5}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{55}{8}\ge\dfrac{55}{8}\forall x\)
Dấu \("="\) xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow x-\dfrac{5}{4}=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
#\(Toru\)

\(A=\left[\frac{6x^2}{x^3-1}-\frac{2x-2}{x^2+x+1}-\frac{1}{x-1}\right]:\frac{x^2+9}{\left(x-1\right)\left(9-4x\right)}\)
\(=\left[\frac{6x^2}{x^3-1}-\frac{\left(2x-2\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}-\frac{x^2+x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\right]\cdot\frac{\left(x-1\right)\left(9-4x\right)}{x^2+9}\)
\(=\frac{6x^2-\left(2x^2-4x+2\right)-x^2-x-1}{\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}\cdot\frac{\left(x-1\right)\left(9-4x\right)}{x^2+9}\)
\(=\frac{5x^2-2x^2+4x-2-x-1}{\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\cdot\frac{\left(9-4x\right)}{x^2+9}\)
\(=\frac{3x^2+3x-3}{\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\cdot\frac{\left(9-4x\right)}{x^2+9}\)
Biểu thức A bạn viết đúng chưa?


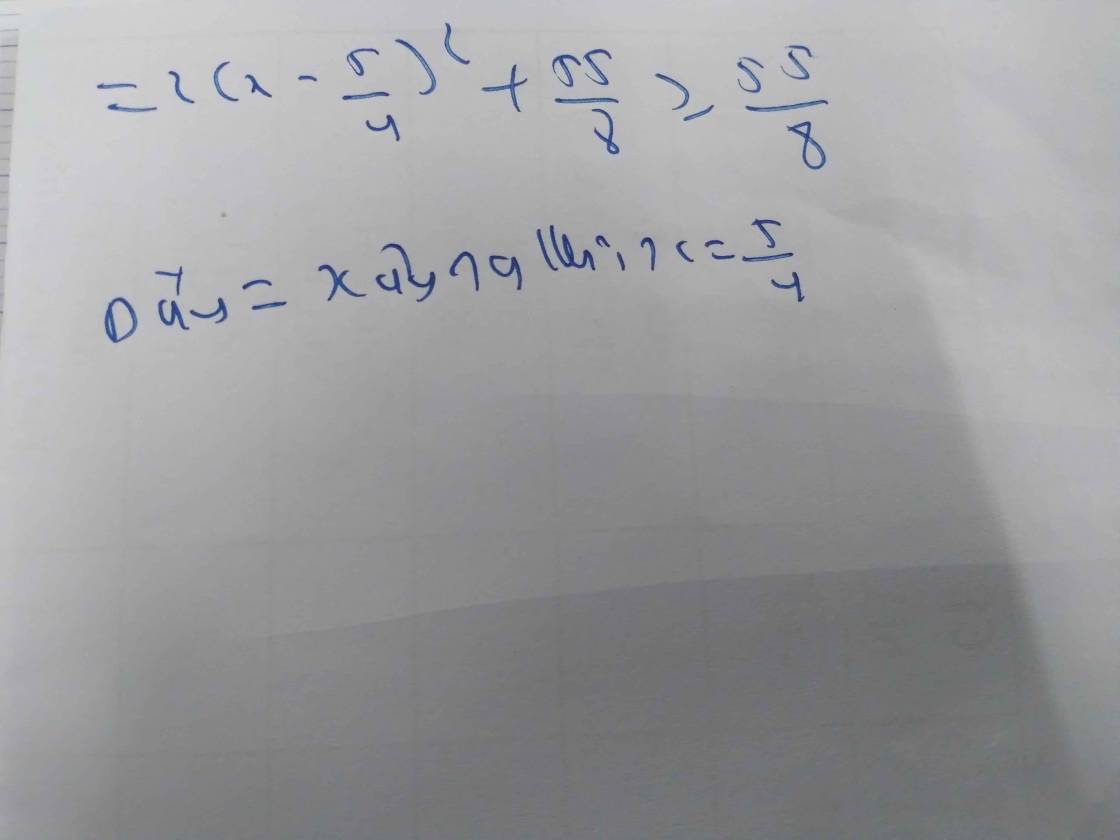
\(A=x^2-2x+9=x^2-2x+1+8=\left(x-1\right)^2+8\)
ta có: \(\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\forall x\in R\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2+8\ge8\forall x\in R\)
dấu "=" xảy ra khi x - 1 = 0 => x = 1
vậy min A = 8 khi và chỉ khi x = 1