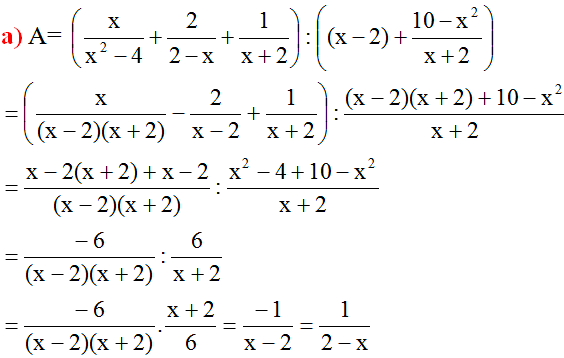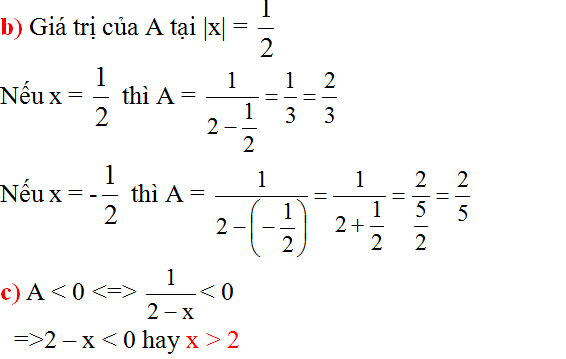Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Lời giải:
ĐK: $x\neq \pm 2; x\neq 0$
a)
\(A=\left[\frac{x+2}{(x+2)(x-2)}+\frac{2x}{(x-2)(x+2)}+\frac{x-2}{(x-2)(x+2)}\right].\frac{2-x}{x}=\frac{x+2+2x+x-2}{(x-2)(x+2)}.\frac{-(x-2)}{x}\)
\(=\frac{4x}{(x-2)(x+2)}.\frac{-(x-2)}{x}=\frac{-4}{x+2}\)
b) Để $A=1\Leftrightarrow \frac{-4}{x+2}=1$
$\Leftrightarrow x+2=-4$
$\Leftrightarrow x=-6$ (thỏa ĐKXĐ)
Vậy $x=-6$

Lời giải của bạn Nhật Linh đúng rồi, tuy nhiên cần thêm điều kiện để A có nghĩa: \(x\ne\pm2\)

\(a,\frac{x}{xy-y^2}+\frac{2x-y}{xy-x^2}:\left(\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{y}\right)\)
\(=\left(\frac{x}{y\left(x-y\right)}+\frac{y-2x}{x\left(x-y\right)}\right):\left(\frac{y}{xy}+\frac{x}{xy}\right)\)
\(=\left(\frac{x-y}{x\left(x-y\right)}\right):\left(\frac{x+y}{xy}\right)\)
\(=\frac{1}{x}.\frac{xy}{x+y}=\frac{y}{x+y}\)

a: \(E=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}:\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{x-1}+\dfrac{2-x^2}{x\left(x-1\right)}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}:\dfrac{x^2-1+x+2-x^2}{x\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\cdot\dfrac{x\left(x-1\right)}{x+1}=\dfrac{x^2}{x-1}\)
b: |x-3|=2
=>x-3=2 hoặc x-3=-2
=>x=5(nhận) hoặc x=1(loại)
Khi x=5 thì \(E=\dfrac{5^2}{5-1}=\dfrac{25}{4}\)
c: Để E=1/2 thì \(\dfrac{x^2}{x-1}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-x+1=0\)
hay \(x\in\varnothing\)
f) \(A=\dfrac{x^2}{x-1}=\dfrac{x^2-x+x-1+1}{x-1}=\dfrac{x\left(x-1\right)+x-1+1}{x-1}=x+1+\dfrac{1}{x-1}=x-1+\dfrac{1}{x-1}+2\ge2\sqrt{\left(x-1\right).\dfrac{1}{x-1}}+2=4\)\(A=4\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
-Vậy \(A_{min}=4\)