
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) ĐKXĐ `x + 3 ne 0 ` và `x -3 ne 0` và ` 9 -x^2 ne 0`
`<=> x ne -3 ` và `x ne 3` và `(3-x)(3+x) ne 0`
`<=> x ne -3` và `x ne 3`
b) Với `x ne +-3` ta có:
`P= 3/(x+3) + 1/(x-3)- 18/(9-x^2)`
`P= [3(x-3)]/[(x-3)(x+3)] + (x+3)/[(x-3)(x+3)] + 18/[(x-3)(x+3)]`
`P= (3x-9)/[(x-3)(x+3)] + (x+3)/[(x-3)(x+3)] + 18/[(x-3)(x+3)]`
`P= (3x-9+x+3+18)/[(x-3)(x+3)]`
`P= (4x +12)/[(x-3)(x+3)]`
`P= (4(x+3))/[(x-3)(x+3)]`
`P= 4/(x-3)`
Vậy `P= 4/(x-3)` khi `x ne +-3`
c) Để `P=4`
`=> 4/(x-3) =4`
`=> 4(x-3) = 4`
`<=> 4x - 12=4`
`<=> 4x = 16
`<=> x= 4` (thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
Vậy `x=4` thì `P =4`
a) P xác định <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+3\ne0\\x-3\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne-3\\x\ne3\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=>\(x\ne\pm3\)
b)Với \(x\ne\pm3\)
\(P=\dfrac{3}{x+3}+\dfrac{1}{x-3}-\dfrac{18}{9-x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{3}{x+3}+\dfrac{1}{x-3}+\dfrac{18}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\left(x-3\right)+\left(x+3\right)+18}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x-9+x+3+18}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{4x+12}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{4\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{4}{x-3}\)
c)Với \(x\ne\pm3\)
P=4 <=>\(\dfrac{4}{x-3}=4\)
<=>\(4x-12=4\)
<=>\(4x=16\)
<=>x=4(tm)
Vậy x=4

a: ĐKXĐ: x<>1; x<>2; x<>3
\(K=\left(\dfrac{x^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{x^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)}\right)\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}{x^4+2x^2+1-x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3-x^2+x^3-3x^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x^2+1+x\right)\left(x^2+1-x\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^3-4x^2}{\left(x-2\right)}\cdot\dfrac{1}{\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x^4+x^2+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x^2}{x^4+x^2+1}\)
b:
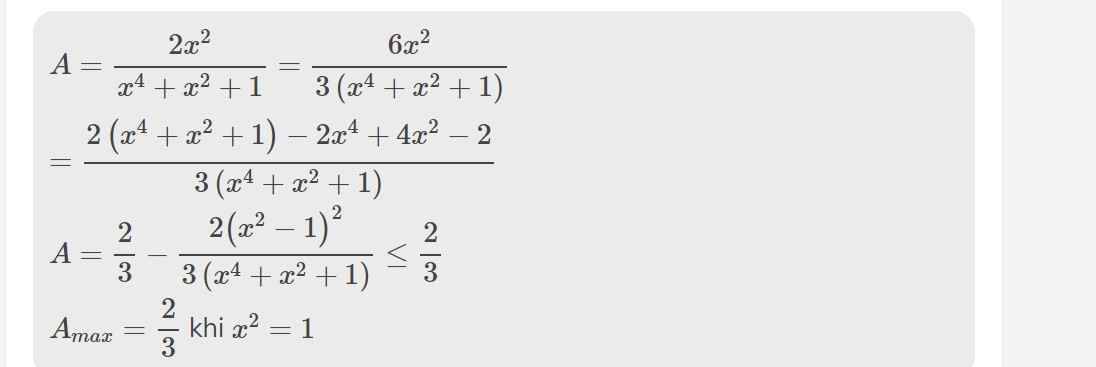

\(a,A=\dfrac{1}{x-2}+\dfrac{1}{x+2}+\dfrac{x^2+1}{x^2-4}\left(dkxd:x\ne\pm2\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{x+2+x-2+x^2+1}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+2x+1}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{x^2-4}\)
Vậy \(A=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{x^2-4}\)
\(b,\) Theo đề, ta có : \(-2< x< 2\)
\(\Rightarrow x-2< 0;x+2>0;\left(x+1\right)^2>0\)
\(\Rightarrow A< 0\) hay phân thức luôn có giá trị âm

a: |2x-3|=1
=>2x-3=1 hoặc 2x-3=-1
=>x=1(nhận) hoặc x=2(loại)
KHi x=1 thì \(A=\dfrac{1+1^2}{2-1}=2\)
b: ĐKXĐ: x<>-1; x<>2
\(B=\dfrac{2x^2-4x+3x+3-2x^2-1}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{-x+2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{-1}{x+1}\)

ĐKXĐ: \(x^3+64\ne0\Rightarrow x^3\ne-64\)
\(\Rightarrow x\ne-4\)

a) Ta có: \(P=\left(\dfrac{3}{x+1}+\dfrac{x-9}{x^2-1}+\dfrac{2}{1-x}\right):\dfrac{x-3}{x^2-1}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{3\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}+\dfrac{x-9}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}-\dfrac{2\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\right):\dfrac{x-3}{x^2-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x-3+x-9-2x-2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{x-3}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x-14}{x-3}\)
b) Ta có: \(x^2-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\left(loại\right)\\x=-3\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay x=-3 vào biểu thức \(P=\dfrac{2x-14}{x-3}\), ta được:
\(P=\dfrac{2\cdot\left(-3\right)-14}{-3-3}=\dfrac{-20}{-6}=\dfrac{10}{3}\)
Vậy: Khi \(x^2-9=0\) thì \(P=\dfrac{10}{3}\)
c) Để P nguyên thì \(2x-14⋮x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-6-8⋮x-3\)
mà \(2x-6⋮x-3\)
nên \(-8⋮x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-3\inƯ\left(-8\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-3\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;4;-4;8;-8\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{4;2;5;1;7;-1;11;-5\right\}\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được: \(x\in\left\{4;2;5;7;11;-5\right\}\)
Vậy: Để P nguyên thì \(x\in\left\{4;2;5;7;11;-5\right\}\)

a) x ≠ -5.
b) Ta có P = ( x + 5 ) 2 x + 5 = x + 5
c) Ta có P = 1 Û x = -4 (TMĐK)
d) Ta có P = 0 Û x = -5 (loại). Do vậy x ∈ ∅ .

Bổ sung phần c và d luôn:
c, C = \(\dfrac{2}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\dfrac{x^2-1}{2x^2+3}\) = \(\dfrac{2}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 5(x2 - 1) = 2(2x2 + 3)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 5x2 - 5 = 4x2 + 6
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = 11
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 - 11 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) (x - \(\sqrt{11}\))(x + \(\sqrt{11}\)) = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-\sqrt{11}=0\\x+\sqrt{11}=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{11}\left(TM\right)\\x=-\sqrt{11}\left(TM\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
d, Ta có: \(\dfrac{x^2-1}{2x^2+3}\) = \(\dfrac{x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}-\dfrac{5}{2}}{2\left(x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) - \(\dfrac{5}{4\left(x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)}\)
C nguyên \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\dfrac{5}{4\left(x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)}\) nguyên \(\Leftrightarrow\) 5 \(⋮\) 4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) \(\in\) Ư(5)
Xét các TH:
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = 5 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-1}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = -5 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-11}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{11}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = 1 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-5}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{5}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = -1 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-7}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{7}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
Vậy không có giá trị nào của x \(\in\) Z thỏa mãn C \(\in\) Z
Chúc bn học tốt! (Ko bt đề sai hay ko nữa :v)

ĐKXĐ: \(x^2-x+1\ne0\)
=>\(x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}\ne0\)
=>\(\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ne0\)(luôn đúng)
=>\(x\in R\)