Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Bài 3
a) x² + 10x + 25
= x² + 2.x.5 + 5²
= (x + 5)²
b) 8x - 16 - x²
= -(x² - 8x + 16)
= -(x² - 2.x.4 + 4²)
= -(x - 4)²
c) x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1
= x³ + 3.x².1 + 3.x.1² + 1³
= (x + 1)³
d) (x + y)² - 9x²
= (x + y)² - (3x)²
= (x + y - 3x)(x + y + 3x)
= (y - 2x)(4x + y)
e) (x + 5)² - (2x - 1)²
= (x + 5 - 2x + 1)(x + 5 + 2x - 1)
= (6 - x)(3x + 4)
Bài 4
a) x² - 9 = 0
x² = 9
x = 3 hoặc x = -3
b) (x - 4)² - 36 = 0
(x - 4 - 6)(x - 4 + 6) = 0
(x - 10)(x + 2) = 0
x - 10 = 0 hoặc x + 2 = 0
*) x - 10 = 0
x = 10
*) x + 2 = 0
x = -2
Vậy x = -2; x = 10
c) x² - 10x = -25
x² - 10x + 25 = 0
(x - 5)² = 0
x - 5 = 0
x = 5
d) x² + 5x + 6 = 0
x² + 2x + 3x + 6 = 0
(x² + 2x) + (3x + 6) = 0
x(x + 2) + 3(x + 2) = 0
(x + 2)(x + 3) = 0
x + 2 = 0 hoặc x + 3 = 0
*) x + 2 = 0
x = -2
*) x + 3 = 0
x = -3
Vậy x = -3; x = -2

Câu 1:
a) 2x(3x+2) - 3x(2x+3) = 6x^2+4x - 6x^2-9x = -5x
b) \(\left(x+2\right)^3+\left(x-3\right)^2-x^2\left(x+5\right)\)
\(=x^3+6x^2+12x+8+x^2-6x+9-x^3-5x^2\)
\(=2x^2+6x+17\)
c) \(\left(3x^3-4x^2+6x\right)\div\left(3x\right)=x^2-\dfrac{4}{3}x+2\)

Bài 1:
a: \(=6x^3-10x^2+6x\)
b: \(=-2x^3-10x^2-6x\)
Bài 4:
a: =>3x+10-2x=0
=>x=-10
c: =>3x2-3x2+6x=36
=>6x=36
hay x=6
Bài 1:
\(a,=6x^3-10x^2+6x\\ b,=-2x^3-10x^2-6x\)
Bài 4:
\(a,\Leftrightarrow3x+10-2x=0\Leftrightarrow x=-10\\ b,\Leftrightarrow x\left(2x^2+9x-5\right)-\left(2x^3+9x^2+x+4,5\right)=3,5\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^3+9x^2-5x-2x^3-9x^2-x-4,5=3,5\\ \Leftrightarrow-6x=8\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\\ c,\Leftrightarrow3x^2-3x^2+6x=36\Leftrightarrow x=6\)
Bài 1:
\(a,=7xy\left(2x-3y+4xy\right)\\ b,=x\left(x+y\right)-5\left(x+y\right)=\left(x-5\right)\left(x+y\right)\\ c,=\left(x-y\right)\left(10x+8\right)=2\left(5x+4\right)\left(x-y\right)\\ d,=\left(3x+1-x-1\right)\left(3x+1+x+1\right)\\ =2x\left(4x+2\right)=4x\left(2x+1\right)\\ e,=5\left[\left(x-y\right)^2-4z^2\right]=5\left(x-y-2z\right)\left(x-y+2z\right)\\ f,=x^2+8x-x-8=\left(x+8\right)\left(x-1\right)\\ g,\left(x+y\right)^3-\left(x+y\right)=\left(x+y\right)\left[\left(x+y\right)^2-1\right]\\ =\left(x+y\right)\left(x+y-1\right)\left(x+y+1\right)\\ h,=x^2+3x+x+3=\left(x+3\right)\left(x+1\right)\)

Câu 2:
a: \(\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)-x\left(x+3\right)+7=0\)
=>\(x^2-1-x^2-3x+7=0\)
=>-3x+6=0
=>-3x=-6
=>\(x=\dfrac{-6}{-3}=2\)
b: \(2x^3-22x^2+36x=0\)
=>\(2x\left(x^2-11x+18\right)=0\)
=>\(x\left(x^2-11x+18\right)=0\)
=>\(x\left(x^2-2x-9x+18\right)=0\)
=>\(x\left[x\left(x-2\right)-9\left(x-2\right)\right]=0\)
=>\(x\left(x-2\right)\left(x-9\right)=0\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-2=0\\x-9=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=2\\x=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
Câu 4:
1: Diện tích cỏ cần thay là:
\(105\cdot68=7140\left(m^2\right)\)
Số tiền BQL sân cần trả là:
\(7140\cdot120000=856800000\left(đồng\right)\)
2:
a: Xét tứ giác ABDC có
M là trung điểm chung của AD và BC
=>ABDC là hình bình hành
Hình bình hành ABDC có \(\widehat{BAC}=90^0\)
nên ABDC là hình chữ nhật
b: Xét ΔADE có
H,M lần lượt là trung điểm của AE,AD
=>HM là đường trung bình của ΔADE
=>HM//DE
=>BC//DE
=>\(\widehat{EDB}=\widehat{DBM}\)(hai góc so le trong)(1)
Ta có: ABDC là hình chữ nhật
=>AD=BC
mà \(MD=\dfrac{AD}{2};MB=\dfrac{BC}{2}\)
nên MD=MB
=>ΔMBD cân tại M
=>\(\widehat{MDB}=\widehat{MBD}\left(2\right)\)
Từ (1) và (2) suy ra \(\widehat{MDB}=\widehat{EDB}\)
=>\(\widehat{ADB}=\widehat{EDB}\)
=>DB là phân giác của góc ADE

b: \(8x^2-48x+6xy-36y\)
\(=8x\left(x-6\right)+6y\left(x-6\right)\)
\(=2\left(x-6\right)\left(4x+3y\right)\)
d: \(a^2-2ab+b^2-4\)
\(=\left(a-b\right)^2-4\)
\(=\left(a-b-2\right)\left(a-b+2\right)\)

a) \(=\left(x+6y\right)\left(x-6y\right)-\left(x-6y\right)\)
\(=\left(x-6y\right)\left(x-6y-1\right)\)
b) \(=x\left(x^2-8x+16\right)\)
\(=x\left(x-4\right)^2\)
c) \(=2\left(x-y\right)^2-18\)
\(=2\left[\left(x-y\right)^2-3^2\right]\)
\(=2\left(x-y+3\right)\left(x-y-3\right)\)
a: \(x^2-36y^2-x+6y\)
\(=\left(x-6y\right)\left(x+6y\right)-\left(x-6y\right)\)
\(=\left(x-6y\right)\left(x+6y-1\right)\)
b: \(x^3-8x^2+16x\)
\(=x\left(x^2-8x+16\right)\)
\(=x\left(x-4\right)^2\)
c: \(2x^2-4xy+2y^2-18\)
\(=2\left(x^2-2xy+y^2-9\right)\)
\(=2\left(x-y-3\right)\left(x-y+3\right)\)
d: \(3x^2-7x-10\)
\(=3x^2+3x-10x-10\)
\(=3x\left(x+1\right)-10\left(x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(3x-10\right)\)

a: Ta có: \(x^2-36y^2-x+6y\)
\(=\left(x-6y\right)\left(x+6y\right)-\left(x-6y\right)\)
\(=\left(x-6y\right)\left(x+6y-1\right)\)
b: Ta có: \(16x-8x^2+x^3\)
\(=x\left(x^2-8x+16\right)\)
\(=x\left(x-4\right)^2\)
c: Ta có: \(2x^2-4xy+2y^2-18\)
\(=2\left(x^2-2xy+y^2-9\right)\)
\(=2\cdot\left[\left(x-y\right)^2-9\right]\)
\(=2\left(x-y-3\right)\left(x-y+3\right)\)
d: Ta có: \(3x^2-7x-10\)
\(=3x^2+3x-10x-10\)
\(=3x\left(x+1\right)-10\left(x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(3x-10\right)\)
e: Ta có: \(x^4-x^2-30\)
\(=x^4-6x^2+5x^2-30\)
\(=x^2\left(x^2-6\right)+5\left(x^2-6\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-6\right)\left(x^2+5\right)\)
f: Ta có: \(x^2-xy-2y^2\)
\(=x^2-2xy+xy-2y^2\)
\(=x\left(x-2y\right)+y\left(x-2y\right)\)
\(=\left(x-2y\right)\left(x+y\right)\)
g: Ta có: \(x^4-13x^2y^2+4y^4\)
\(=x^4-4x^2y^2+4y^4-9x^2y^2\)
\(=\left(x^2-2y^2\right)^2-\left(3xy\right)^2\)
\(=\left(x^2-3xy-2y^2\right)\left(x^2-3xy+2y^2\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-3xy-2y^2\right)\left(x^2-xy-2xy+2y^2\right)\)
\(=\left[x\left(x-y\right)-2y\left(x-y\right)\right]\left(x^2-3xy-2y^2\right)\)
\(=\left(x-y\right)\left(x-2y\right)\left(x^2-3xy-2y^2\right)\)
h: Ta có: \(\left(x^2-2x\right)^2-2\left(x^2-2x\right)-3\)
\(=\left(x^2-2x\right)^2-3\left(x^2-2x\right)+\left(x^2-2x\right)-3\)
\(=\left(x^2-2x\right)\left(x^2-2x-3\right)+\left(x^2-2x-3\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-2x-3\right)\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)\cdot\left(x-1\right)^2\)
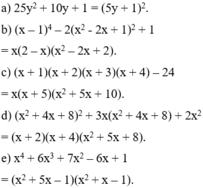
a) Ta có: \(\left(2x-1\right)^2-25=0\)
hay \(\left(2x-1\right)^2-5^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(2x-1-5\right)\left(2x-1+5\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(2x-6\right)\left(2x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-6=0\\2x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=6\\2x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(x\in\left\{3;-2\right\}\)
b) Ta có: \(8x^2-50x=0\Rightarrow x\left(8x-50\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\8x-50=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\8x=50\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\frac{50}{8}=\frac{25}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(x\in\left\{0;\frac{25}{4}\right\}\)
c) Ta có: \(\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+7\right)+2\left(x^2-4\right)-5\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+7\right)+2\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)-5\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left[\left(x^2+2x+7\right)+2\left(x+2\right)-5\right]=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+7+2x+4-5\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+4x+6\right)=0\)(1)
Ta có: \(x^2+4x+6=x^2+4x+4+2=\left(x+2\right)^2+2\)
mà \(\left(x+2\right)^2\ge0\forall x\)
nên \(\left(x+2\right)^2+2\ge2>0\forall x\)
nên \(x^2+4x+6=0\) là điều vô lý (2)
Từ (1) và (2) suy ra
\(x-2=0\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Vậy: x=2
Thanks bn