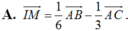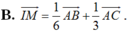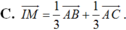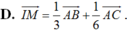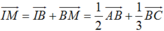Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1,Ta có luôn tồn tại một điểm K sao cho \(4\overrightarrow{AB}-\overrightarrow{AC}=3\overrightarrow{AK}\).(*) Thật vậy:
VT(*) = \(4\left(\overrightarrow{AK}+\overrightarrow{KB}\right)-\left(\overrightarrow{AK}+\overrightarrow{KC}\right)=3\overrightarrow{AK}+4\overrightarrow{KB}-\overrightarrow{KC}\) (**)
Từ (*) và (**) ta có : \(4\overrightarrow{KB}-\overrightarrow{KC}=\overrightarrow{0}\) ⇔\(4\overrightarrow{KB}=\overrightarrow{KC}\) ⇒ B nằm giữa K và C sao cho 4KB = KC= \(\dfrac{4}{3}\) .BC.
Khi đó ta có : \(\left|4\overrightarrow{AB}-\overrightarrow{AC}\right|=\left|\overrightarrow{3AK}\right|=3AK\)
Ap dụng định lí Py-ta-go cho tam giác ABC vuông tại A ta được:
BC2= AB2 + AC2 ⇒BC = \(\sqrt{2^2+2^2}=2\sqrt{2}\)⇒ KC = \(\dfrac{4}{3}\).BC = \(\dfrac{4}{3}\). \(2\sqrt{2}\)
⇒KC = \(\dfrac{8\sqrt{2}}{3}\)
Ta có : tam giác ABC vuông cân tại A nên \(\widehat{ACB}=\widehat{ACK}=45^O\)
Ap dụng định lí cosin ta có : Trong tam giác ACK có
AK = \(\sqrt{AC^2+KC^2-2AK.KC.\cos\widehat{ACK}}=\sqrt{2^2+\left(\dfrac{8\sqrt{2}}{3}\right)^2-2.2.\dfrac{8\sqrt{2}}{3}.\cos45^O}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{17}}{3}\)
⇒3AK=2\(\sqrt{17}\)⇒ \(\left|4\overrightarrow{AB}-\overrightarrow{AC}\right|\)=2\(\sqrt{17}\)
VẬY.....................
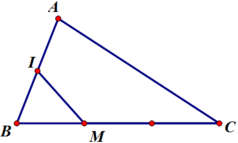
Câu 2: AM=3MB => vt AC + vt CM = 3vtMC + 3vtCB
<=>vtCM - 3vtMC = 3vtCB -vtAC
<=>vtCM = 1/4 vtCA + 3/4 vtCB
(Mk mới học Toán 10 nên có sai thì thông cảm nha!!!)

a/ Có AM= 3MB\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{AM}=3\overrightarrow{MB}\)
Theo quy tắc 3 điểm=> \(\overrightarrow{CM}=\overrightarrow{CA}+\overrightarrow{AM}\)
và \(\overrightarrow{CM}=\overrightarrow{CB}-\overrightarrow{MB}\)
Cộng vế vs vế=> \(2\overrightarrow{CM}=\overrightarrow{CA}+\overrightarrow{AM}+\overrightarrow{CB}-\overrightarrow{MB}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\overrightarrow{CM}=\overrightarrow{CA}+\overrightarrow{MB}+\overrightarrow{CB}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\overrightarrow{CM}=\overrightarrow{CA}+\frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{CB}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6\overrightarrow{CM}=3\overrightarrow{CA}+2\overrightarrow{\:AB}+3\overrightarrow{CB}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6\overrightarrow{CM}=\overrightarrow{CA}+5\overrightarrow{CB}\) ( vì \(2\overrightarrow{CA}+2\overrightarrow{AB}=2\overrightarrow{CB}\) )
b/ Làm tương tự câu a
c/ Theo quy tắc trung điểm có:
\(2\overrightarrow{CM}=\overrightarrow{CA}+\overrightarrow{CB}\)
\(2\overrightarrow{AN}=\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{AC}\)
\(\overrightarrow{AB}=\overrightarrow{AC}+\overrightarrow{CB}=2\overrightarrow{AN}+\overrightarrow{BA}+2\overrightarrow{CM}+\overrightarrow{AC}\)
\(=2\overrightarrow{AN}+\overrightarrow{BC}+2\overrightarrow{CM}\)
Có \(\overrightarrow{BC}=2\overrightarrow{BN}=2\left(\overrightarrow{BA}+\overrightarrow{AN}\right)\)
=>\(\overrightarrow{AB}=2\overrightarrow{AN}+2\overrightarrow{BA}+2\overrightarrow{AN}+2\overrightarrow{CM}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\overrightarrow{AB}=4\overrightarrow{AN}+2\overrightarrow{CM}\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{AB}=\frac{4}{3}\overrightarrow{AN}+\frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{CM}\)

Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\frac{1}{x+3y-1}=X\\\frac{1}{2x-y+3}=Y\end{matrix}\right.\)
Hệ phương trình trở thành:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2X-Y=5\\X+2Y=5\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4X-2Y=10\\X+2Y=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5X=15\\X+2Y=5\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}X=3\\Y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\frac{1}{x+3y-1}=3\\\frac{1}{2x-y+3}=1\end{matrix}\right.\) (nhân chéo) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+3y-1=\frac{1}{3}\\2x-y+3=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+3y=\frac{4}{3}\\2x-y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+3y=\frac{4}{3}\\6x-3y=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+3y=\frac{4}{3}\\7x=-\frac{14}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\frac{2}{3}\\y=\frac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy nghiệm của hệ là \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(-\frac{2}{3};\frac{2}{3}\right)\)

Chọn C.
Theo định lí hàm cosin, ta có : ![]()
Do MC = 2MB nên BM = 1/3.BC = 2.
Theo định lí hàm cosin, ta có: AM2 = AB2 + BM2 - 2AB.BM.cos B = 42 + 22 -2.4.2.1/2 = 12
Do đó: ![]() .
.