Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\\\\\\\end{matrix}\right.\prod\limits^{ }_{ }\int_{ }^{ }dx\sinh_{ }^{ }⋮\begin{matrix}&&&\\&&&\\&&&\\&&&\\&&&\\&&&\end{matrix}\right.\Cap\begin{matrix}&&\\&&\\&&\\&&\\&&\\&&\end{matrix}\right.\)

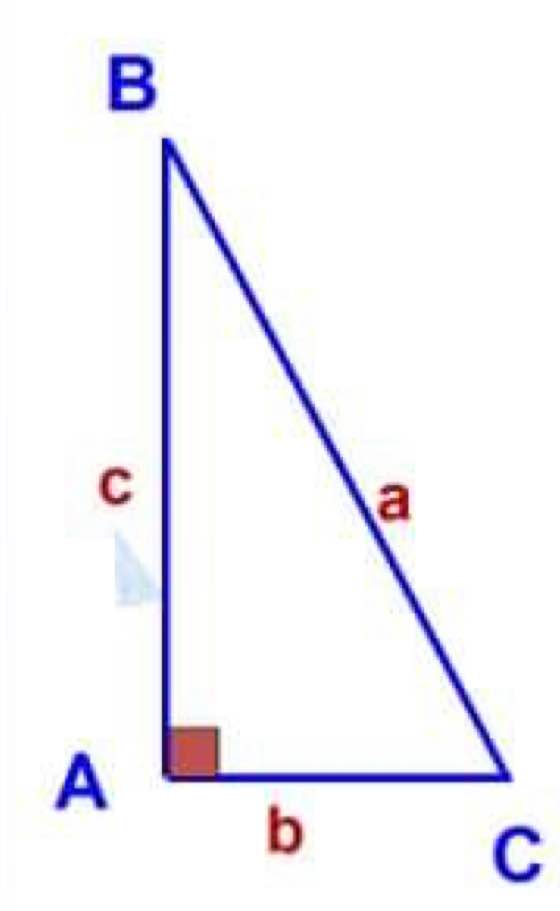
a: \(\sin\widehat{B}=\cos\widehat{C}=\dfrac{AC}{BC}\)
\(\cos\widehat{B}=\sin\widehat{C}=\dfrac{AB}{BC}\)
\(\tan\widehat{B}=\cot\widehat{C}=\dfrac{AC}{AB}\)
\(\cot\widehat{B}=\tan\widehat{C}=\dfrac{AB}{AC}\)

a = 60cm
p = 160/2 = 80cm
p = \(\dfrac{a+b+c}{2}\) (1) => \(\dfrac{2p-a}{2}\) = \(\dfrac{b+c}{2}\)
Vì a, p là 1 hằng số nên để S đạt GTLN <=> (p-b) và (p-c) đạt GTLN
Áp dụng bđt Cosin, ta có:
\(\sqrt{\left(p-b\right)\left(p-c\right)}\) <= \(\dfrac{p-b+p-c}{2}\) = \(\dfrac{2p-b-c}{2}\)
=> \(\dfrac{S}{\sqrt{p\left(p-a\right)}}\) <= \(p-\dfrac{b+c}{2}\) = \(p-\dfrac{2p-a}{2}\) = \(\dfrac{a}{2}\)
=> 2S <= \(a\sqrt{p\left(p-a\right)}\) = \(60\sqrt{80.\left(80-60\right)}\) = 2400
=> S <= 1200 (\(cm^2\))
Dấu "=" xảy ra
<=> \(p-b\) = \(p-c\)
<=> b = c
Thay b = c vào (1), ta được:
p = \(\dfrac{a+2b}{2}\) => 80 = \(\dfrac{60+2b}{2}\) => b = c = 50 (cm)
=> đpcm