Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Đặt CT muối \(RCO_3\)
\(RCO_3\rightarrow\left(t^o\right)RO+CO_2\) (1)
\(n_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2}=15.0,01=0,15\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{BaCO_3}=\dfrac{19,7}{197}=0,1\left(mol\right)\)
`@`TH1: Chỉ tạo ra kết tủa
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+CO_2\rightarrow BaCO_3\downarrow+H_2O\)
0,1 0,1 0,1 ( mol )
Theo ptr (1) \(n_{RCO_3}=n_{CO_2}=0,1\left(mol\right)\)
\(M_{RCO_3}=\dfrac{20}{0,1}=200\) \((g/mol)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow R=140\) \((g/mol)\) (loại )
`@`TH2: Tạo ra 2 muối
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+CO_2\rightarrow BaCO_3\downarrow+H_2O\)
0,15 ( mol )
0,1 0,1 0,1 ( mol )
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+2CO_2\rightarrow Ba\left(HCO_3\right)_2\)
0,05 0,1 ( mol )
Theo ptr (1): \(n_{RCO_3}=n_{RO}=0,1+0,1=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
\(M_{RCO_3}=\dfrac{20}{0,2}=100\) \((g/mol)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow R=40\) \((g/mol)\) `->` R là Canxi ( Ca )
\(m_{CaO}=0,2\left(40+16\right)=11,2\left(g\right)\)

\(MCO_3-^{t^o}\rightarrow MO+CO_2\)
\(n_{BaCO_3}=0,1\left(mol\right);n_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2}=0,15\left(mol\right)\)
Bảo toàn nguyên tố Ba => \(n_{Ba\left(HCO_3\right)_2}=0,05\left(mol\right)\)
Bảo toàn nguyên tố C =>\(n_{CO_2}=n_{BaCO_3}+n_{Ba\left(HCO_3\right)_2}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
Bảo toàn khối lượng => \(m_B=m_{muối}-m_{CO_2}=20-0,2.44=11,2\left(g\right)\)
Theo PT ta có : \(n_{MCO_3}=n_{CO_2}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
=> \(M_{MCO_3}=\dfrac{20}{0,2}=100\)
=> M + 60 =100
=> M=40 (Ca)
=> CT muối : CaCO3

a. Đặt CT muối: \(RCO_3\)
\(RCO_3\rightarrow\left(t^o\right)RO+CO_2\) (1)
\(n_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2}=\dfrac{200.17,1}{171.100}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{BaCO_3}=\dfrac{29,55}{197}=0,15\left(mol\right)\)
`@` TH1: Chỉ tạo ra kết tủa
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+CO_2\rightarrow BaCO_3\downarrow+H_2O\)
0,15 0,15 0,15 ( mol )
Theo ptr (1): \(n_{RCO_3}=n_{RO}=n_{CO_2}=0,15\left(mol\right)\)
\(M_{RCO_3}=\dfrac{21}{0,15}=140\) \((g/mol)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow R=80\) ( loại )
`@` TH2: Ba(OH)2 hết
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+CO_2\rightarrow BaCO_3\downarrow+H_2O\)
0,2 ( mol )
0,15 0,15 0,15 ( mol )
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+2CO_2\rightarrow Ba\left(HCO_3\right)_2\)
0,05 0,1 ( mol )
Theo ptr (1): \(n_{RCO_3}=n_{RO}=n_{CO_2}=0,15+0,1=0,25\left(mol\right)\)
\(M_{RCO_3}=\dfrac{21}{0,25}=84\) \((g/mol)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow R=24\) `->` R là Mg
\(n_{MgO}=0,25.\left(24+16\right)=10\left(g\right)\)
b.\(n_{MgCO_3}=\dfrac{4,2}{84}=0,05\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{HCl}=0,05.3=0,15\left(mol\right)\)
\(m_{HCl}=50.1,15=57,5\left(g\right)\)
\(MgCO_3+2HCl\rightarrow MgCl_2+CO_2+H_2O\)
0,05 < 0,15 ( mol )
0,05 0,1 0,05 0,05 ( mol )
\(m_{ddspứ}=4,2+57,5-0,05.44=59,5\left(g\right)\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\%m_{MgCl_2}=\dfrac{0,05.95}{59,5}.100=7,98\%\\\%m_{HCl\left(dư\right)}=\dfrac{\left(0,15-0,1\right).36,5}{59,5}.100=3,06\%\end{matrix}\right.\)

Giả sử kim loại hóa trị II là A.
Ta có: nBa(OH)2 = 0,1 (mol)
nBaCO3 = 0,05 (mol)
\(ACO_3\underrightarrow{t^o}AO+CO_2\)
- TH1: Ba(OH)2 dư.
PT: \(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+CO_2\rightarrow BaCO_3+H_2O\)
Theo PT: \(n_{ACO_3}=n_{CO_2}=n_{BaCO_3}=0,05\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow M_{ACO_3}=\dfrac{15}{0,05}=300\left(g/mol\right)\Rightarrow M_A=240\left(g/mol\right)\)
→ Không có chất nào thỏa mãn.
- TH2: Ba(OH)2 hết.
PT: \(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+CO_2\rightarrow BaCO_3+H_2O\)
______0,05_____0,05_____0,05 (mol)
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+2CO_2\rightarrow Ba\left(HCO_3\right)_2\)
___0,05_____0,1 (mol)
⇒ nCO2 = 0,05 + 0,1 = 0,15 (mol)
Theo PT: \(n_{ACO_3}=n_{CO_2}=0,15\left(mol\right)\Rightarrow M_A=\dfrac{15}{0,15}=100\left(g/mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow M_A=40\left(g/mol\right)\)
→ A là Ca.
Vậy: CTHH cần tìm là CaCO3

m C O 2 = m m u o i - m r a n = 14,2 - 7,6 = 6,6g
⇒ n C O 2 = 6,6/44 = 0,15mol
n K O H : n C O 2 = 0,1:0,15 < 1
Vậy chỉ tạo muối K H C O 3 .
⇒ n K H C O 3 = n K O H = 0,1 mol
⇒ m K H C O 3 = 0,1.100 = 10g
⇒ Chọn D.

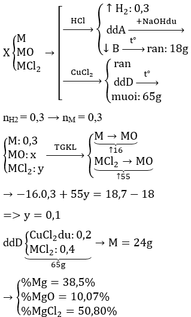
a) Đặt số mol của MO, M(OH)2, MCO3 tương ứng là x, y, z.
Nếu tạo muối trung hòa ta có các phản ứng:
MO + H2SO4 →MSO4 + H2O (1)
M(OH)2 + H2SO4 →MSO4 + 2H2O (2)
MCO3 + H2SO4 →MSO4 + H2O + CO2 (3)
Nếu tạo muối axít ta có các phản ứng:
MO + 2H2SO4 →M(HSO4)2 + H2O (4)
M(OH)2 + 2H2SO4 →M(HSO4)2 + 2H2O (5)
MCO3 + 2H2SO4 →M(HSO4)2 + H2O + CO2 (6)
Ta có :
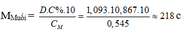
– TH1: Nếu muối là MSO4 M + 96 = 218 M = 122 (loại)
– TH2: Nếu là muối M(HSO4)2 M + 97.2 = 218 M = 24 (Mg)
Vậy xảy ra phản ứng (4, 5, 6) tạo muối Mg(HSO4)2
b) Theo (4, 5, 6) Số mol CO2 = 0,448/22,4 = 0,02 molz = 0,02 (I)
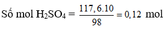
2x + 2y + 2z = 0,12 (II)
Đề bài: 40x + 58y + 84z = 3,64 (III)
Giải hệ (I, II, III): x = 0,02; y = 0,02; z = 0,02
%MgO = 40.0,02.100/3,64 = 21,98%
%Mg(OH)2 = 58.0,02.100/3,64 = 31,87%
%MgCO3 = 84.0,02.100/3,64 = 46,15%


a)
$MCO_3 \xrightarrow{t^o} MO + CO_2$
$CO_2 + Ba(OH)_2 \to BaCO_3 + H_2O$
$CO_2 + Ba(OH)_2 \to Ba(HCO_3)_2$
b)
$n_{Ba(OH)_2} = 0,15(mol) ; n_{BaCO_3} = \dfrac{19,7}{197} = 0,1(mol)$
$n_{Ba(HCO_3)_2} = n_{Ba(OH)_2} - n_{BaCO_3} = 0,05(mol)$
$n_{CO_2} = n_{BaCO_3} + 2n_{Ba(HCO_3)_2} = 0,2(mol)$
$n_{MCO_3} = n_{CO_2} = 0,2(mol)$
$m_A = m_{MCO_3} - m_{CO_2} = 20 - 0,2.44 = 11,2(gam)$
c)
$M_{MCO_3} = M + 60 = \dfrac{20}{0,2} = 100$
$\Rightarrow M = 40(Canxi)$
Vậy CTHH : $CaCO_3$